©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2019; 25(22): 2752-2762
Published online Jun 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i22.2752
Published online Jun 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i22.2752
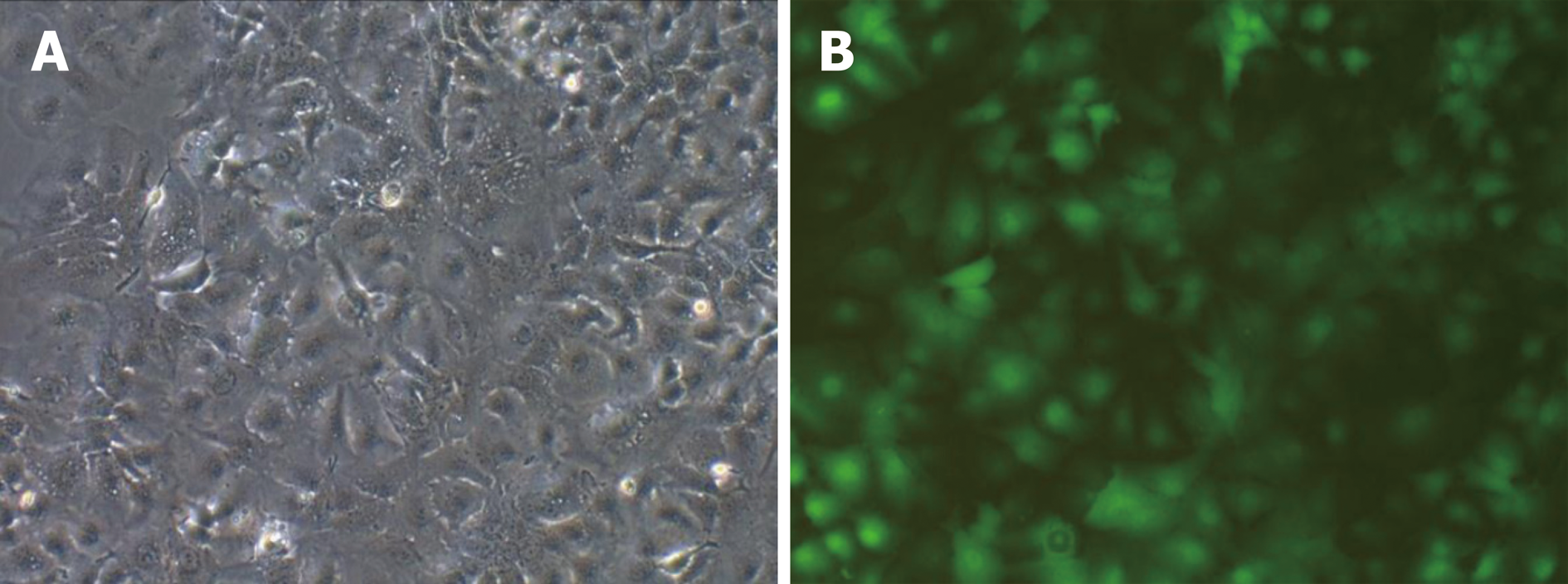
Figure 1 Green fluorescent protein was detected 72 h after lentiviral transfection (fluorescence microscopy × 200).
A: HepG2 cells in bright vision; B: HepG2 cells in green fluorescence vision.
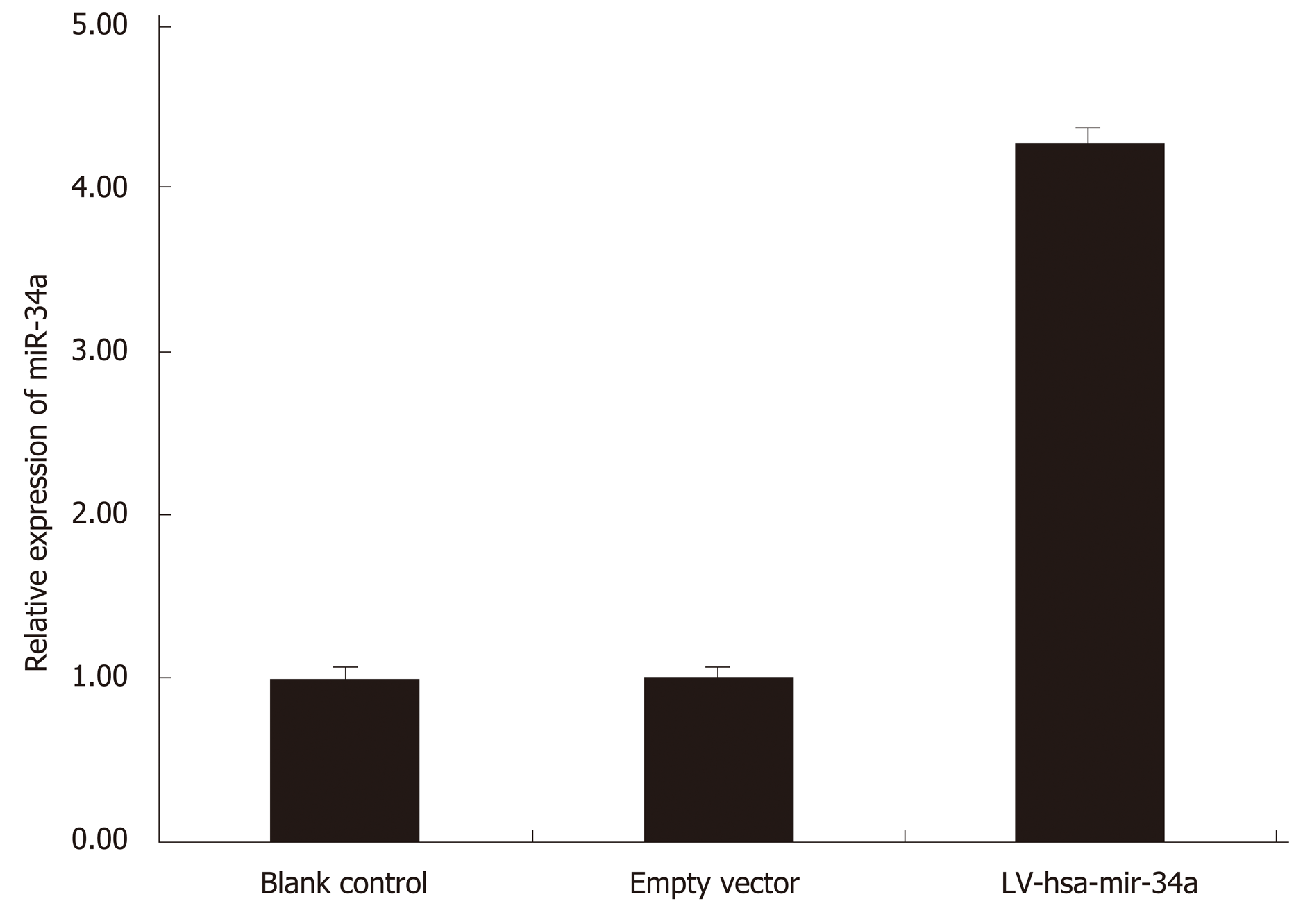
Figure 2 LV-hsa-mir-34a was transfected into HepG2 cells for 72 h.
Expression of miR-34a-5p was detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction before and after transfection.
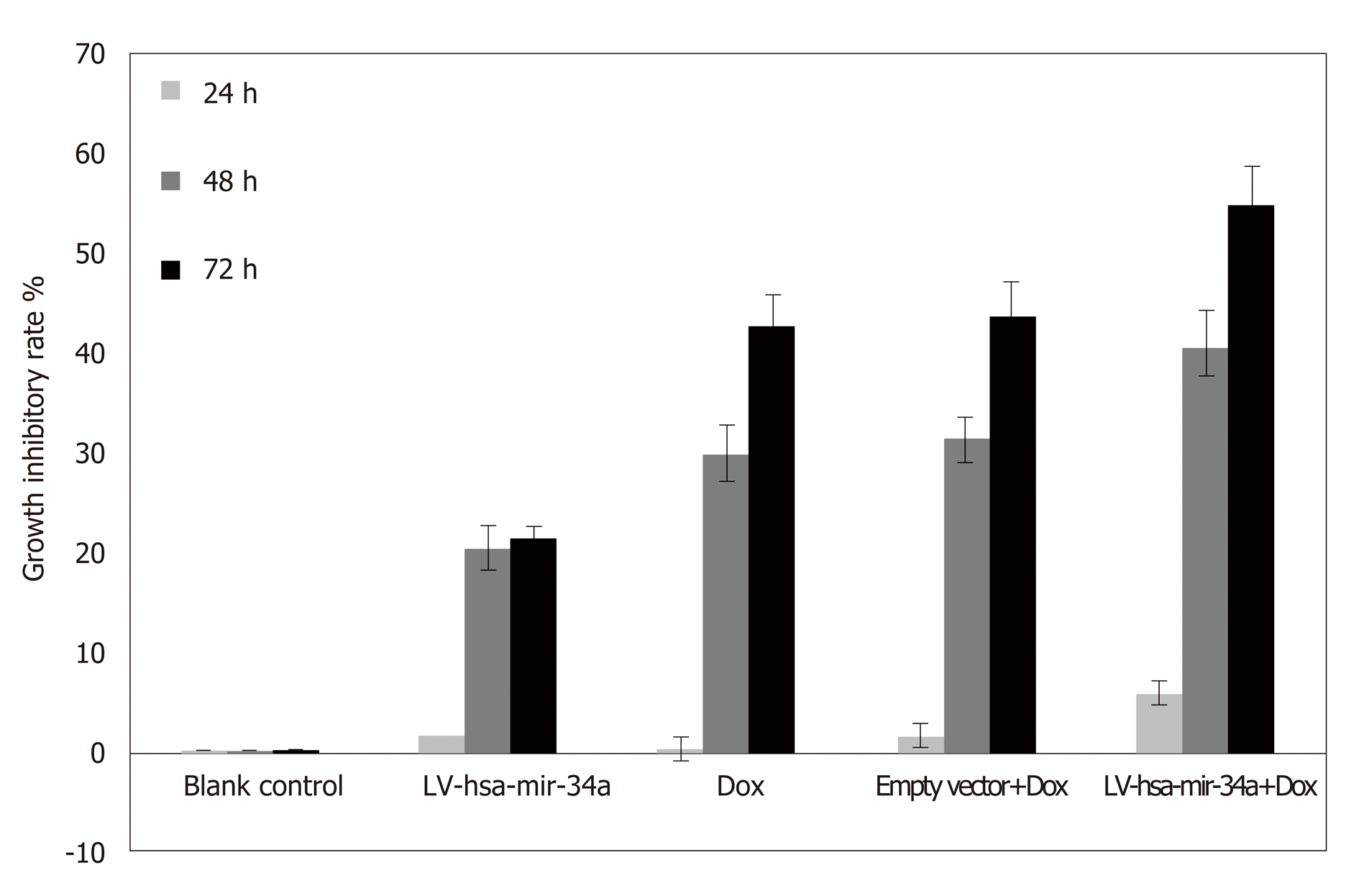
Figure 3 Growth inhibition rate of HepG2 cells treated with LV-hsa-mir-34a transfection combined with doxorubicin.
Dox: Doxorubicin.
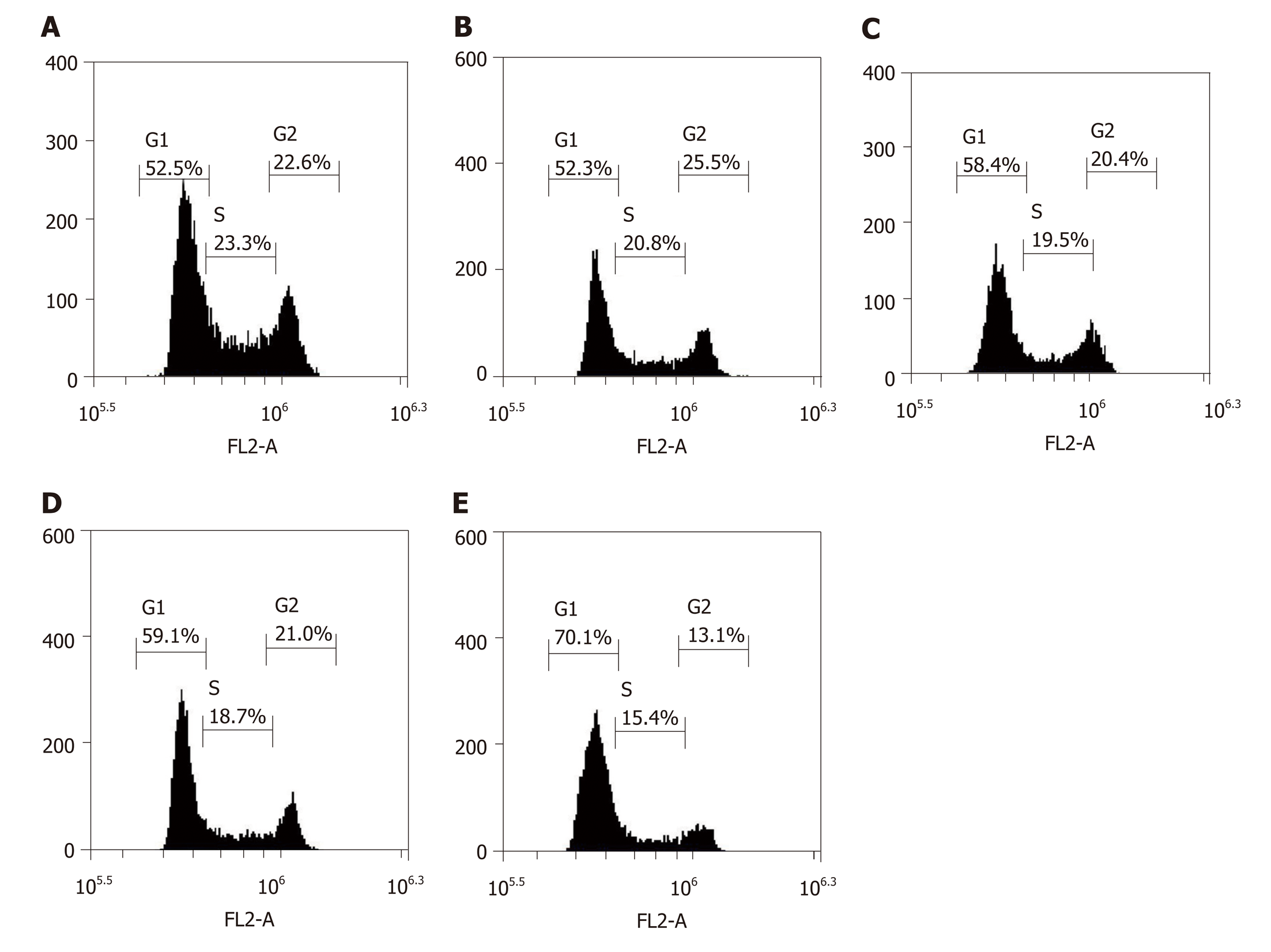
Figure 4 Proportion of G1 phase cells in each group after HepG2 cells were treated for 72 h.
A: Blank control group; B: LV-hsa-mir-34a group; C: Doxorubicin treatment group; D: Empty vector + doxorubicin treatment group; E: LV-hsa-mir-34a + doxorubicin treatment group.
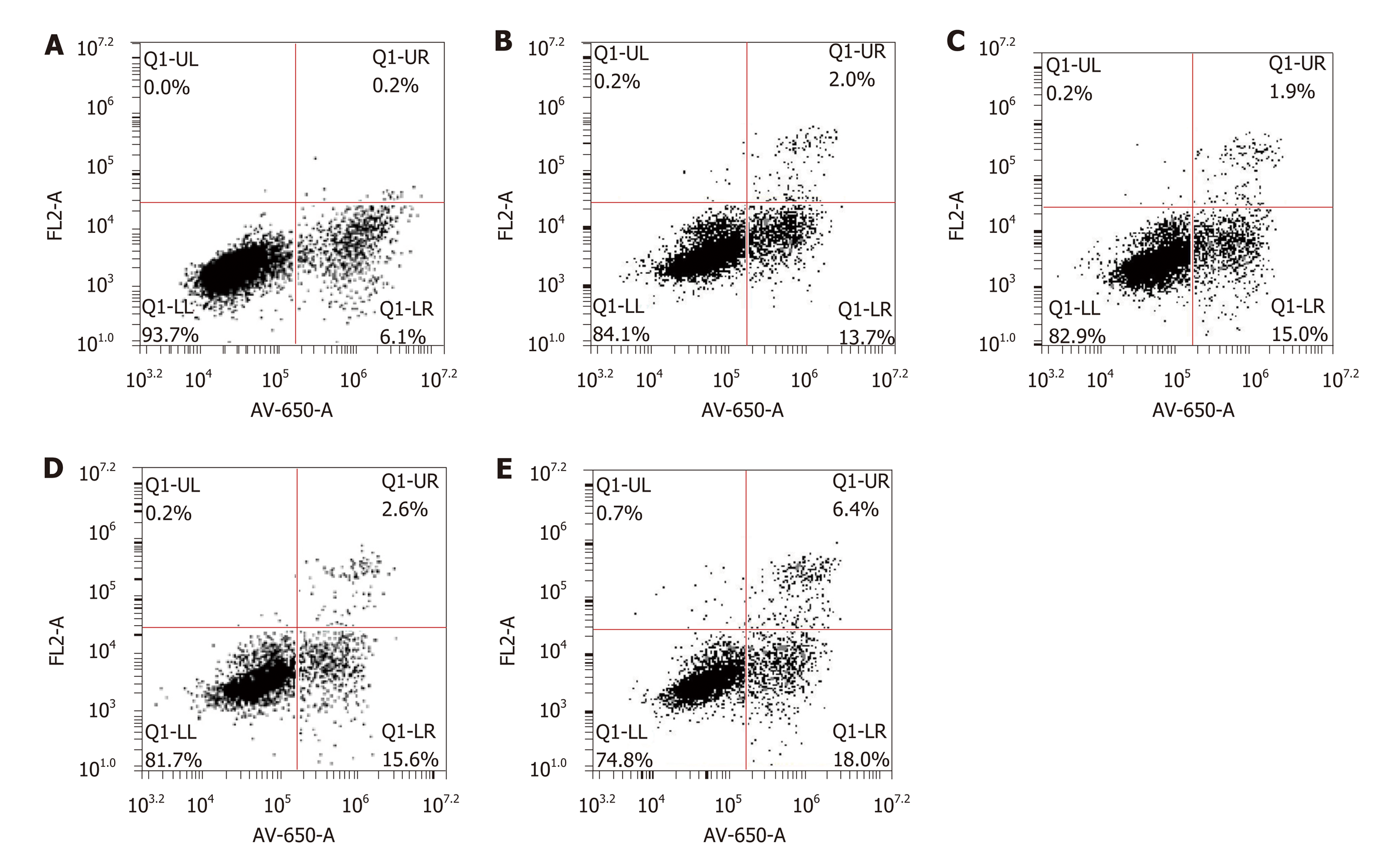
Figure 5 The proportion of apoptotic cells in each group after HepG2 cells were treated for 72 h.
A: Blank control group; B: LV-hsa-mir-34a group; C: Doxorubicin treatment group; D: Empty vector + doxorubicin treatment group; E: LV-hsa-mir-34a + doxorubicin treatment group.
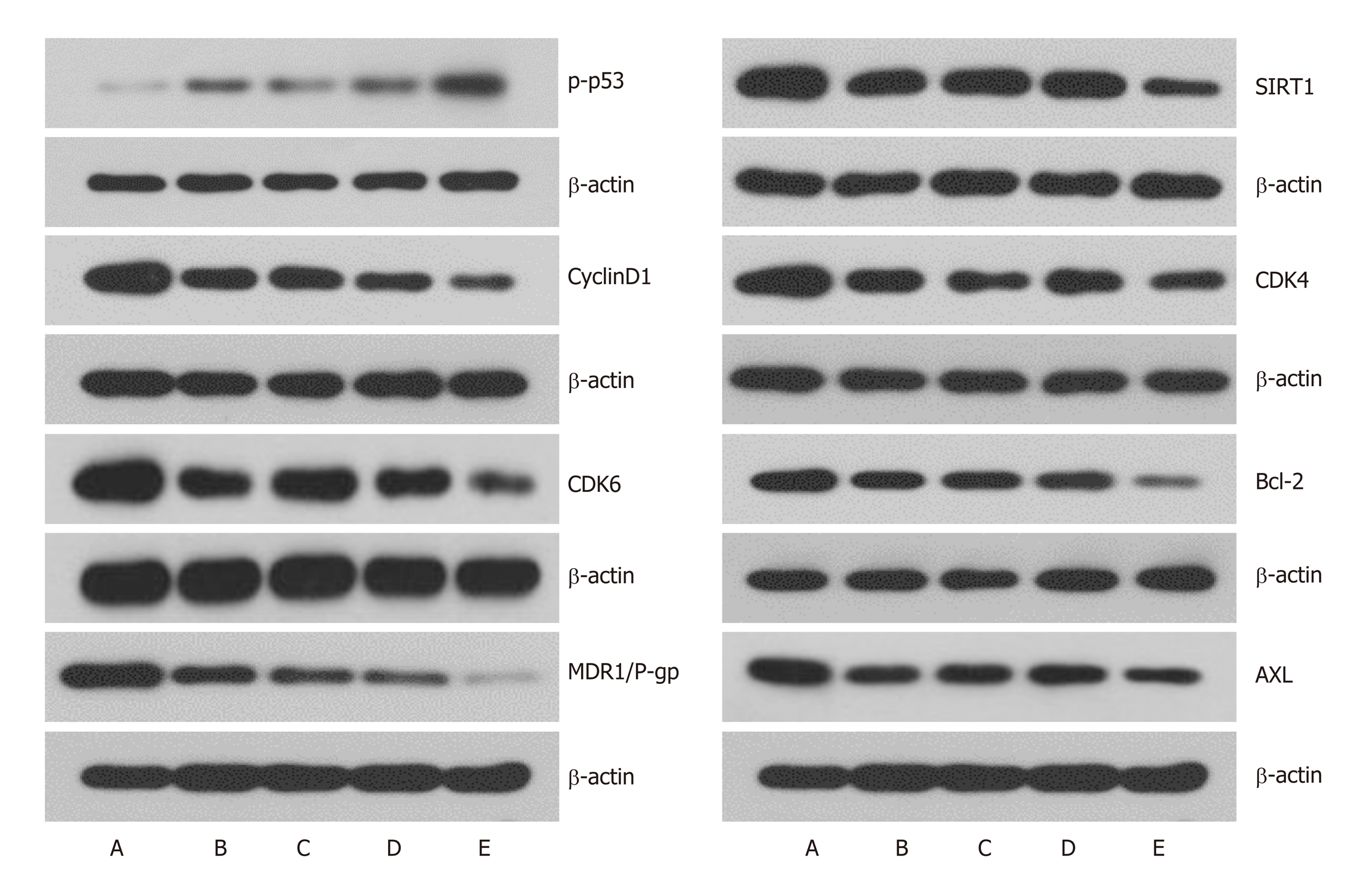
Figure 6 Effects of LV-hsa-mir-34a transfection combined with doxorubicin incubation for 72 h on the expression of related proteins in HepG2 cells.
A: Blank control group; B: LV-hsa-mir-34a group; C: Doxorubicin treatment group; D: Empty vector + doxorubicin treatment group; E: LV-hsa-mir-34a + doxorubicin treatment group. MDR: Multidrug resistance protein; CDK: Cyclin-dependent kinase; SIRT: Sirtuin.
- Citation: Zheng SZ, Sun P, Wang JP, Liu Y, Gong W, Liu J. MiR-34a overexpression enhances the inhibitory effect of doxorubicin on HepG2 cells. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(22): 2752-2762
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i22/2752.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i22.2752