©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2018; 24(44): 5005-5012
Published online Nov 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i44.5005
Published online Nov 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i44.5005
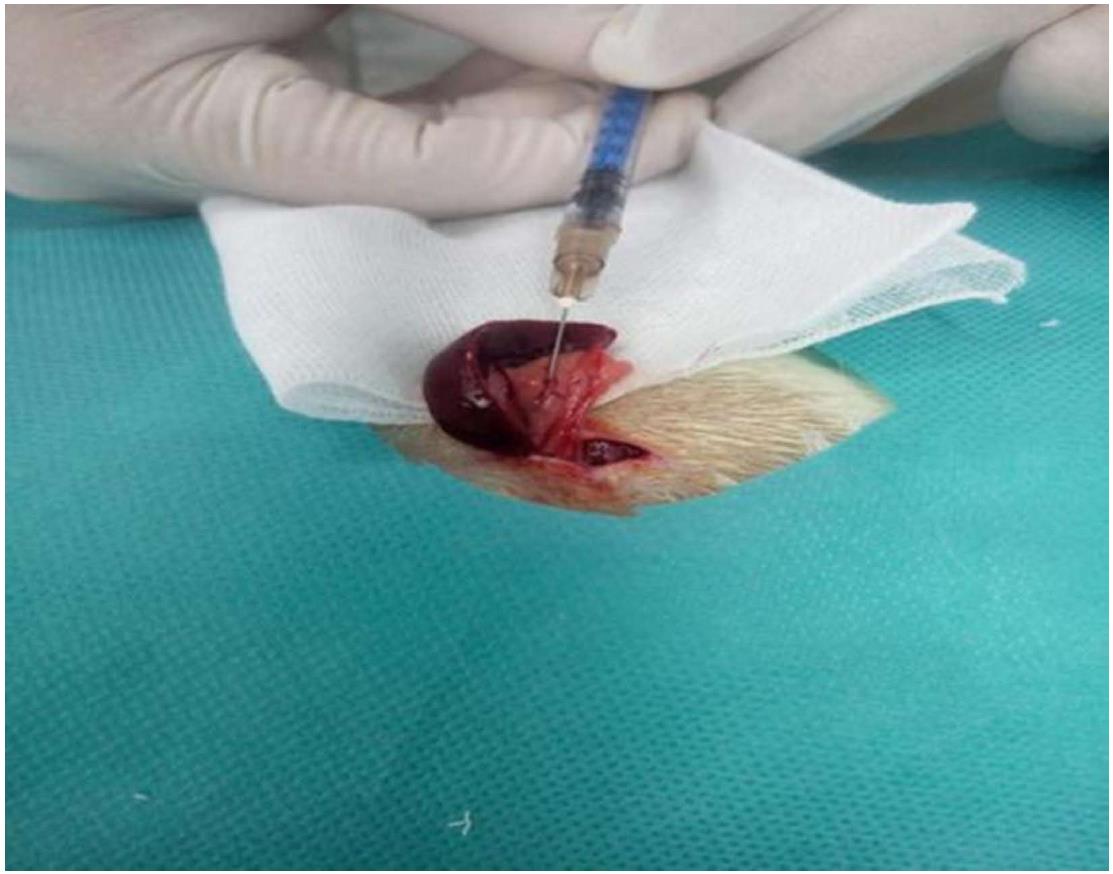
Figure 1 Development of a rat model of heterogeneous hepatic injury.
After anesthesia and splenic vein dissection, 0.25% colchicine at a dose of 0.4 mL/kg was injected via the splenic vein.
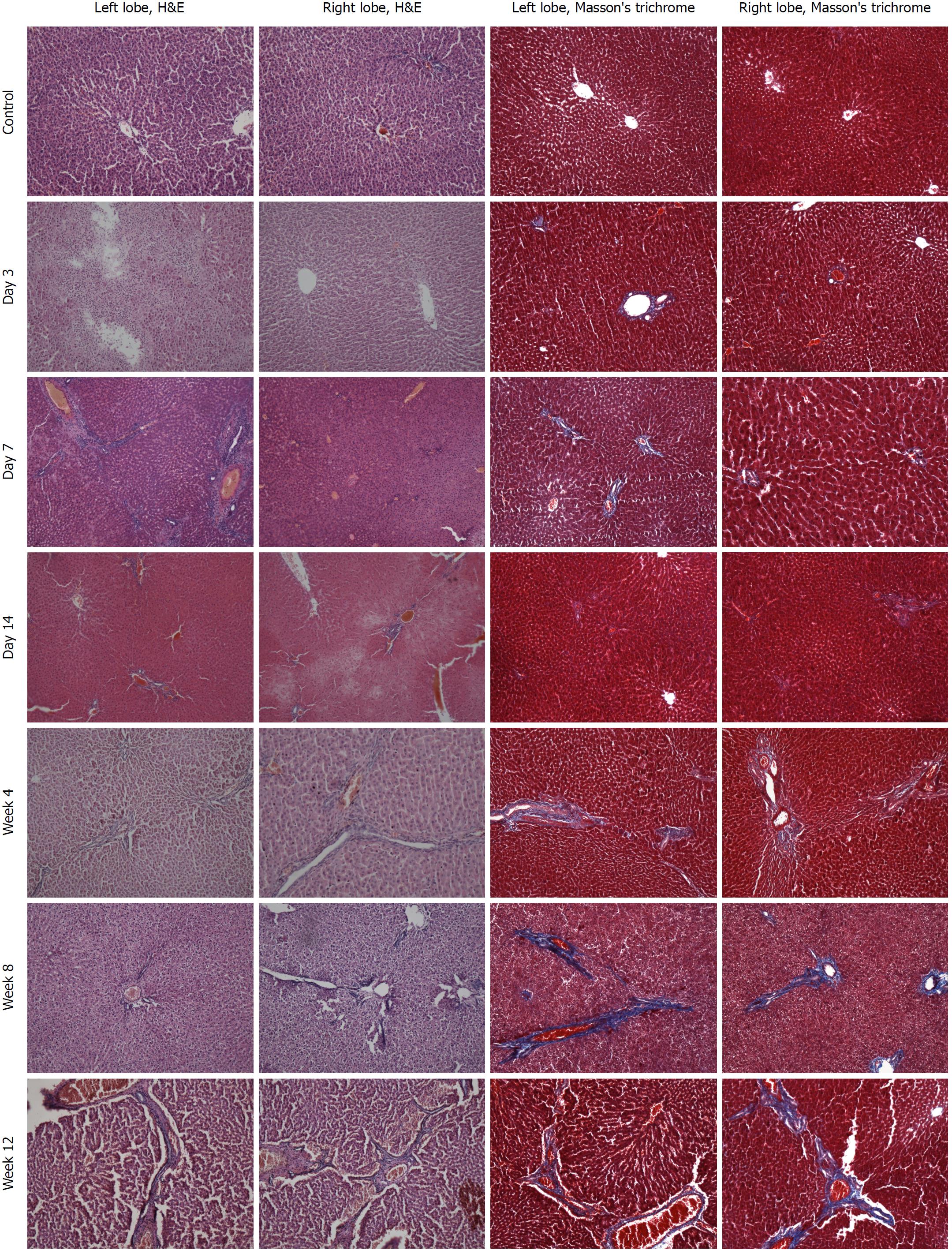
Figure 2 Histopathological changes of the liver (× 100).
H&E staining of sections of the left lobe (1st column) and right lobe (2nd column) of the liver, and Masson’s trichrome staining of sections of the left lobe (3rd column) and right lobe (4th column) of the liver were performed in the control group (1st row) and at each time point after injection of colchicine (2nd to 7th rows). No obvious pathological changes were observed in the control group. The hepatic injury was different between the left and right lobes at each time point. At day 3 after colchicine injection, there was massive inflammatory cells infiltration, hepatocellular edema, and mild liver necrosis. At day 14, reduced inflammation and increased necrosis were observed, while fibrosis was not detected. At week 4, cholestasis and early fibrosis were observed. At weeks 8 and 12, there was further fibrosis.
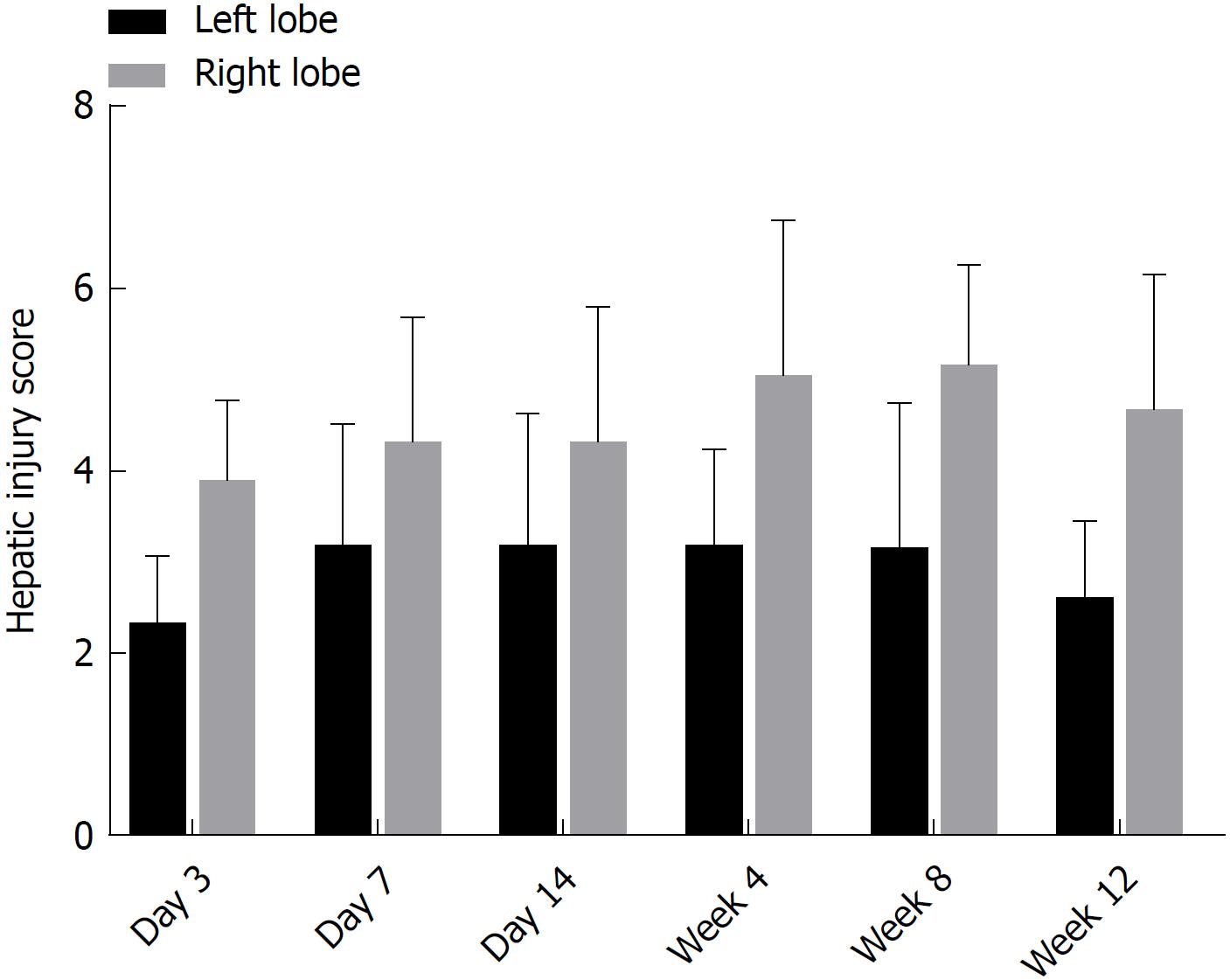
Figure 3 Comparisons of hepatic injury scores between the left and right lobes of rats in the colchicine group at each time point.
Difference in hepatic injury between the left and right lobes of colchicine group at each time point was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
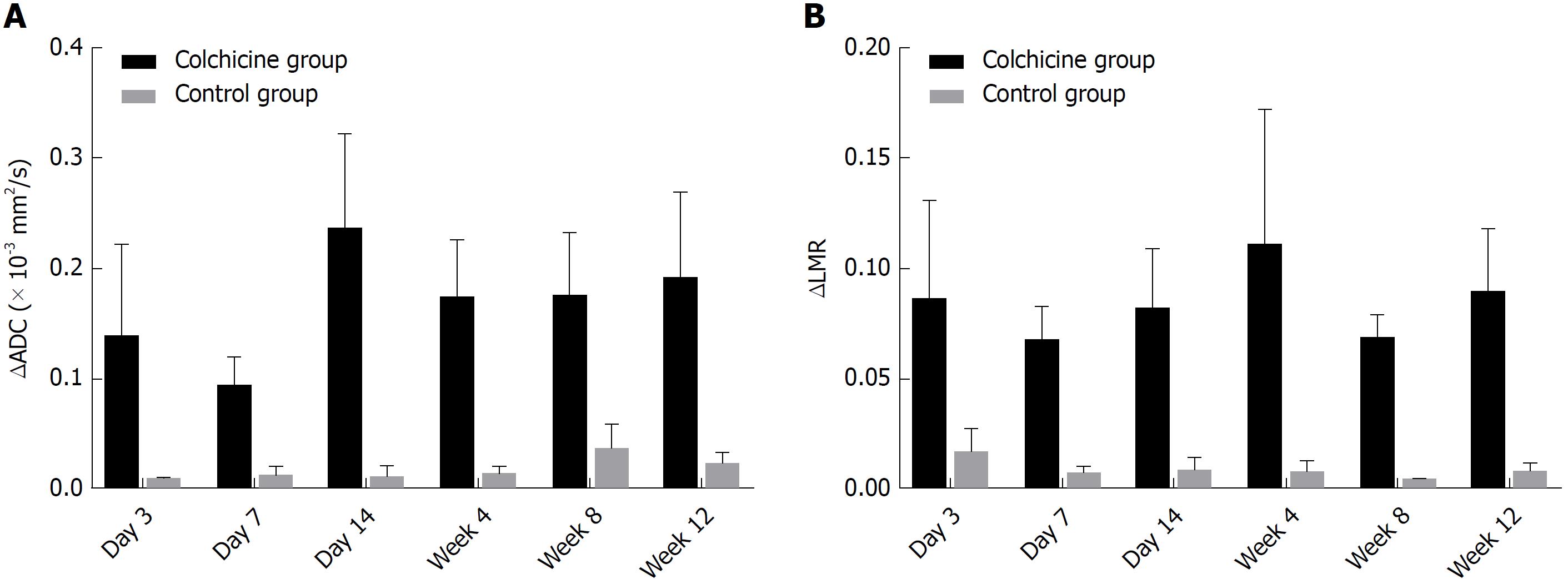
Figure 4 Comparisons of the difference of apparent diffusion coefficient (A) and the difference of liver-to-muscle ratio (B) between the colchicine group and the control group at each time point.
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. A statistically significant difference was noted in ΔADC (A) and ΔLMR (B) between the colchicine group and the control group (P < 0.05). ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient; LMR: Liver-to-muscle ratio.
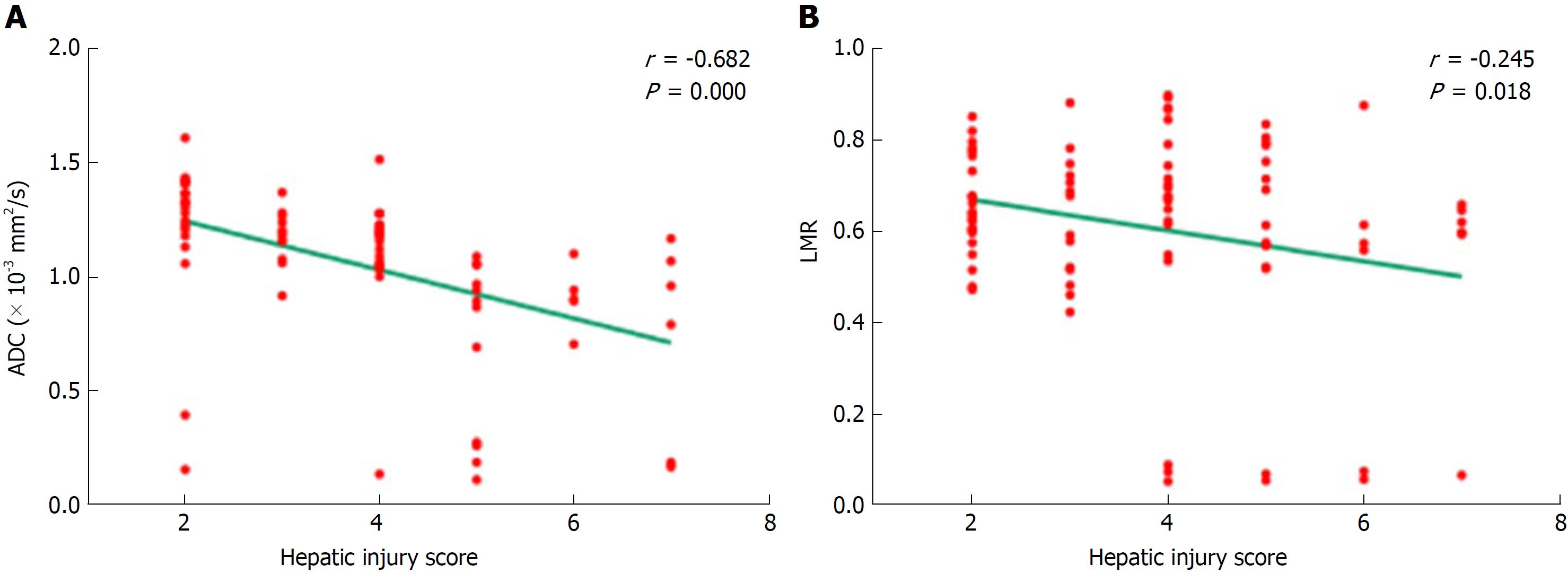
Figure 5 Correlations between magnetic resonance imaging variables and hepatic injury scores based on the scoring criteria.
ADC values and LMR decreased as hepatic injury scores increased, and the correlations were statistically significant. ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient; LMR: Liver-to-muscle ratio.
- Citation: Zhang YY, Zhang CX, Li Y, Jiang X, Wang YF, Sun Y, Wang J, Ji WY, Liu Y. Development of a novel rat model of heterogeneous hepatic injury by injection with colchicine via the splenic vein. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(44): 5005-5012
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i44/5005.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i44.5005