©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2018; 24(41): 4652-4662
Published online Nov 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652
Published online Nov 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652
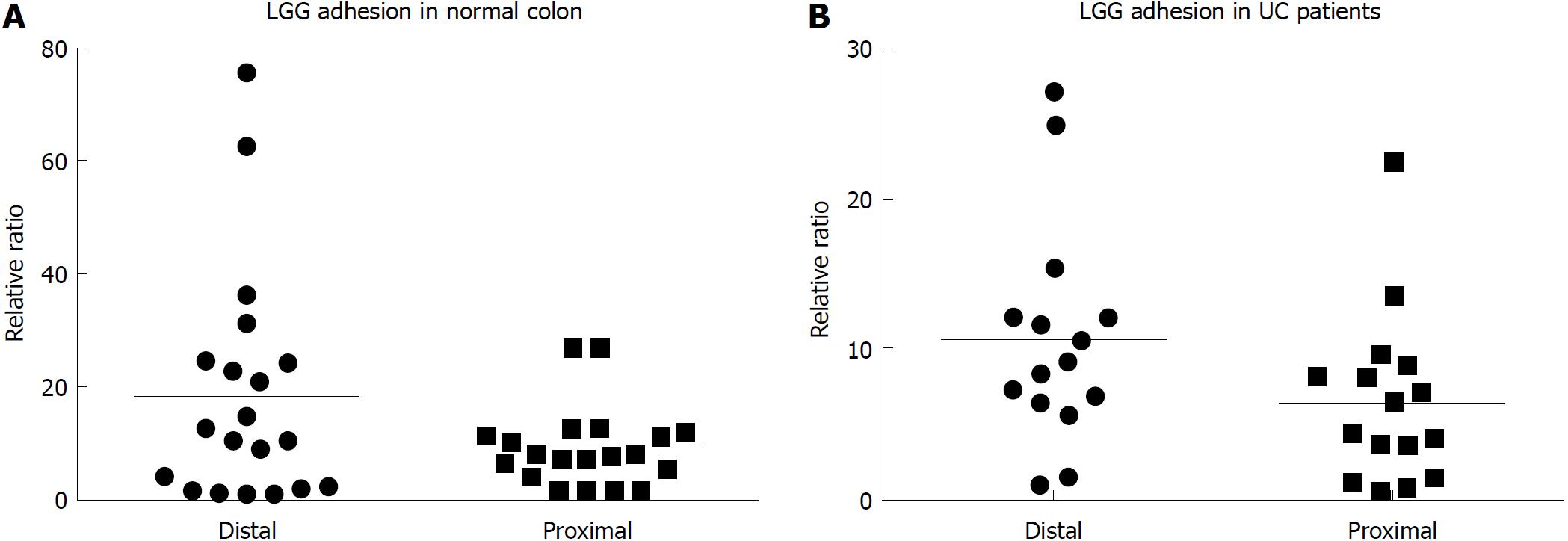
Figure 1 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG adhesion in the normal colon and ulcerative colitis patients’ colon was evaluated by the ex vivo organ culture experimental model.
A: Mucosal Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) quantification from total bioptic samples showed consistent adhesion in mucosal biopsies, with a trend toward higher LGG concentrations in distal specimens compared with proximal specimens (n = 20 per group); B: Mucosal LGG quantification from bioptic samples from ulcerative colitis patients confirmed consistent bacterial adhesion after incubation (n = 15 per group). The bars represent the mean values. LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
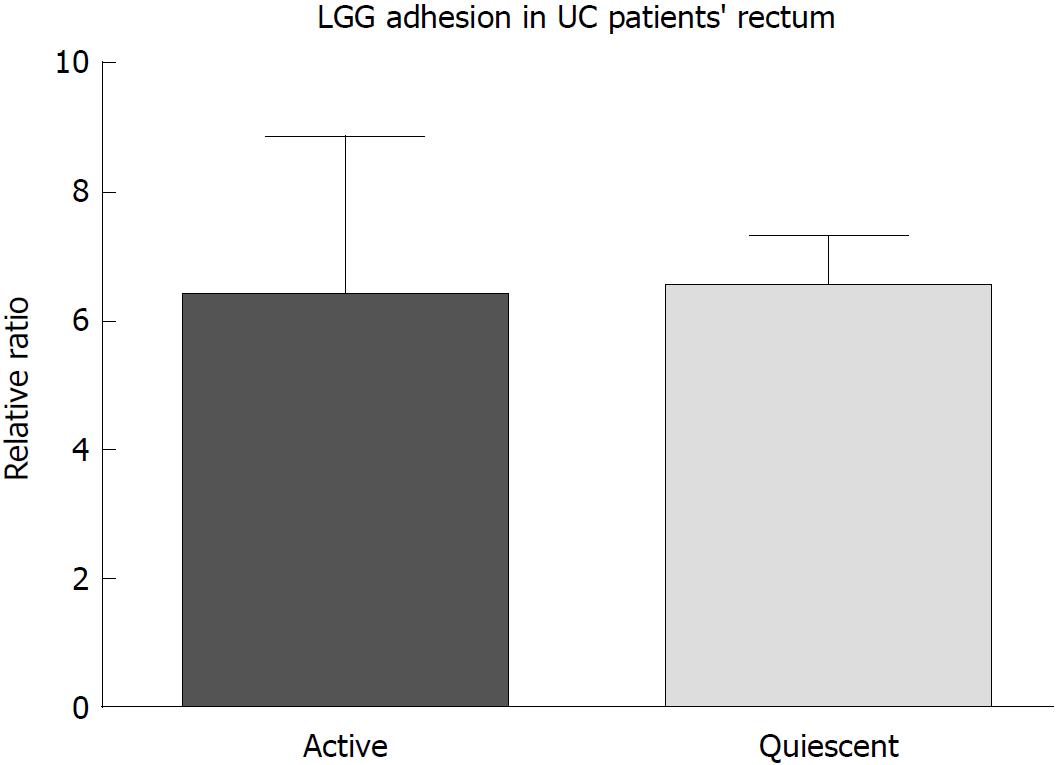
Figure 2 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG adhesion in bioptic samples from the rectum of ulcerative colitis patients was evaluated by the ex vivo organ culture experimental model.
Similar concentrations of adherent Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG were found in the mucosa from ulcerative colitis patients without and with active endoscopic inflammation, as defined by Mayo Endoscopic Scores of ≤ 1 and 2, respectively (n = 15 per group). Mean ± standard error is represented. LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
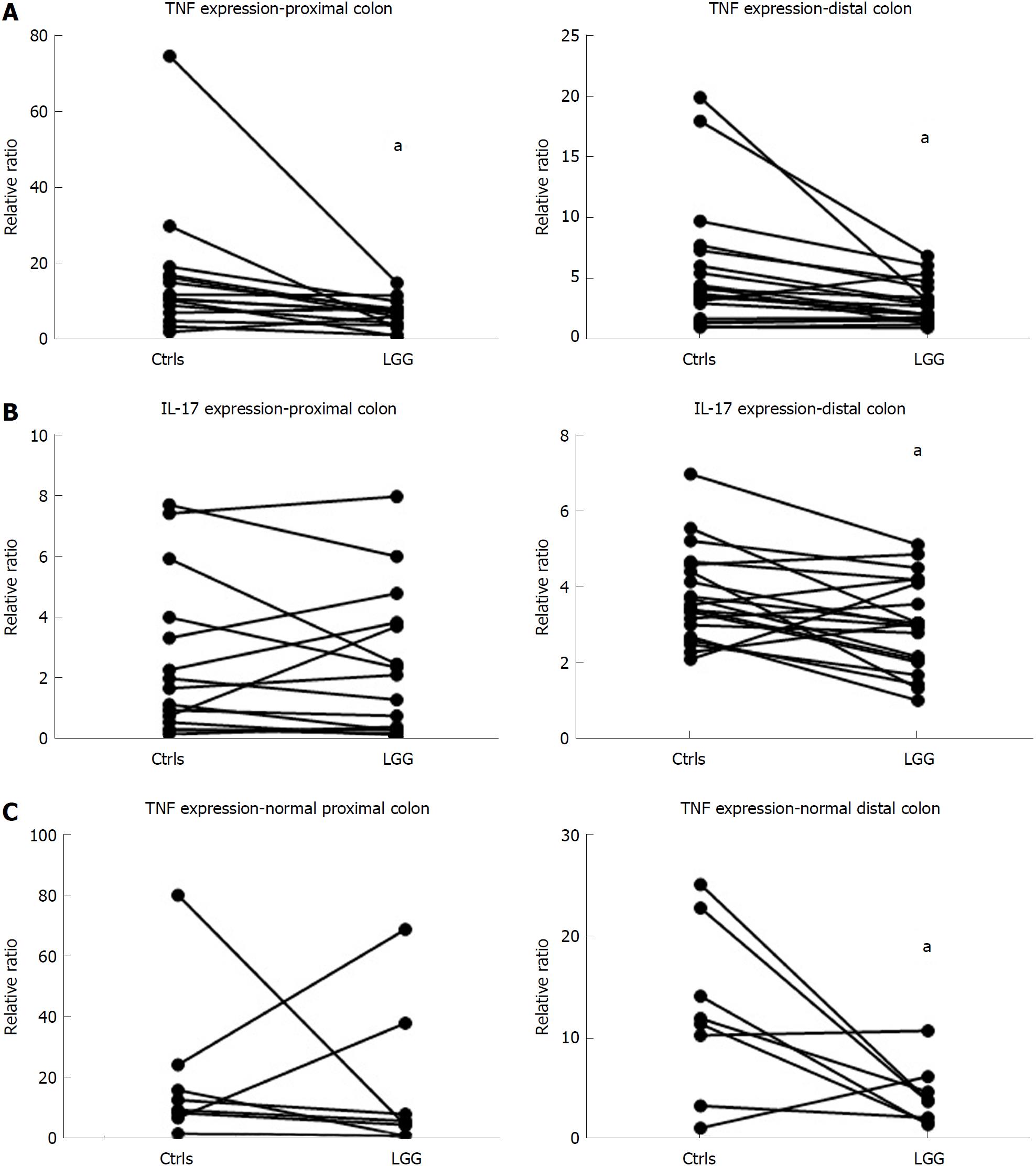
Figure 3 Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on cytokine expression in the colon was evaluated by the ex vivo organ culture experimental model.
A: Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) mRNA quantification in proximal (n = 15) and distal (n = 20) colon biopsies from ulcerative colitis (UC) patients incubated with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) conditioned media (CM) and control biopsies; B: IL-17 mRNA quantification in proximal and distal colon biopsies from UC patients incubated with LGG CM and control biopsies; C: TNFα mRNA quantification in proximal and distal colon biopsies (n = 8 per group) from normal subjects incubated with LGG CM and control biopsies. aP < 0.05. TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
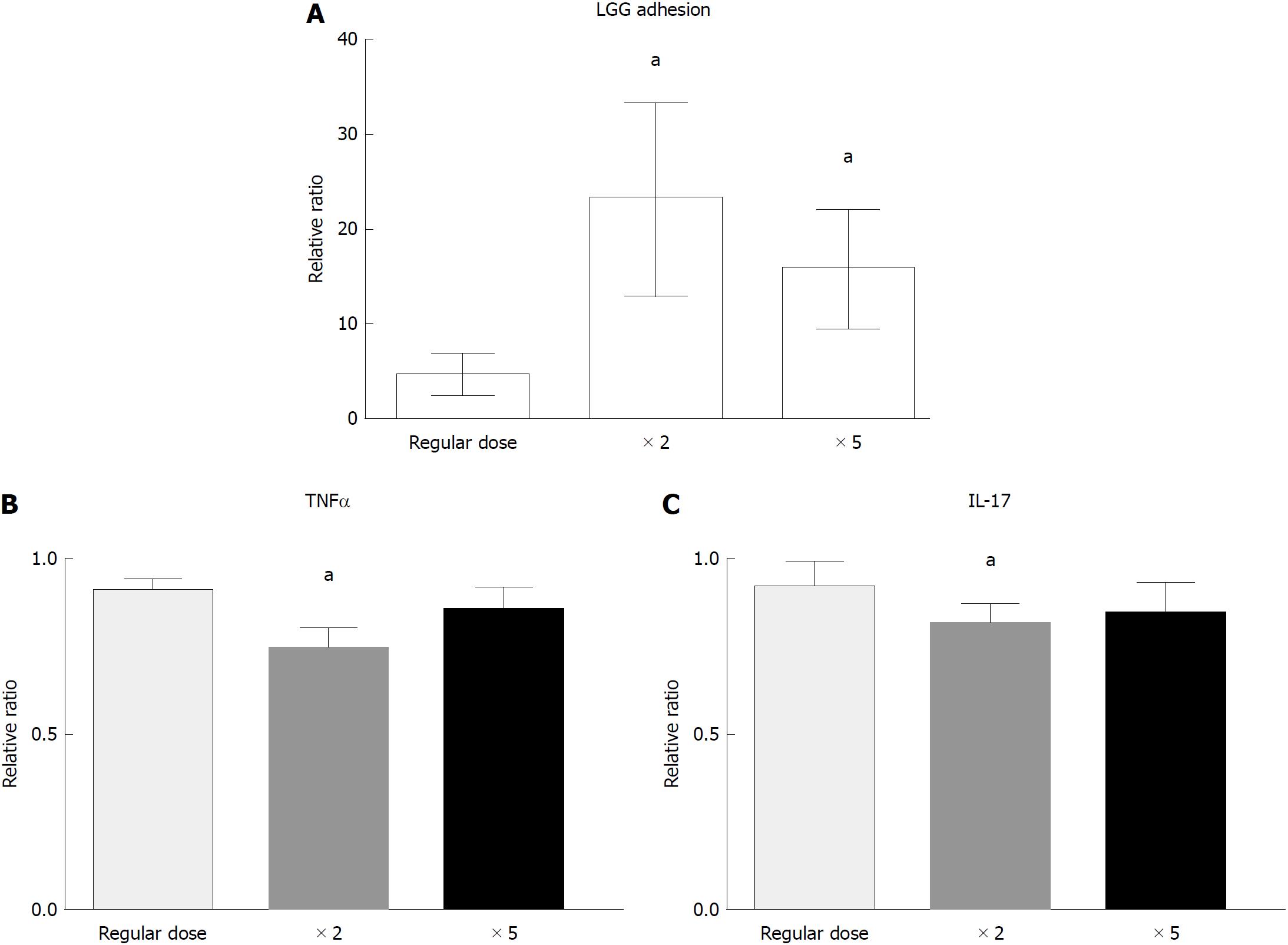
Figure 4 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG dose-finding study in the ex vivo organ culture experimental model.
A: Mucosal Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) quantification in distal colon bioptic samples after incubation with a regular (6 × 106 CFU), double or 5-times dose of LGG. aP < 0.05 vs regular dose (n = 8 per group); B: TNFα mRNA quantification in distal colon bioptic samples incubated with a regular (1:10), double (2:10) or 5-times (5:10) dose of LGG conditioned media (CM) (n = 10 per group); C: IL-17 mRNA quantification in distal colon bioptic samples incubated with a regular (1:10), double (2:10) or 5-times (5:10) dose of LGG CM. Mean ± standard error is represented. aP < 0.05 vs regular dose. TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; CM: Conditioned media.
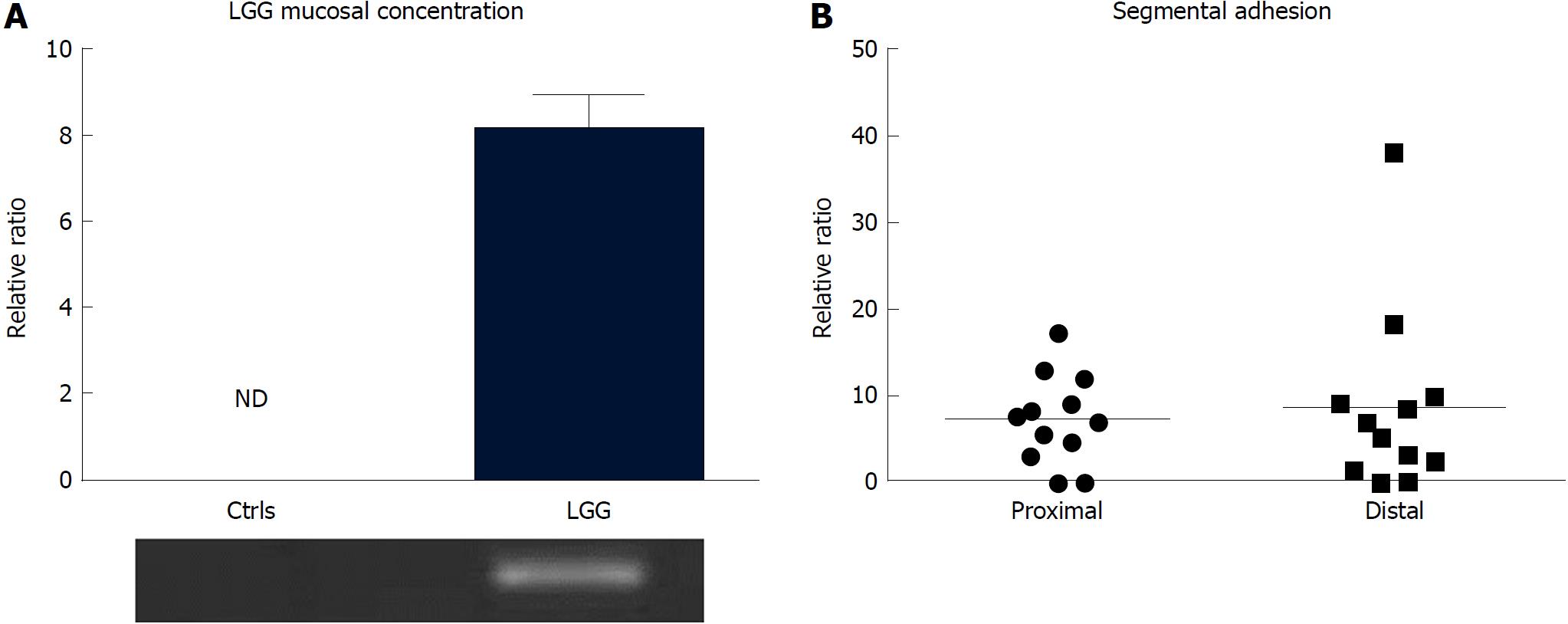
Figure 5 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG adhesion in the normal colon in vivo after 7 d of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG administration.
A: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) detection in the colon of normal subjects who did (n = 12) and did not (n = 10) consume the probiotic formulation. Relative value bars and visualization on an agarose gel are shown. Mean ± standard error is represented; B: Relative segmental adhesion of LGG in the proximal and distal colon biopsies (n = 12 per group), with the bars representing the mean values. ND: Not detectable; LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.
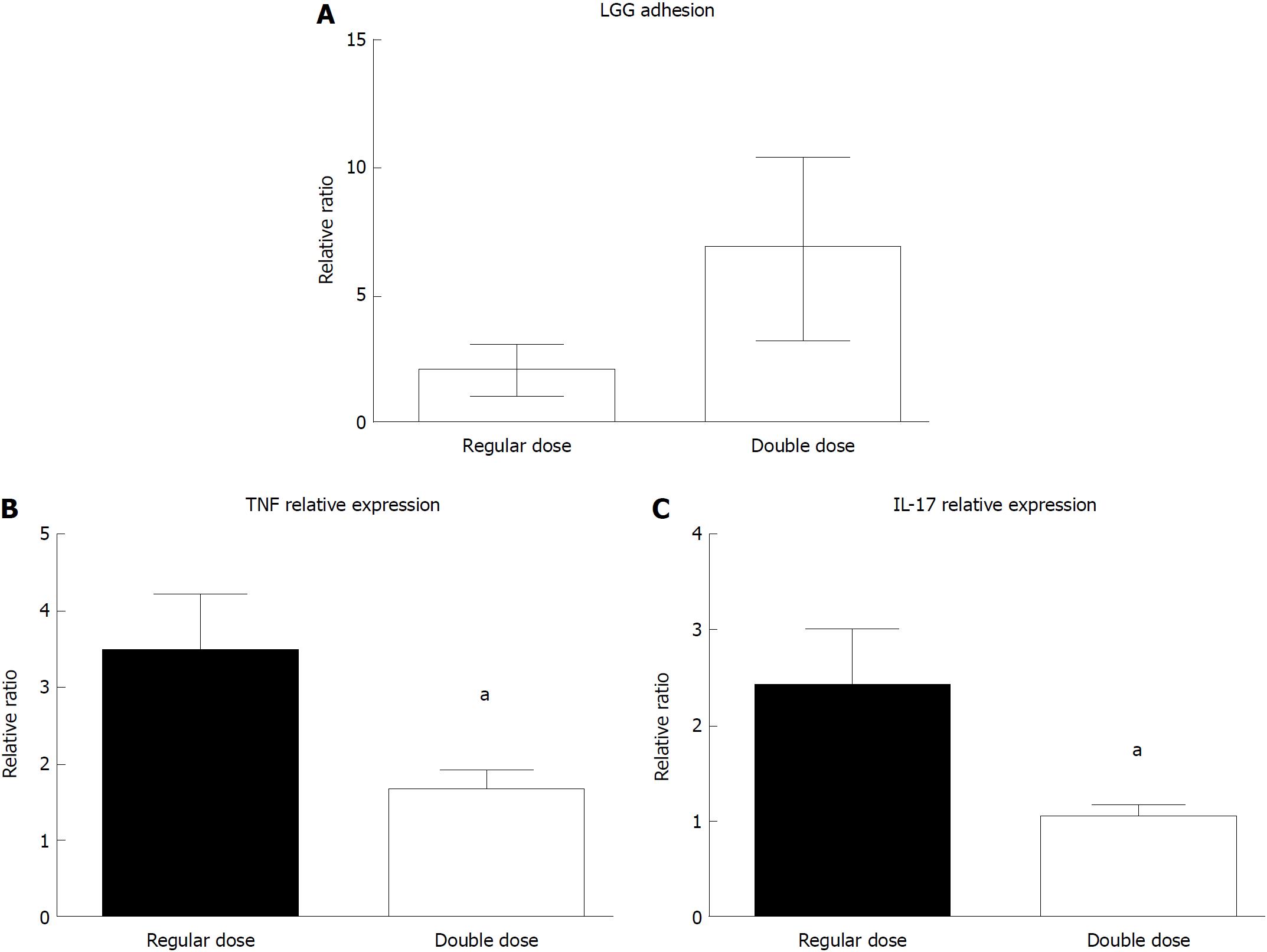
Figure 6 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG adhesion and mucosal effect in the colon of ulcerative colitis patients.
A: Mucosal Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) quantification in colon biopsies of ulcerative colitis (UC) patients who consumed a regular (12 × 109 UFC/die) or a double (24 × 109 UFC/die) dose of LGG supplement for 7 d (n = 10 per group); B: Tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA quantification in colon biopsies from UC patients who consumed a regular or a double dose of LGG supplement for 7 d. Mean ± standard error is represented; C: Interleukin-17 mRNA quantification in colon biopsies from UC patients who consumed a regular or a double dose of LGG supplement for 7 d. aP < 0.05. TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
- Citation: Pagnini C, Corleto VD, Martorelli M, Lanini C, D’Ambra G, Di Giulio E, Delle Fave G. Mucosal adhesion and anti-inflammatory effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in the human colonic mucosa: A proof-of-concept study. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(41): 4652-4662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i41/4652.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652