©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2018; 24(4): 537-542
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.537
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.537
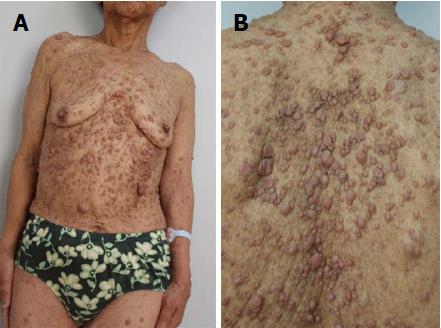
Figure 1 General appearance.
A and B: A patient diagnosed with neurofibromatosis type 1 presented with café au lait spots on the skin. 300 mm × 225 mm (300 × 300 DPI).
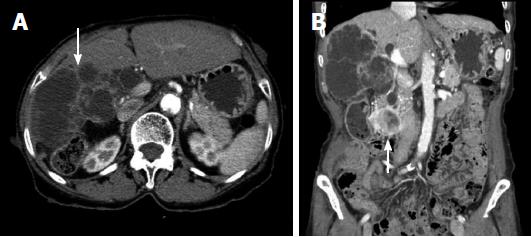
Figure 2 Computed tomography.
A: A low-attenuated multilocular mass with septation, and a mural nodule containing a soft tissue-enhancing lesion in the right hepatic lobe (white arrow); B: Diffuse intrahepatic duct (IHD) dilatation, especially in the right hepatic lobe, with a suspicious soft tissue lesion connected to the IHD. A 1.7-cm-sized, well-demarcated enhancing mass is observed in the third portion of the duodenum (white arrow). 300 mm × 225 mm (300 × 300 DPI).
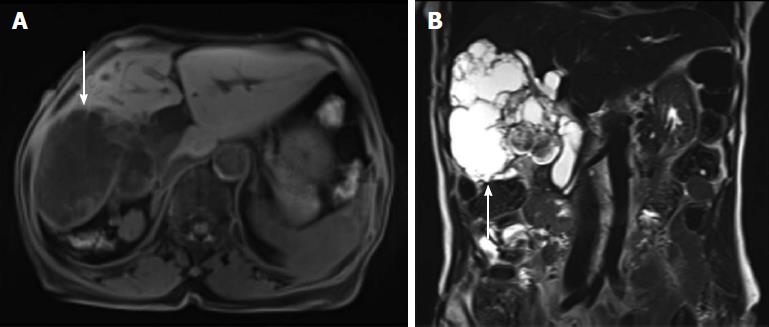
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
A: A lobulated cystic mass in the right hepatic lobe with multifocal intramural enhancing nodules (white arrow); B: The connection of the cystic mass with the intrahepatic duct indicated a malignant transformation (white arrow). 300 mm × 225 mm (300 × 300 DPI).
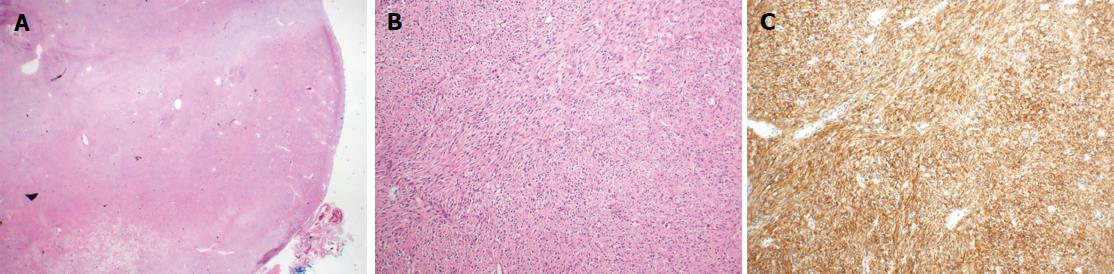
Figure 4 Histologic findings of gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
A: A mass with rounded border, resected from the third portion of the duodenum. (HE, 40 × magnification); B: The resected duodenal mass contained many spindle cells. (HE, 100 ×); C: Positive immunohistochemistry for c-kit suggested GIST. (c-kit immunostain, 100 ×). 300 mm × 225 mm (300 × 300 DPI). GIST: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
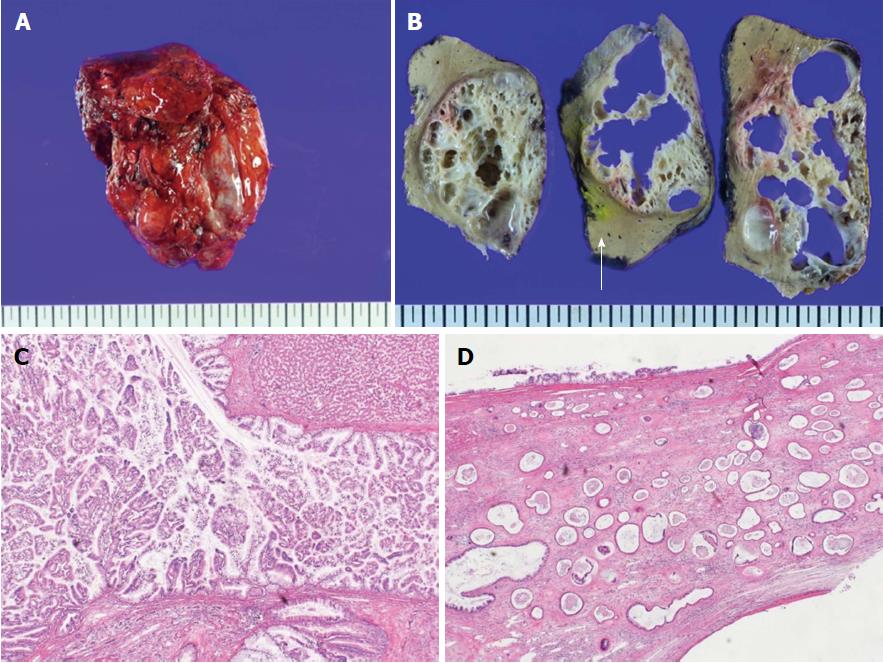
Figure 5 Histologic findings of intraductal papillary neoplasm of bile duct.
A: The resected hepatic mass was a multilocular cystic neoplasm with septation and a mural nodule; B: It had communication to segmental bile duct, although it was not connected to main bile duct (white arrow: Main bile duct); C: In the dilated bile duct, normal epithelial lining with abrupt papillary epithelial portions suggests IPNB. (HE, 100 ×); D: Multifocal stromal invasion multifocal stromal invasion with a tubulopapillary mucin component, suggestive of invasive adenocarcinoma with high-grade dyplasia. (HE, 40 ×). 300 mm × 225 mm (300 × 300 DPI).
- Citation: Lee JM, Lee JM, Hyun JJ, Choi HS, Kim ES, Keum B, Jeen YT, Chun HJ, Lee HS, Kim CD, Kim DS, Kim JY. Intraductal papillary bile duct adenocarcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumor in a case of neurofibromatosis type 1. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(4): 537-542
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i4/537.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.537