©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2018; 24(4): 519-536
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.519
Published online Jan 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.519
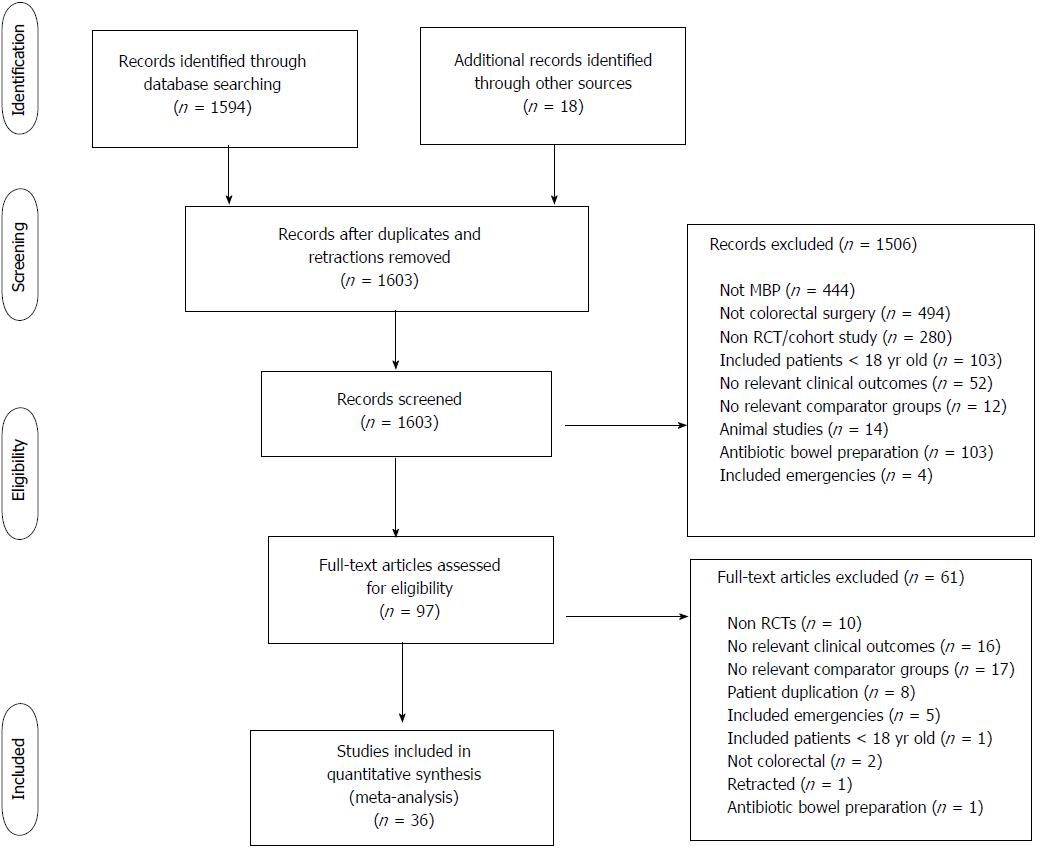
Figure 1 PRISMA diagram showing identification of relevant studies from initial search, PRISMA: Preferred reporting Items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
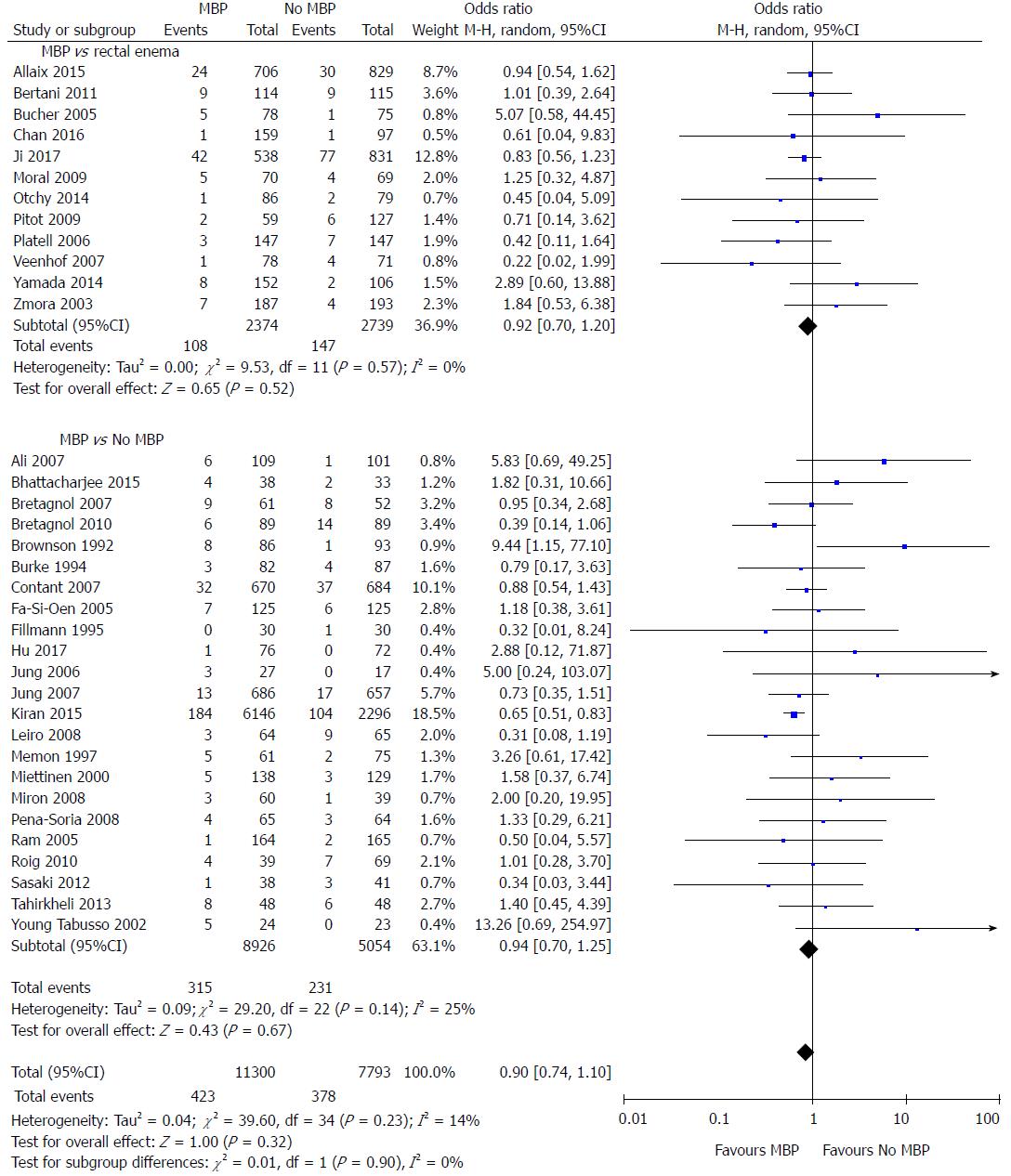
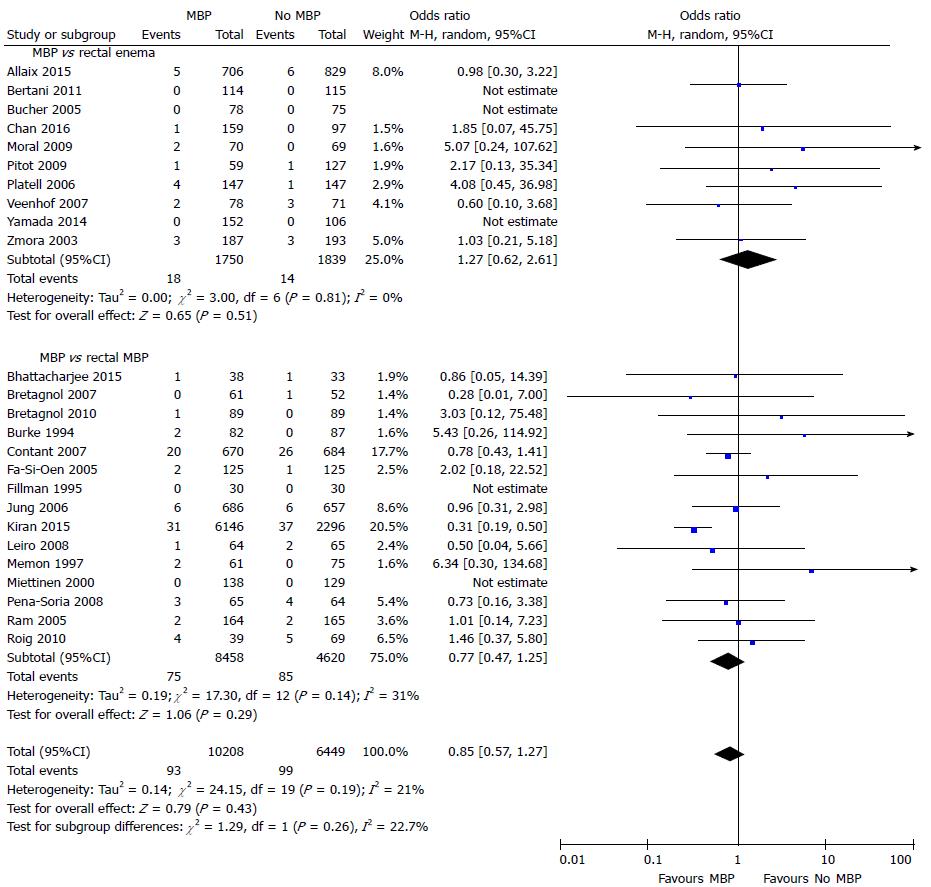
Figure 2 Forest plot comparing overall anastomotic leak rate for patients receiving mechanical bowel preparation vs either a single rectal enema (top) or absolutely no preparation (bottom).
A Mantel-Haenszel random effects model was used to perform the meta-analysis and odds ratios are quoted including 95% confidence intervals. MBP: Mechanical bowel preparation.
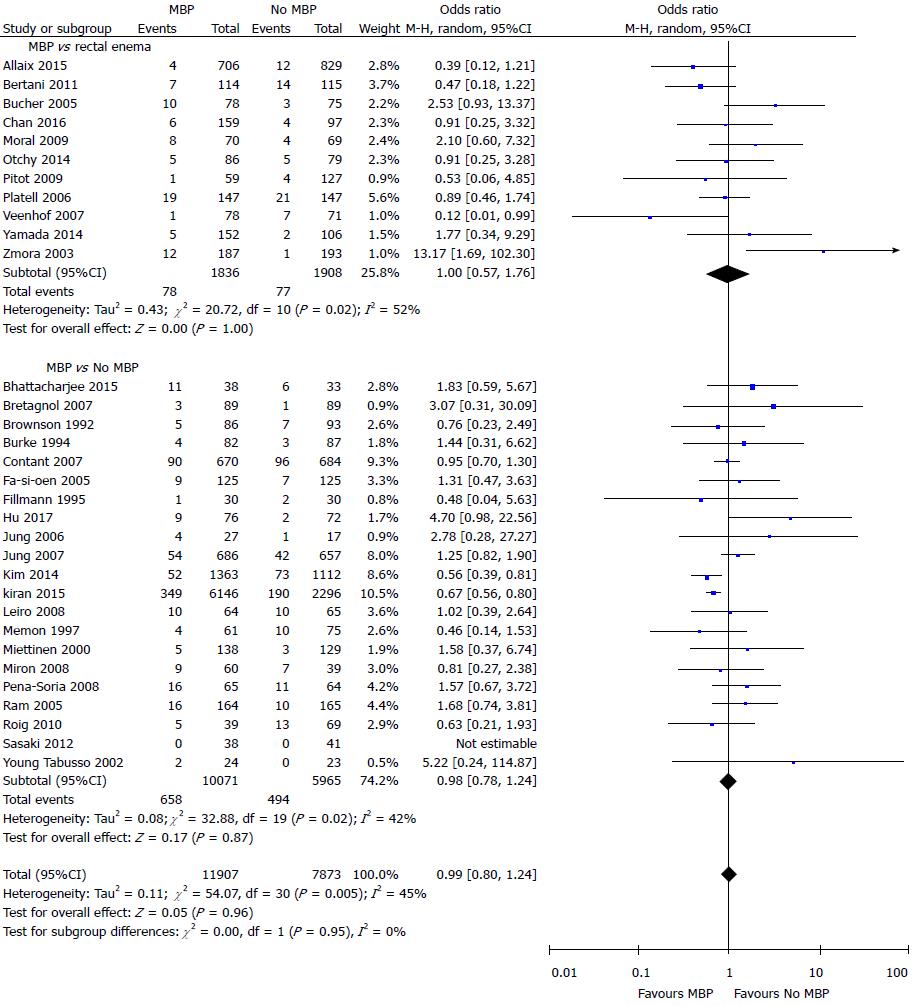
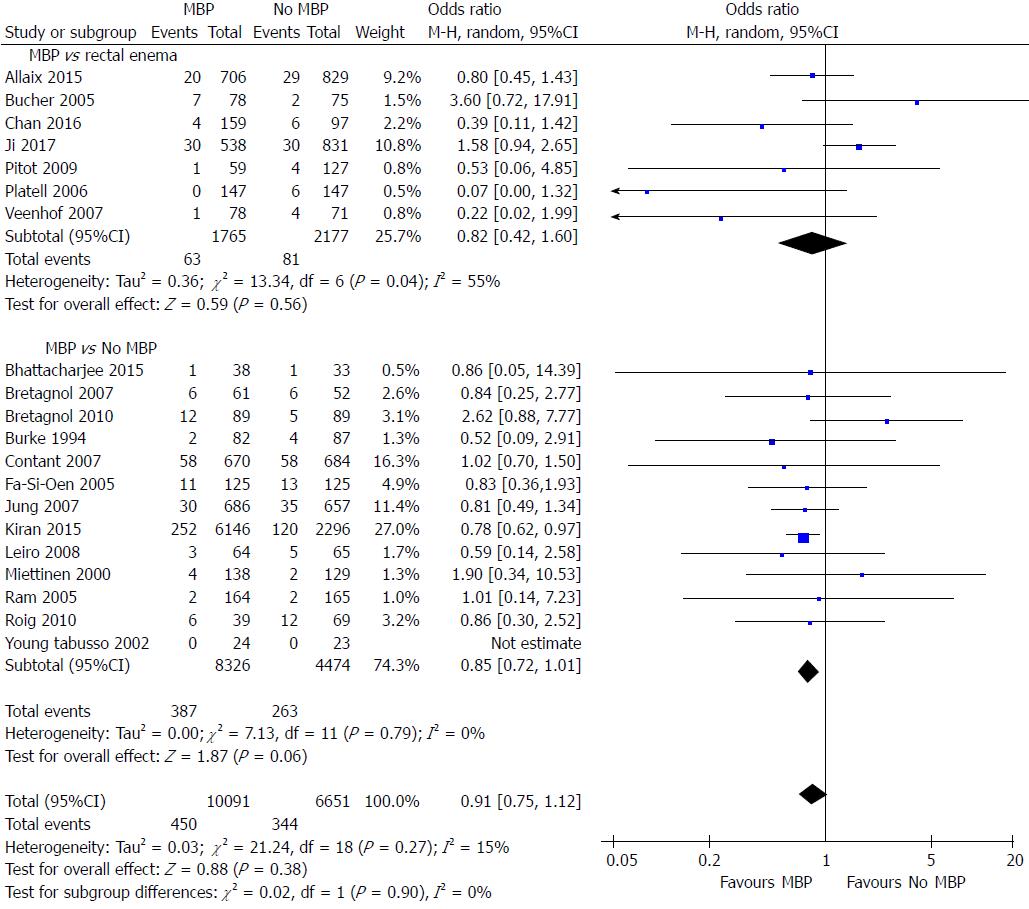
Figure 3 Forest plot comparing overall surgical site infection rates for patients receiving mechanical bowel preparation vs either a single rectal enema (top) or absolutely no preparation (bottom).
A Mantel-Haenszel random effects model was used to perform the meta-analysis and odds ratios are quoted including 95% confidence intervals. MBP: Mechanical bowel preparation.
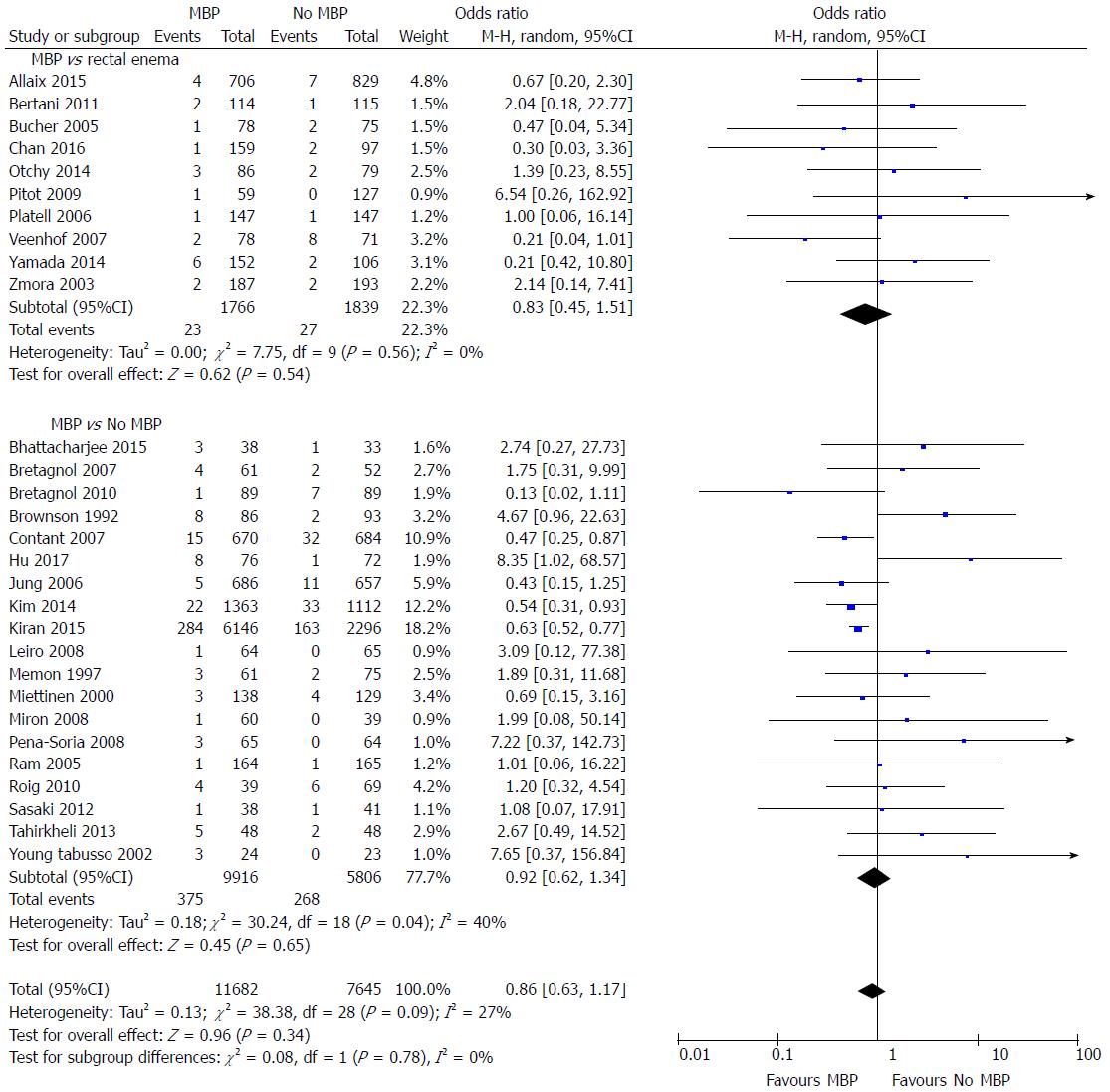
Figure 4 Forest plot comparing overall intra-abdominal collection rates for patients receiving mechanical bowel preparation vs either a single rectal enema (top) or absolutely no preparation (bottom).
A Mantel-Haenszel random effects model was used to perform the meta-analysis and odds ratios are quoted including 95% confidence intervals. MBP: Mechanical bowel preparation.
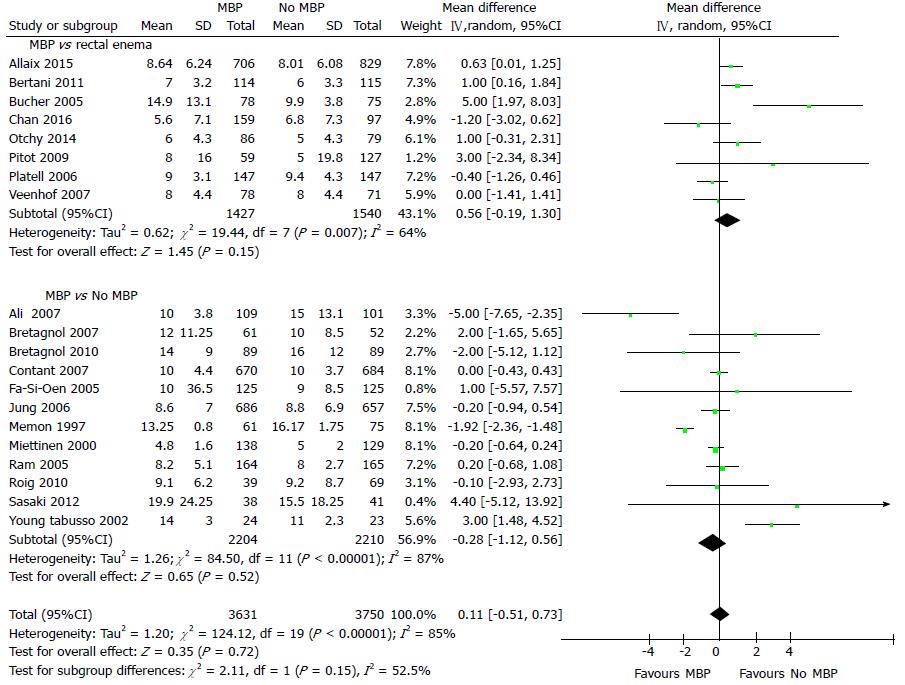
Figure 5 Forest plot comparing overall hospital length of stay for patients receiving mechanical bowel preparation vs either a single rectal enema (top) or absolutely no preparation (bottom).
An inverse-variance random effects model was used to perform the meta-analysis and mean differences are quoted including 95% confidence intervals. MBP: Mechanical bowel preparation.
Figure 6 Forest plot comparing overall mortality rates for patients receiving mechanical bowel preparation vs either a single rectal enema (top) or absolutely no preparation (bottom).
A Mantel-Haenszel random effects model was used to perform the meta-analysis and odds ratios are quoted including 95% confidence intervals. MBP: Mechanical bowel preparation.
Figure 7 Forest plot comparing overall reoperation rates for patients receiving mechanical bowel preparation vs either a single rectal enema (top) or absolutely no preparation (bottom).
A Mantel-Haenszel random effects model was used to perform the meta-analysis and odds ratios are quoted including 95% confidence intervals. MBP: Mechanical bowel preparation.
- Citation: Rollins KE, Javanmard-Emamghissi H, Lobo DN. Impact of mechanical bowel preparation in elective colorectal surgery: A meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(4): 519-536
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i4/519.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i4.519