©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2017; 23(5): 926-930
Published online Feb 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.926
Published online Feb 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.926
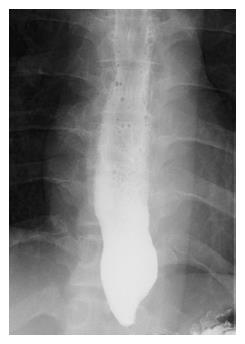
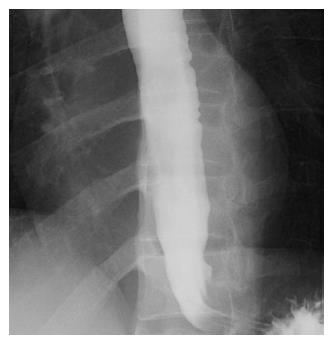
Figure 1 Subtle dilated distal esophageal lumen with acute tapering at the lower esophageal sphincter and narrowing at the esophagogastric junction was shown in esophagography.
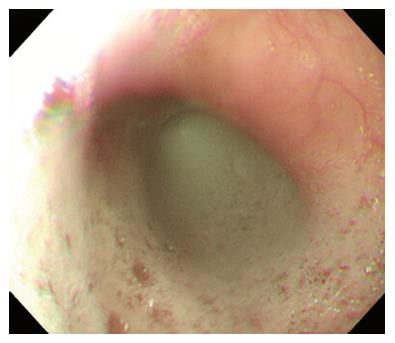
Figure 2 Dilation of the esophageal lumen and retention of food remnants in the esophagus was identified during endoscopy.
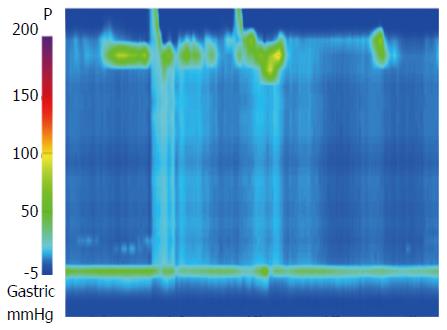
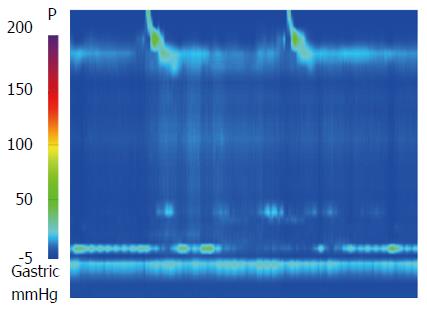
Figure 3 Mean integrated relaxation pressure 22.
9 mmHg over test swallows with absent peristalsis was shown in high-resolution manometry.
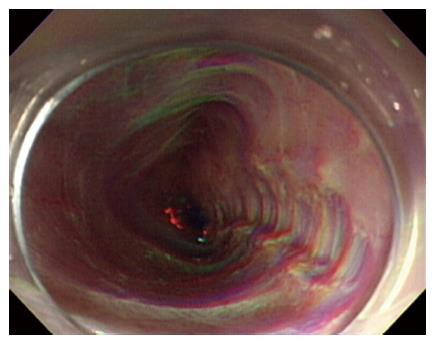
Figure 4 Peroral endoscopic myotomy was performed to treat Guillain-Barre syndrome-associated type I achalasia.
Figure 5 After peroral endoscopic myotomy, smooth passage of a contrast agent into the stomach was shown in follow-up esophagography.
Figure 6 Mean integrated relaxation pressure decreased to 9.
6 mmHg in follow-up high-resolution manometry.
- Citation: Shin SK, Kim KO, Kim EJ, Kim SY, Kim JH, Kim YJ, Chung JW, Kwon KA, Park DK. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for treatment of Guillain-Barre syndrome-associated achalasia: A rare case. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(5): 926-930
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i5/926.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.926