©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2017; 23(44): 7863-7874
Published online Nov 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i44.7863
Published online Nov 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i44.7863
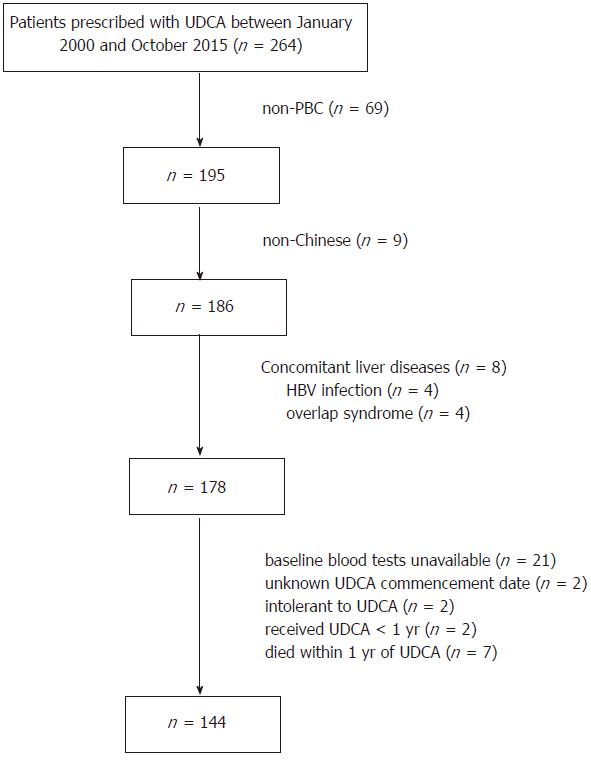
Figure 1 Flowchart illustrating case search and identification process.
HBV: Hepatitis B virus; PBC: Primary biliary cholangitis; UDCA: Ursodeoxycholic acid.
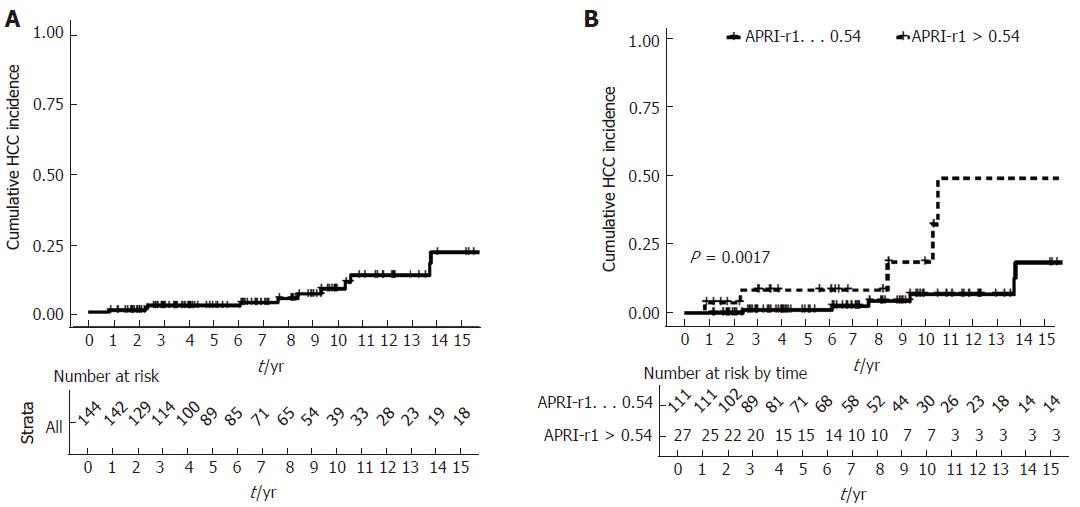
Figure 2 Cumulative hepatocellular carcinoma incidence.
A: Whole cohort; B: Stratified by APRI-r1. APRI-r1: AST/platelet ratio index at 1-year.
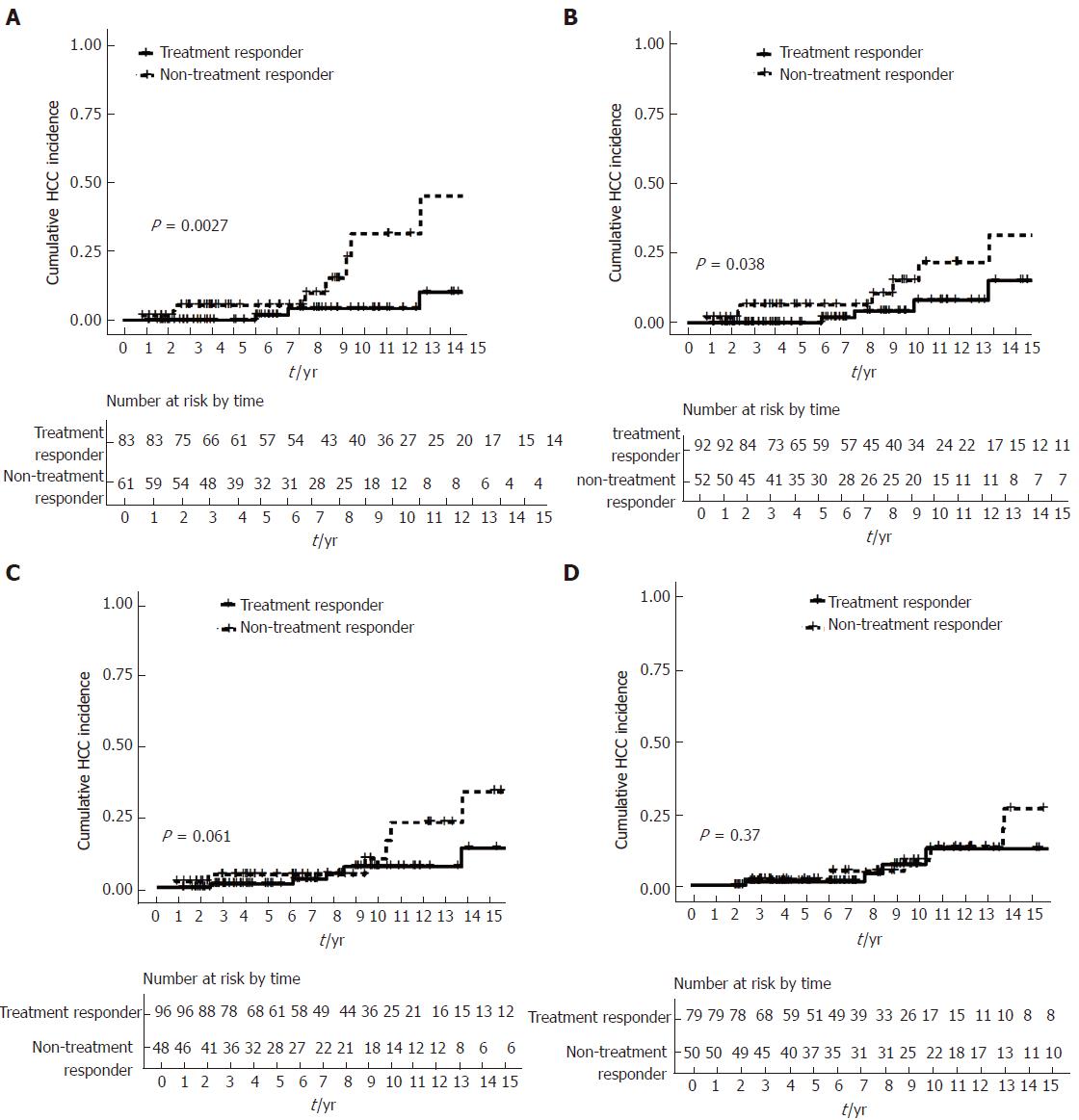
Figure 3 Cumulative hepatocellular carcinoma incidence stratified by treatment response.
A: Rotterdam criteria; B: Paris I criteria; C: Barcelona criteria; D: Toronto criteria.
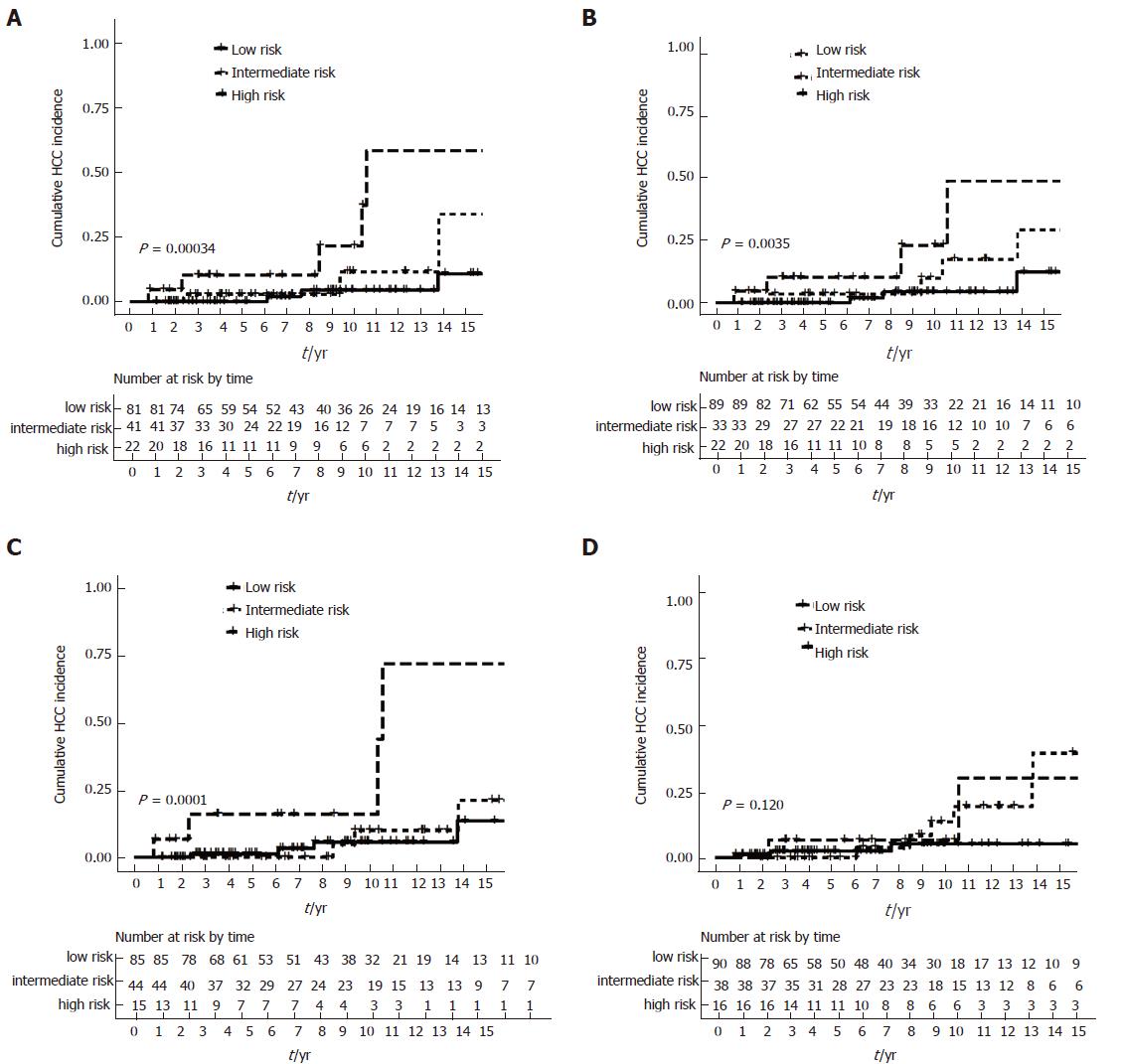
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier survival plot stratified by APRI-r1 and treatment response.
A: Rotterdam criteria; B: Paris I criteria; C: Barcelona criteria; D: Toronto criteria. APRI-r1: AST/platelet ratio index at 1-year; low-risk (biochemical response with APRI-r1 ≤ 0.54), intermediate risk (suboptimal biochemical response with APRI-r1 ≤ 0.54, or biochemical response with APRI-r1 > 0.54) and high risk (suboptimal biochemical response with APRI-r1 > 0.54).
- Citation: Cheung KS, Seto WK, Fung J, Mak LY, Lai CL, Yuen MF. Prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma development by aminotransferase to platelet ratio index in primary biliary cholangitis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(44): 7863-7874
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i44/7863.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i44.7863