©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2017; 23(40): 7292-7302
Published online Oct 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7292
Published online Oct 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7292
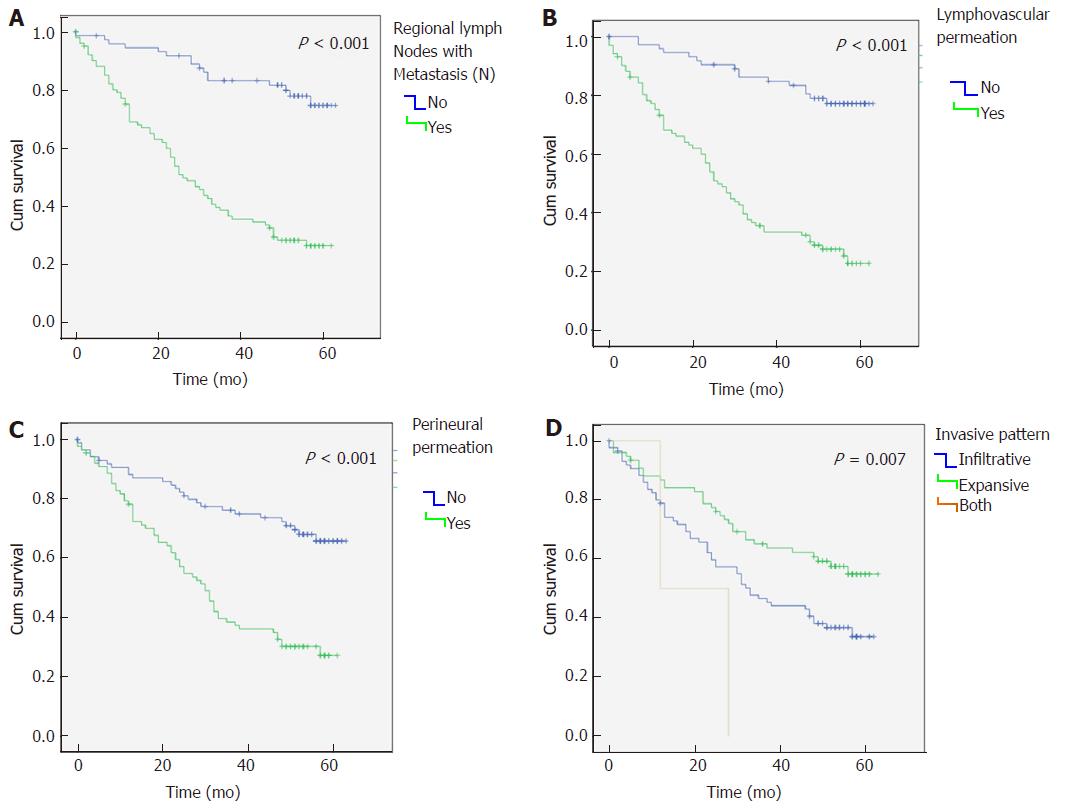
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for overall survival.
Comparison of overall survival in gastric cancer patients considering: A: Regional lymph node metastasis; B: Lymphovascular permeation; C: Perineural permeation; and D: Invasive pattern.
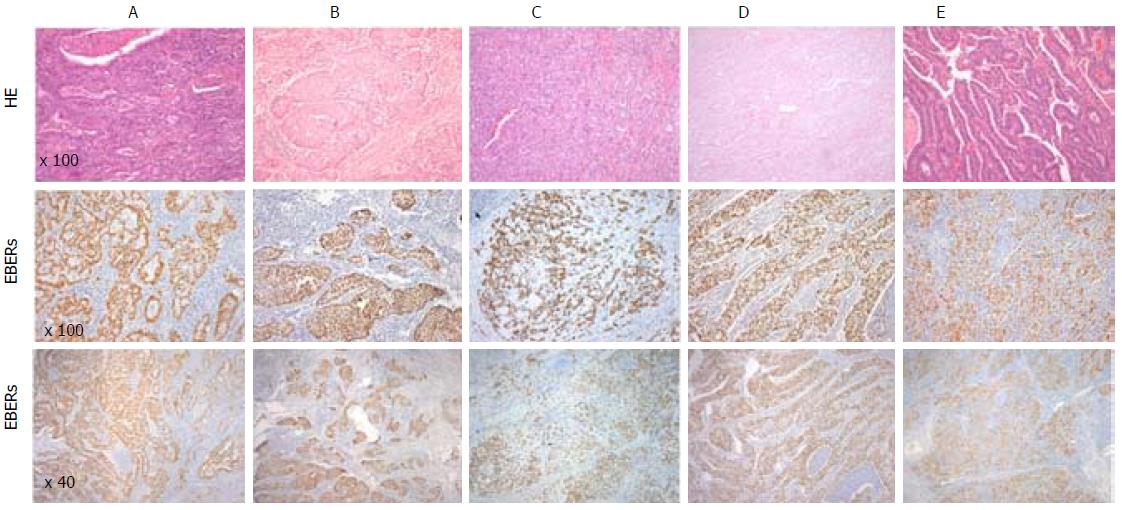
Figure 1 Representative images of EBER-ISH positive results in different histological types of gastric cancer and their respective HE staining.
A: Adenocarcinoma tubular; B: Adenocarcinoma tubular; C: Adenocarcinoma Mixed; D: Adenosquamous Carcinoma; E: Medullary caricnoma. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin stain; EBERs: EBV-encoded small RNAs. Figure 1 Representative images of EBER-ISH positive results in different histological types of gastric cancer and their respective HE staining. A: Adenocarcinoma tubular; B: Adenocarcinoma tubular; C: Adenocarcinoma Mixed; D: Adenosquamous Carcinoma; E: Medullary caricnoma. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin stain; EBERs: EBV-encoded small RNAs.
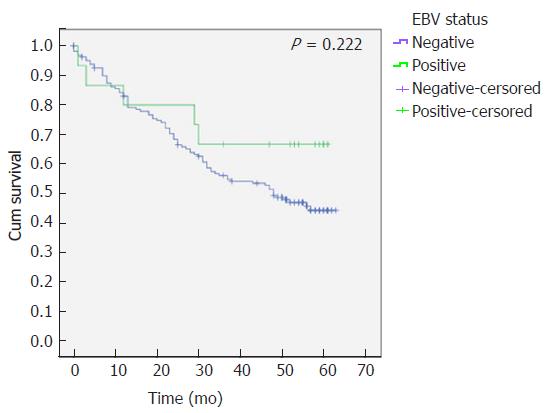
Figure 3 Comparison of overall survival in patients with Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas and Epstein-Barr virus-non associated gastric cancer.
Kaplan-Meier curves with log-rank test estimate the overall survival of gastric cancer patients with and without Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated gastric cancer.
- Citation: Ribeiro J, Oliveira A, Malta M, Oliveira C, Silva F, Galaghar A, Afonso LP, Neves MC, Medeiros R, Pimentel-Nunes P, Sousa H. Clinical and pathological characterization of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas in Portugal. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(40): 7292-7302
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i40/7292.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7292