©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2017; 23(4): 590-602
Published online Jan 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i4.590
Published online Jan 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i4.590
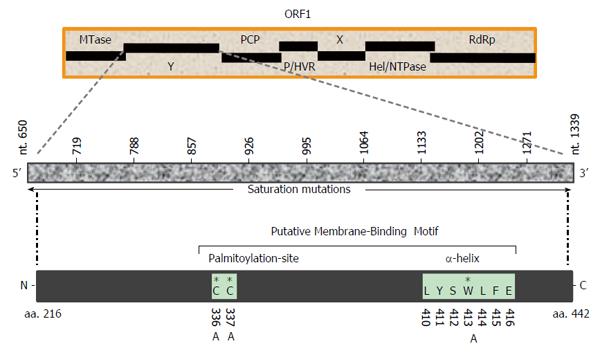
Figure 1 Schematic representation of hepatitis E virus nonstructural polyprotein (ORF1) domain organization, showing the undefined Y-domain.
Saturation mutations covering the entire Y-domain (nts 650-1339; 10 constructs of 68 bases each) as well as specific amino acid (C336, C337 and W413) mutations within the predicted membrane-binding motif are shown. MTase: Methyltransferase; Y: Undefined; PCP: Papin-like cysteine protease; P/HVR: Proline-rich/hypervariable region; X: Macro; Hel/NTPase: Helicase/nucleotide triphosphatase; RdRp: RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
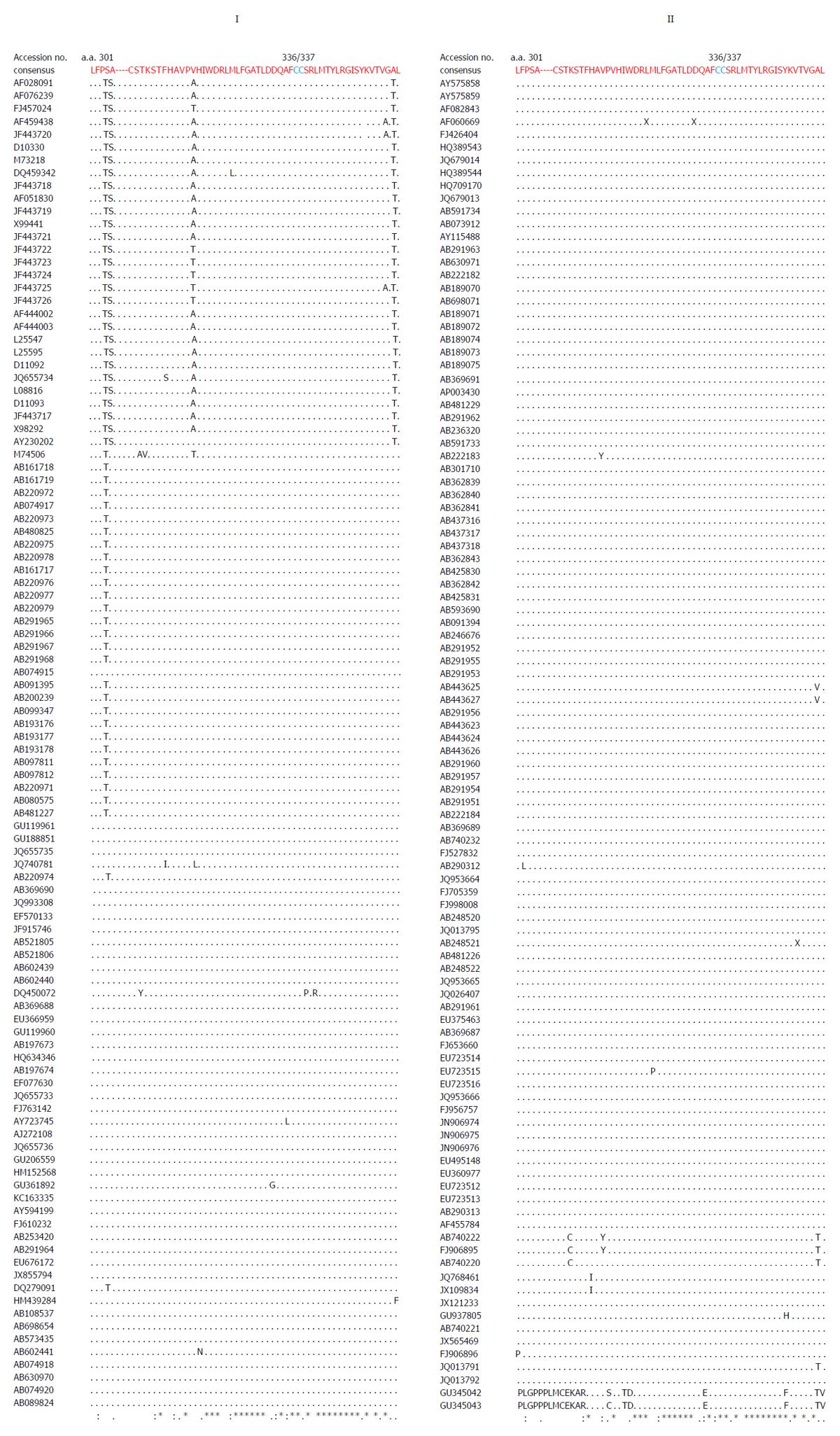
Figure 2 Multiple sequence analysis of ORF1 Y-domain of hepatitis E virus strains (GenBank; n = 206) showing the conservation of predicted palmitoylation-site residues (C336C337).
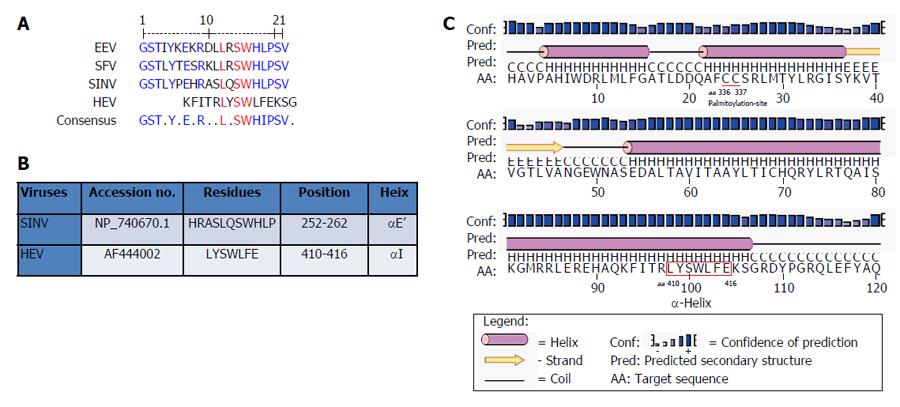
Figure 3 In silico analysis of Y-domain of hepatitis E virus and closely-related viruses.
A: Residue and positional conservation of L310, S312 and W313 (highlighted in red) in the predicted membrane-binding α-helix among HEV, EEV, SFV and SINV; B: Predicted HEV α-helix LYSWLFE counterpart of SINV; C: Secondary structure prediction of α-helix in the HEV Y-domain.
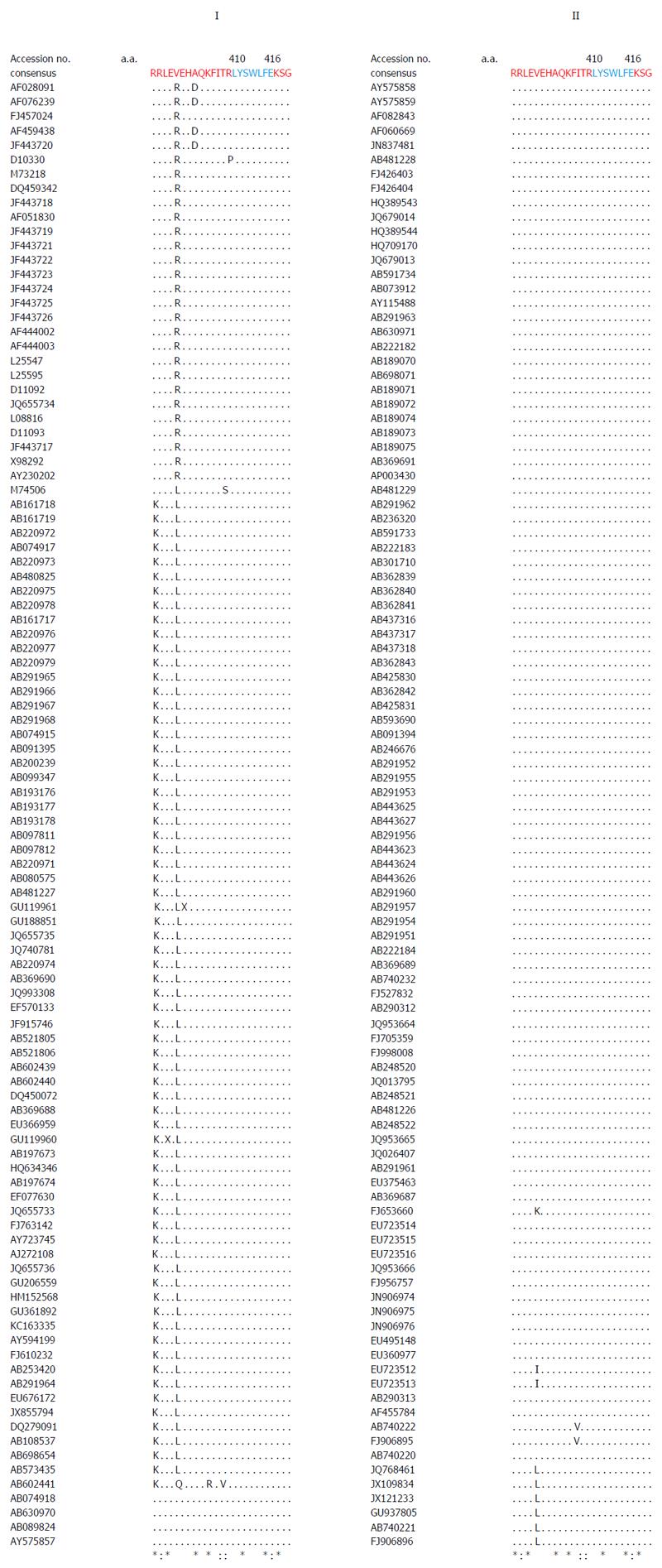
Figure 4 Multiple sequence analysis of human hepatitis E virus strains (GenBank; n = 206), showing the highly conserved segment (L310Y311S312W313L314F315E316) of predicted membrane-binding helix (α1) within the ORF1 Y-domain.
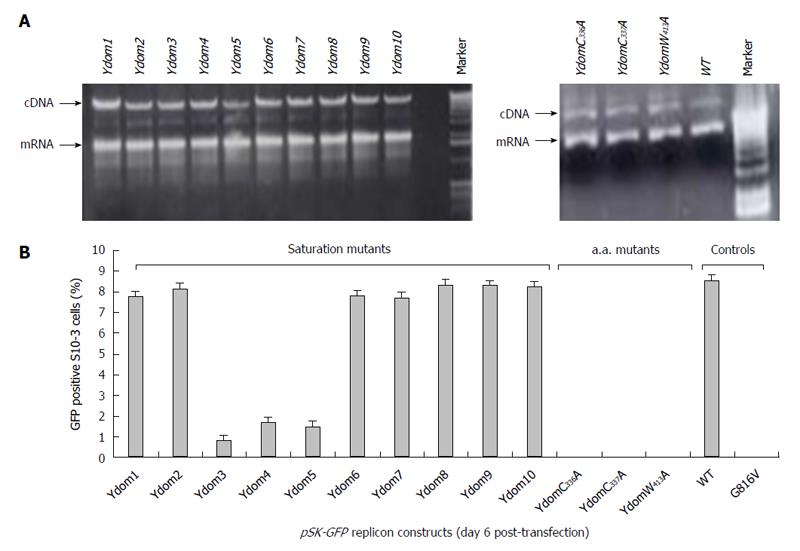
Figure 5 Molecular characterization of hepatitis E virus Y-domain sequences.
A: Agarose-gel electropherograms showing the gross RNA yield of pSK-GFP saturation mutants: Ydom1 to Ydom10 (left panel) and specific amino acid mutants: YdomC336A, YdomC337A and YdomW413A (right panel), compared to wild-type (WT); B: Flow cytometry analysis of GFP-positive S10-3 cells, showing the replication competence of the Y-domain mutant replicons.
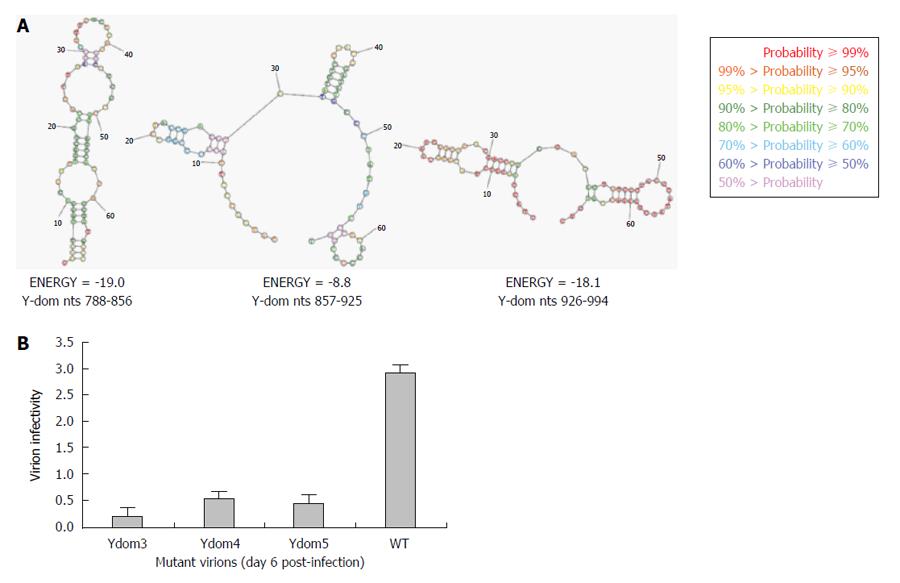
Figure 6 Analysis of Y-domain mutant virions’ infectivity.
A: In silico prediction of stable RNA hairpin/stem-loop structures (wild-type) of three consecutive regions (Ydom3: nts 788-856, Ydom4: nts 857-925 and Ydom5: nts 926-994); B: Flow cytometry analysis of naïve HepG2/C3A cell infectivity by trans-encapsidated virions harboring the three saturation mutant RNAs (Ydom3, Ydom4 and Ydom5).
- Citation: Parvez MK. Mutational analysis of hepatitis E virus ORF1 "Y-domain": Effects on RNA replication and virion infectivity. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(4): 590-602
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i4/590.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i4.590