©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2017; 23(39): 7139-7149
Published online Oct 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i39.7139
Published online Oct 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i39.7139
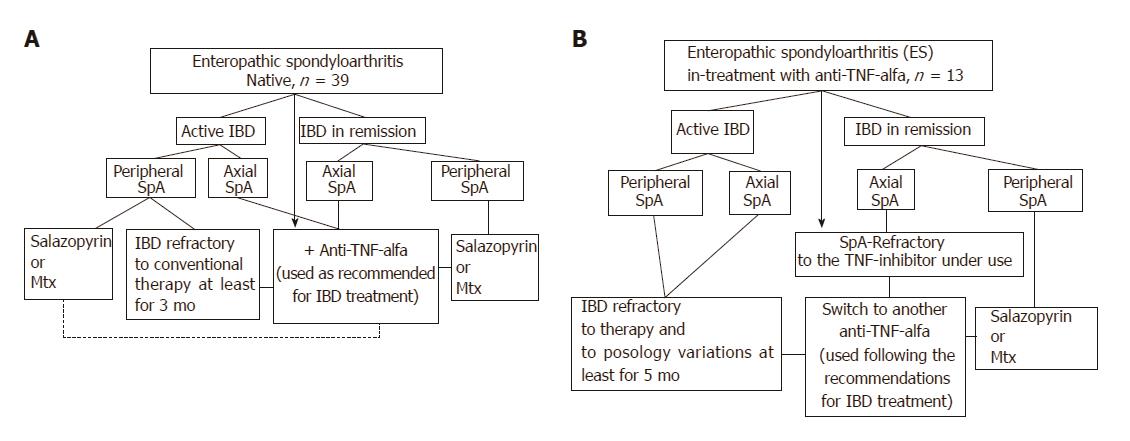
Figure 1 Therapeutic algorithm of the ES-AN patient cohort at the time of entry into the study.
A: ES patients biological drugs-naïve were treated depending on IBD activity and site of the articular involvement, as follows: a) Ax-ES-AN with Ada as the TNF-inhibitor in first-line therapy, due to the absolute contraindication for a long-course treatment with NSAIDs in cases of IBDs; b) Per-ES-AN in cases of active IBD and in those patients who were non-responders to short-course corticosteroid treatment (not > 3 mo) or NSAIDs (not > 2 wk), with DMARD (methotrexate or sulfasalazine), or in cases of ESR > 30 mm/h and/or CRP > 0.5 mg/dL, and polyarticular inflammatory involvement with Ada; c) Per-ES-AN in inactive IBD, with steroids or DMARDs, depending on the number of inflamed joints and systemic inflammation (evaluated by ESR and/or CRP); B: ES patients already in treatment with infliximab for the IBD. In the ES-AN patients already treated with IFX: a) Per-ES-AN with active IBD were switched to Ada; b) Per-ES-AN with IBD in remission received a DMARD in addition to the IFX already in use; c) Ax-ES-AS were switched to Ada, regardless of IBD activity. Dashed line: Patients refractory to therapy. Therapeutic doses: DMARDs were prescribed at the standard dose regimens (salazopyrine 2 gr bid; methotrexate 10-20 mg once a week); Ada was used following the therapeutic dosage and indications for IBDs (160 mg at d 1 and 80 mg after 2 wk, followed by 40 mg every 2 wk). Ada: Adalimumab; AX-ES-AN: Patients with axial spondyloarthritis in the ES-AN cohort; CRP: C-reactive protein; ES: Enteropathic spondyloarthritis; ES-AN: Patients affected by ES in the Ancona’s cohort; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate: DMARD: Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; NSAID: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; Per-ES-AN: Patients with peripheral spondyloarthritis in the ES-AN cohort.
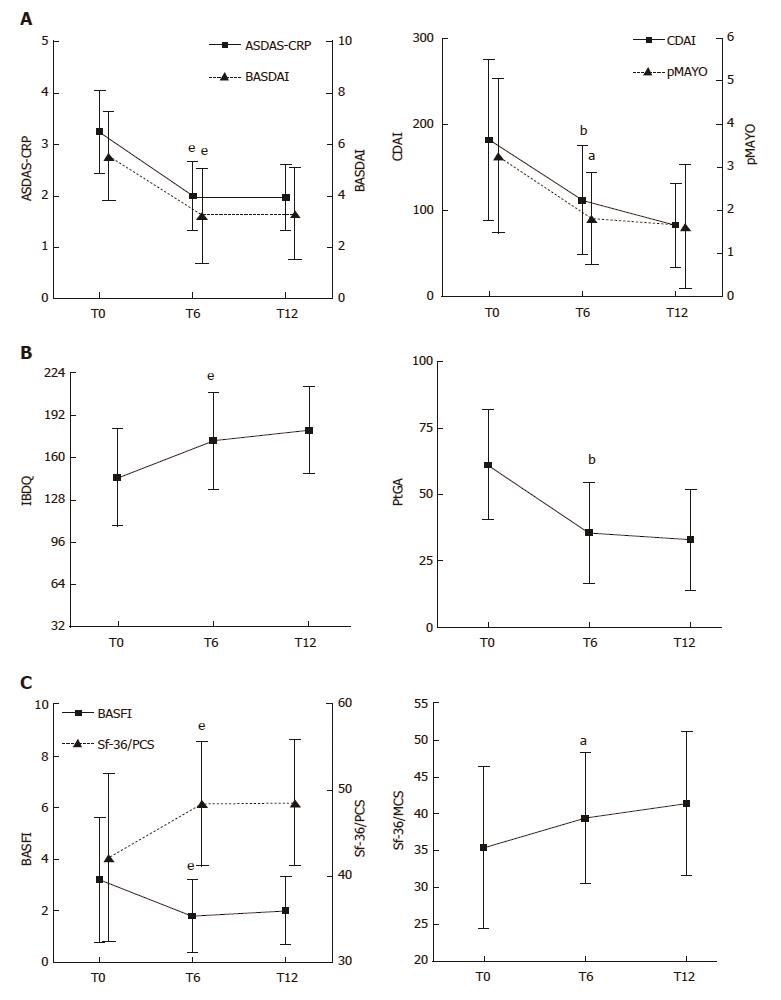
Figure 2 Evaluation of articular-gastrointestinal disease activity and HRQoL in the ES-AN patient cohort at baseline and after adalimumab therapy.
All data of the ES-AN patients were collected at baseline (T0), and after 6 mo (T6) and 12 mo (T12) of therapy. A: Evaluation of the articular disease activity with BASDAI or ASDAS-CRP (Left), and of the gastrointestinal disease activity by CDAI for CD and pMAYO for UC (Right); B: Evaluation of PROs of gastrointestinal disease activity by IBDQ (Left), and of global wellness by the PtGA (Right). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001. ASDAS-CRP: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score/C-Reactive Protein; BASDAI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; CDAI: Crohn’s Disease Activity Index; ES: Enteropathic spondyloarthritis; ES-AN: Patients affected by ES in the Ancona’s cohort; HRQoL: Health-Related Quality of Life; IBDQ: Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire; pMAYO: Partial Mayo score; PROs: Patient reported outcomes.
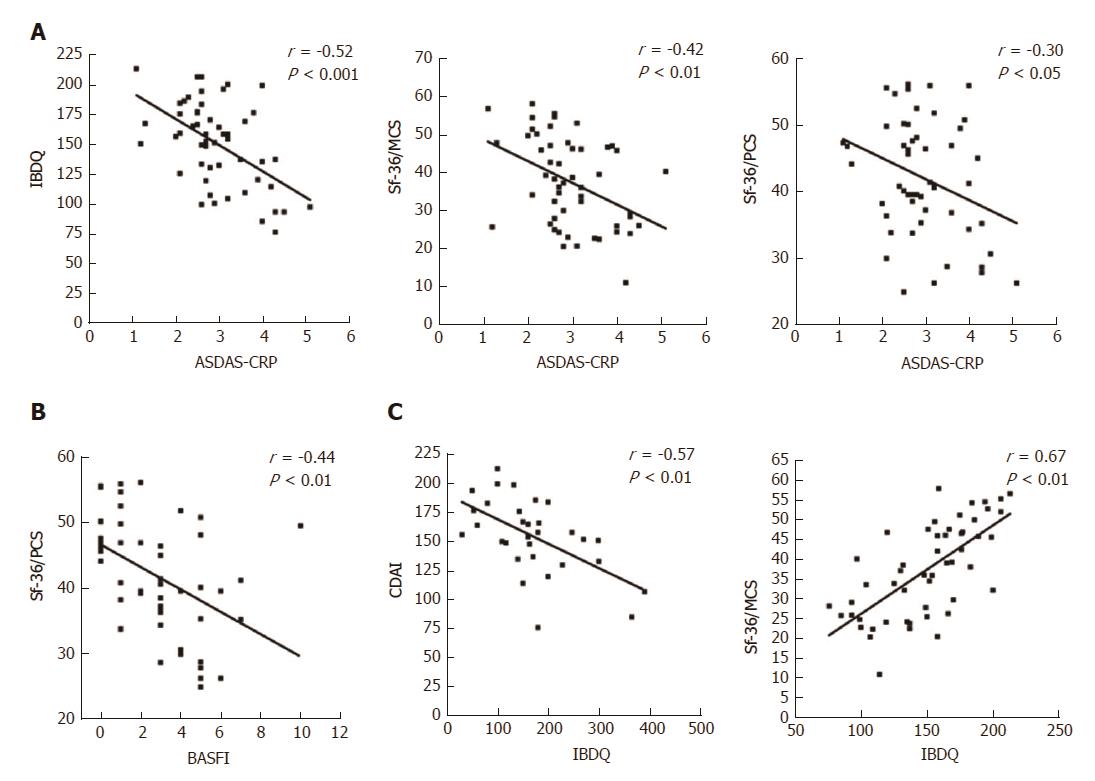
Figure 3 Correlations between articular and gastrointestinal disease activity and HRQoL scores in the ES-AN patient cohort at baseline.
A: Correlation between the PROs of gastrointestinal disease activity (assessed by IBQD) scores and SF-36 summary scores (assessed by PCS and MCS) with articular activity scores (assessed by ASDAS-CRP); B: Correlation of the articular function (assessed by BASFI with SF-36/PCS); C: Correlation of the IBDQ with crohn’s disease gastrointestinal disease activity (assessed by CDAI) and the SF-36/MCS. ASDAS-CRP: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score-C-Reactive Protein; CDAI: Crohn’s Disease Activity Index; ES: Enteropathic spondyloarthritis; ES-AN: Patients affected by ES in the ancona’s cohort; HRQoL: Health-Related Quality of Life; IBDQ: Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire; PROs: Patient reported outcomes; SF-36/MCS: Summary of “Mental Component Score” of the Short Form-36 health survey; SF-36/PCS: Summary of “Physical Component Score” of the Short Form-36 health survey.
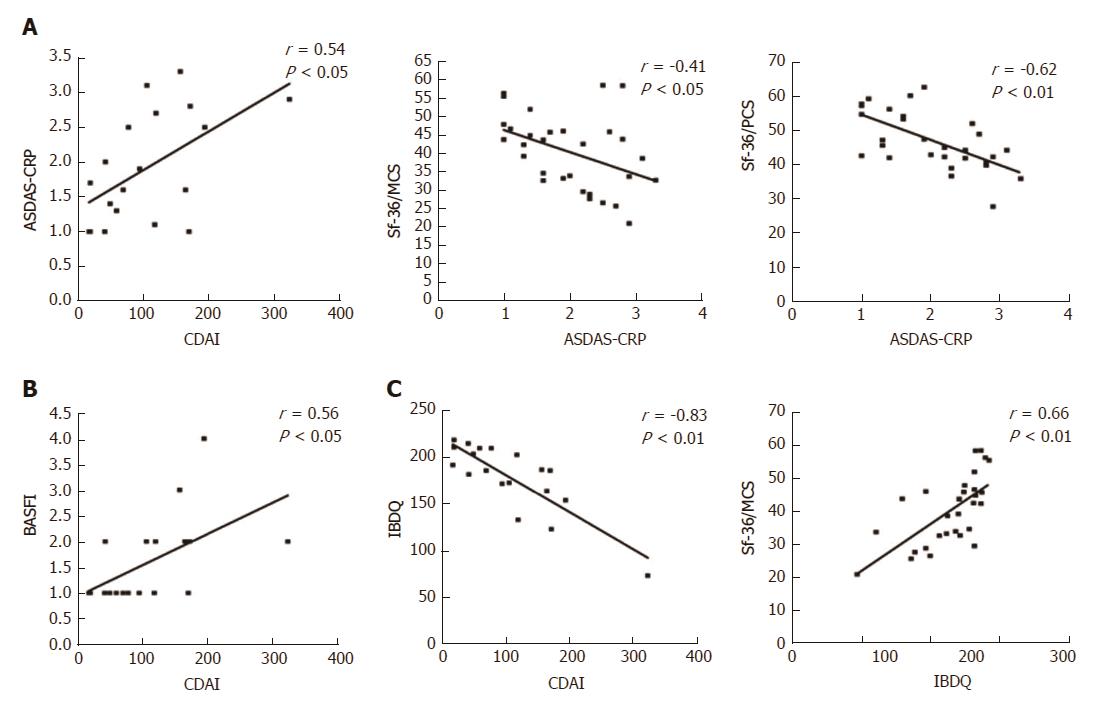
Figure 4 Correlations between articular and gastrointestinal disease activity and HRQoL scores in the ES-AN patient cohort after adalimumab therapy.
A: Evaluation data collected for the 30 ES-AN/Ada patients after 12 mo of therapy, showing correlation between gastrointestinal and articular disease activity in Crohn’s disease patients (assessed by CDAI) and ASDAS-CRP respectively, and between ASDAS-CRP and SF-36 summary scores (PCS and MCS); B: Correlation between CDAI and articular function (assessed by BASFI); C: Correlation between the gastrointestinal quality of life (assessed by IBDQ) and CDAI and SF-36/MCS. ASDAS-CRP: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score-C-Reactive Protein; CDAI: Crohn’s Disease Activity Index; ES-AN: Patients affected by ES in the Ancona’s cohort; ES-AN/Ada: Patients of the ES-AN cohort treated with adalimumab; HRQoL: Health-Related Quality of Life; IBDQ: Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire; SF-36/MCS: Summary of “Mental Component Score” of the Short Form-36 health survey; SF-36/PCS: Summary of “Physical Component Score” of the Short Form-36 health survey; Sf-36/PCS: Summary of “Physical Component Score” of the short form-36 health survey; PROs: Patient reported outcomes.
- Citation: Luchetti MM, Benfaremo D, Ciccia F, Bolognini L, Ciferri M, Farinelli A, Rossini M, Mosca P, Triolo G, Gabrielli A. Adalimumab efficacy in enteropathic spondyloarthritis: A 12-mo observational multidisciplinary study. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(39): 7139-7149
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i39/7139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i39.7139