©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2017; 23(30): 5530-5537
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5530
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5530
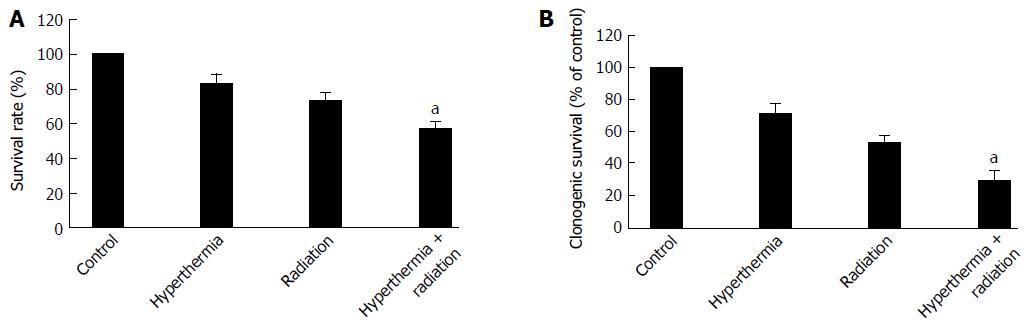
Figure 1 Hyperthermia enhances the cytotoxicity of ionizing radiation to hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
HepG2 cells were treated with hyperthermia (43 °C for 0.5 h) followed by ionizing radiation (4 Gy). After 72 h of incubation, the cells were assessed for cell viability using MTT assay (A), or plated in dishes and incubated for clonogenic survival assay (B). The results are presented as the mean ± SD of three different experiments. aP < 0.05 vs treatment of ionizing radiation alone.
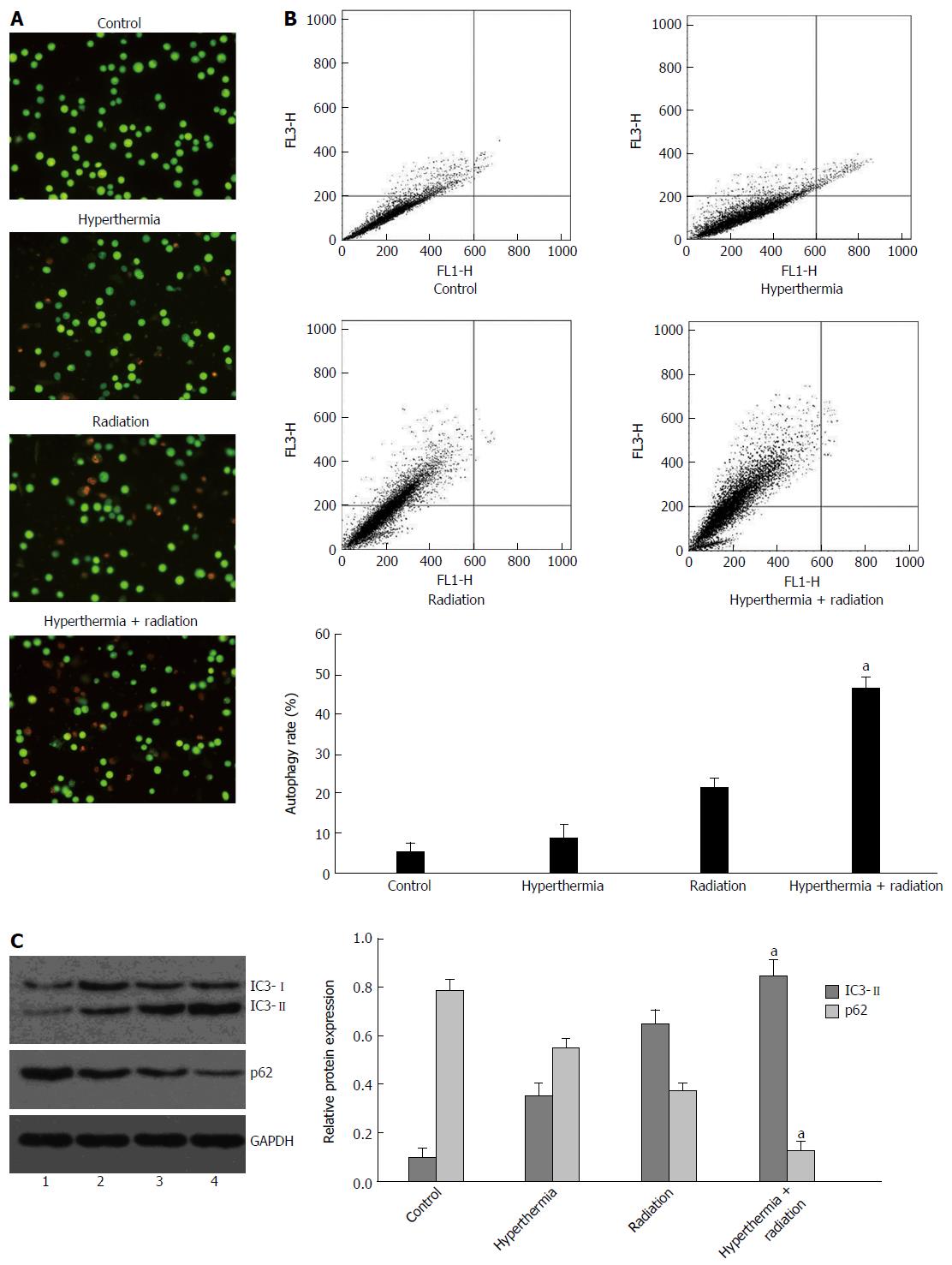
Figure 2 Hyperthermia increases ionizing radiation-induced autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
HepG2 cells were treated with hyperthermia (43 °C for 0.5 h) followed by ionizing radiation (4 Gy). After 72 h of incubation, the cells were assessed for autophagy by flow cytometry using acridine orange staining (A and B), or by Western blot analysis of LC3II and p62 expression (C) (Lane 1: Control; 2: Hyperthermia; 3: Radiation; 4: Hyperthermia + radiation). Results are presented as the mean ± SD of three different experiments, or representative of three different experiments. aP < 0.05 vs treatment of ionizing radiation alone.
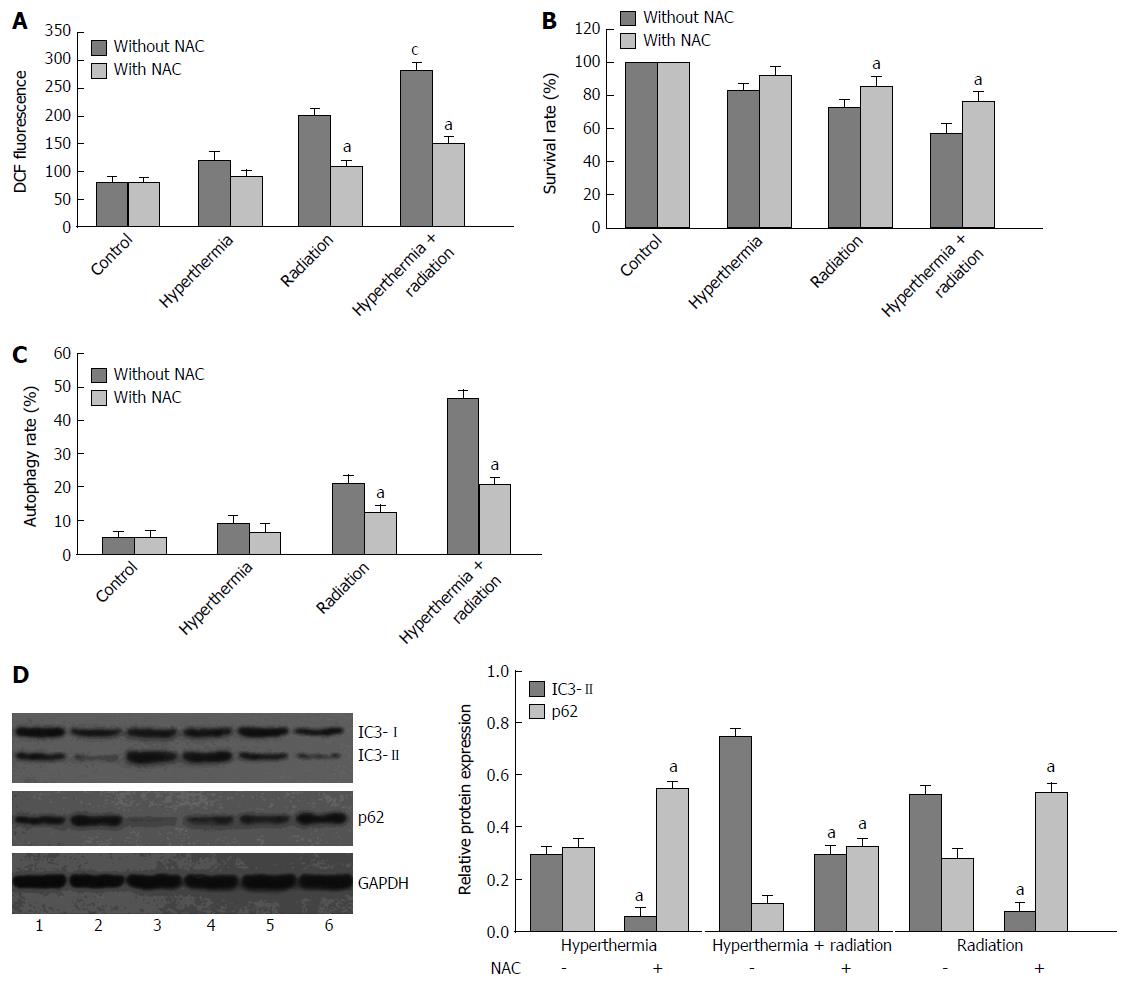
Figure 3 Intracellular reactive oxygen species formation and effect of N-acetylcysteine on the cytotoxicity and cell autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells after treatment with ionizing radiation or hyperthermia.
HepG2 cells were treated with hyperthermia (43 °C for 0.5 h) followed by ionizing radiation (4 Gy). After 72 h of incubation, the cells were assessed for intracellular ROS contents using DCFH-DA (A). HepG2 cells were pretreated with N-acetylcysteine (NAC, 10 mmol/L) for 1 h, and then treated with hyperthermia or ionizing radiation as above. After 72 h of incubation, the cells were assessed for cell viability using MTT assay (B), or for autophagy by flow cytometry using acridine orange staining (C) and by Western blot analysis of LC3II and p62 expression (D) (Lane 1: Hyperthermia; 2: Hyperthermia + NAC; 3: Hyperthermia + radiation; 4: Radiation; 5: Hyperthermia + radiation + NAC; 6: Radiation + NAC). Results are presented as the mean ± SD of three different experiments, or representative of three different experiments. cP < 0.05 vs treatment of ionizing radiation or hyperthermia alone. aP < 0.05 vs no pretreatment of NAC (e.g., radiation vs NAC + radiation).
- Citation: Yuan GJ, Deng JJ, Cao DD, Shi L, Chen X, Lei JJ, Xu XM. Autophagic cell death induced by reactive oxygen species is involved in hyperthermic sensitization to ionizing radiation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(30): 5530-5537
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i30/5530.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5530