©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2017; 23(29): 5422-5430
Published online Aug 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5422
Published online Aug 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5422
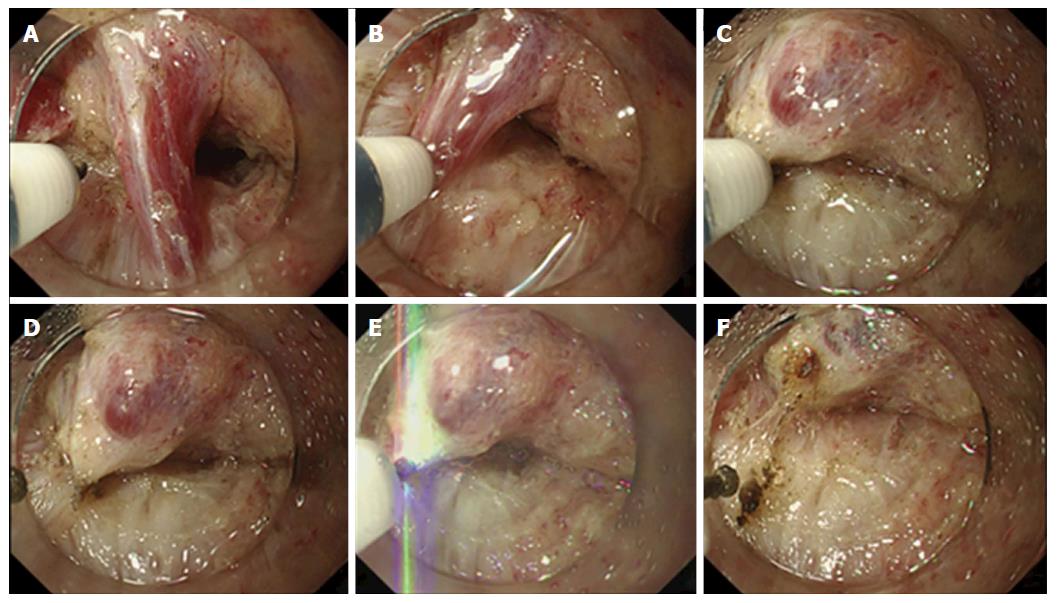
Figure 1 Process of the vessel-sealing with endoknife compression technique.
A: The vessel penetrating between the muscularis propria is exposed; B-D: The vessel is compressed by the FlushKnife-BT 2.5 mm and coagulated using the S method or F method until the color turned white, which indicates a complete desiccation of the vessel. If it does not turn white completely, we tried this method from the other side; E and F: Finally, the vessel is cut with the FlushKnife-BT 2.5 mm using the forced coagulation mode (Effect 3, 50 W).
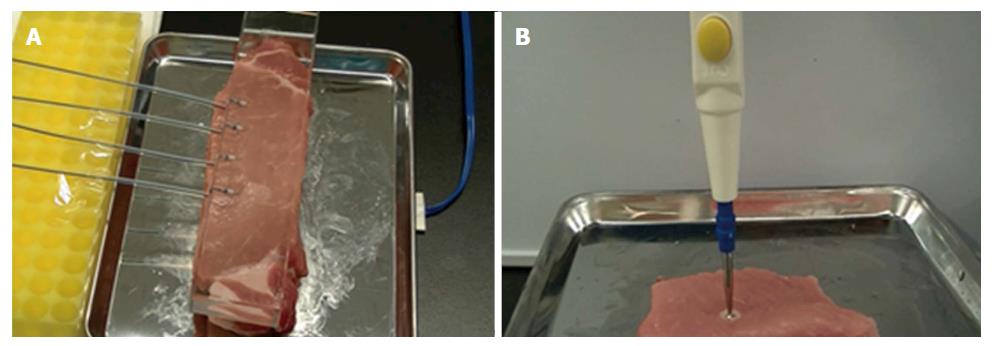
Figure 2 Evaluation of coagulation by an ex vivo model.
A: The FlushKnife-BT 2.5 mm was placed on the fresh pork block and lightly pressed by the transparent glass to apply even pressure to each tip; B: The 3-mm ball tip electrodes were used to investigate the width and depth of the coagulation.
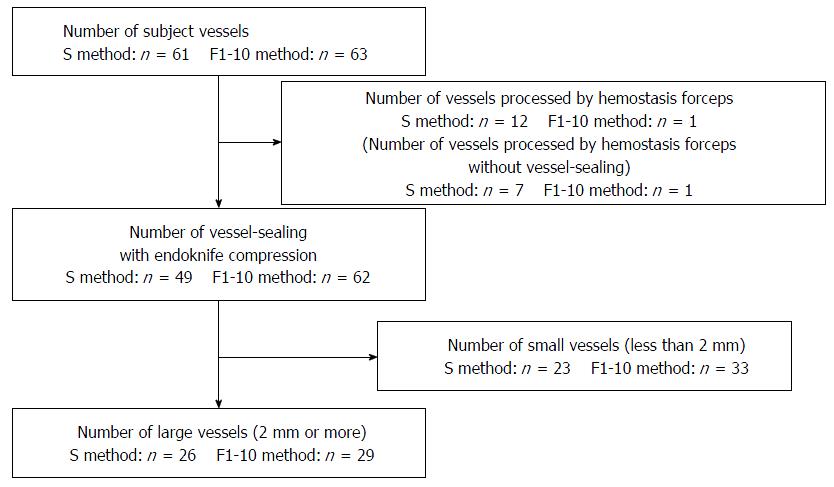
Figure 3 Vessels processed by the vessel-sealing with endoknife compression.
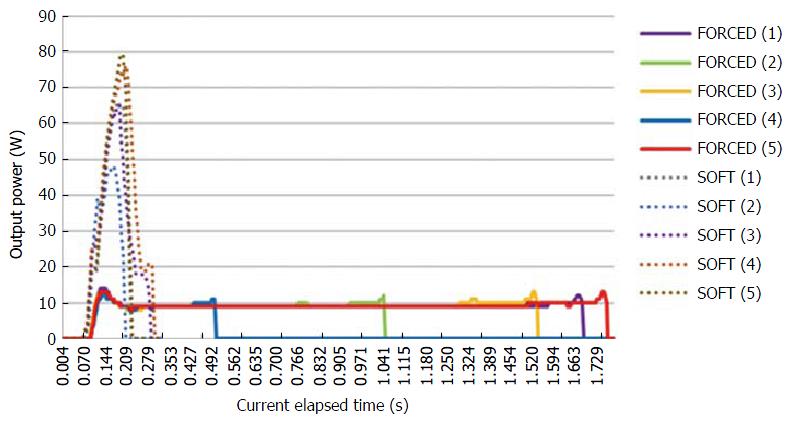
Figure 4 Time-dependent HF power in F1-10 and S methods measured by the VIO DOKU.
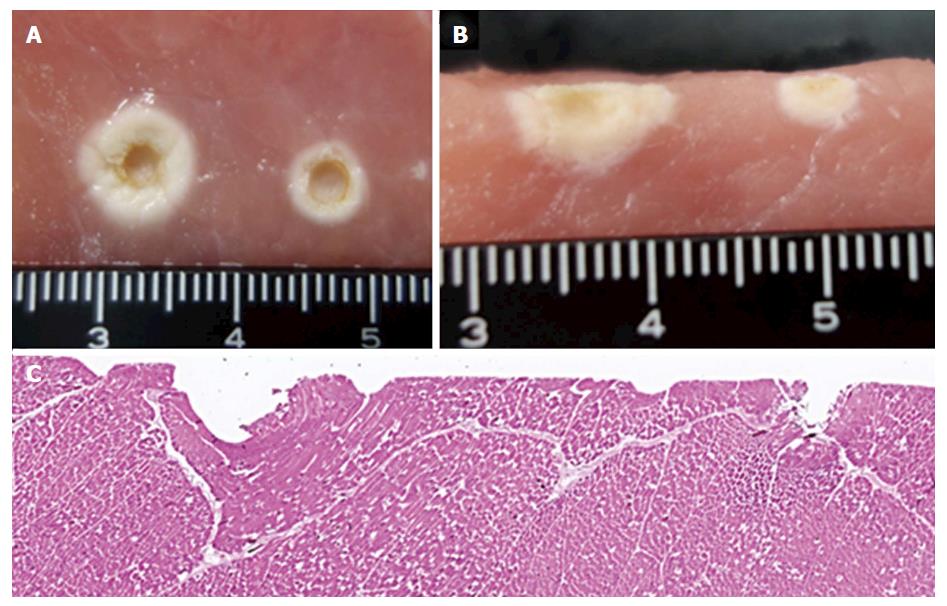
Figure 5 Macroscopic view after coagulation by the ball electrode with a 3-mm tip and microscopic view after coagulation by the FlushKnife-BT in the porcine block.
A: Macroscopic view of the front surface after coagulation using the ball electrode with a 3-mm tip. The coagulation at the left and right is the result of the F1-10 and S methods, respectively; B: Macroscopic view of a transverse section after coagulation using the ball electrode with a 3-mm tip; C: Microscopic view of the hematoxylin-eosin staining after coagulation by the FlushKnife-BT 2.5 mm. The coagulation at the left and right is the result of the F1-10 and S methods, respectively.
- Citation: Ishida T, Toyonaga T, Ohara Y, Nakashige T, Kitamura Y, Ariyoshi R, Takihara H, Baba S, Yoshizaki T, Kawara F, Tanaka S, Morita Y, Umegaki E, Hoshi N, Azuma T. Efficacy of forced coagulation with low high-frequency power setting during endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(29): 5422-5430
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i29/5422.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5422