©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2017; 23(25): 4644-4653
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4644
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4644
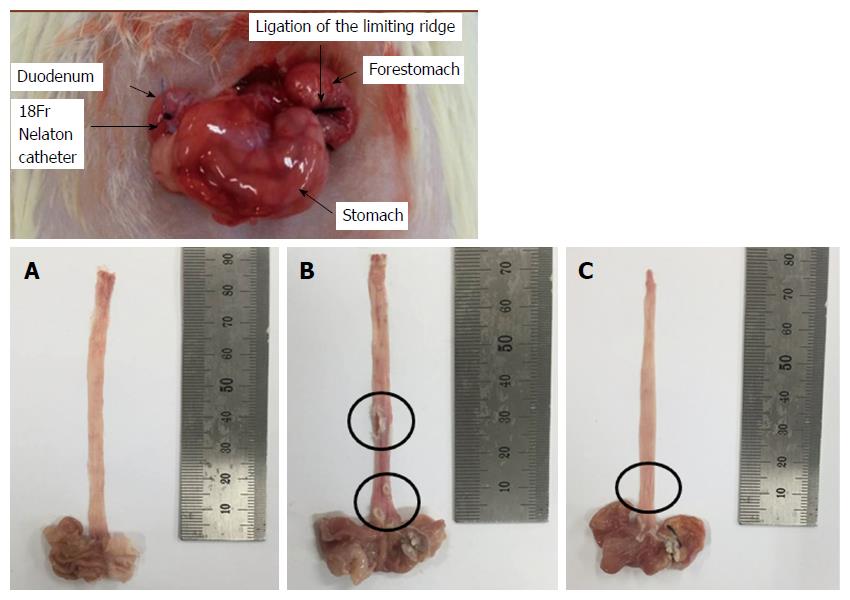
Figure 1 Surgical induction of chronic acid reflux esophagitis and representative image of the degree of esophageal mucosal ulcer in each group of rats.
A: Normal group; B: Untreated chronic acid reflux esophagitis modeled group; C: BHSST-treated group. BHSST: Banhasasim-tang.
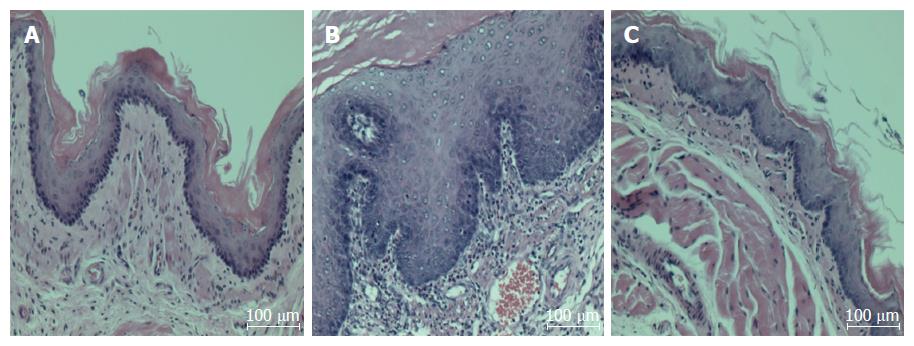
Figure 2 Chronic acid reflux esophagitis and effects of banhasasim-tang treatment.
A: Normal, normal rats; B: Control, untreated CARE modeled-rats; C: BHSST, BHSST-treated (1 g/kg body weight per day) CARE modeled-rats. Histology of the non-CARE esophagus revealed thin epithelium with few inflammatory cells. Whereas, CARE esophagus showed mucosal thickening with basal cell hyperplasia and marked inflammatory cell infiltration. These histological changes were improved by BHSST treatment. H&E staining; original magnification × 200. CARE: Chronic acid reflux esophagitis; BHSST: Banhasasim-tang.
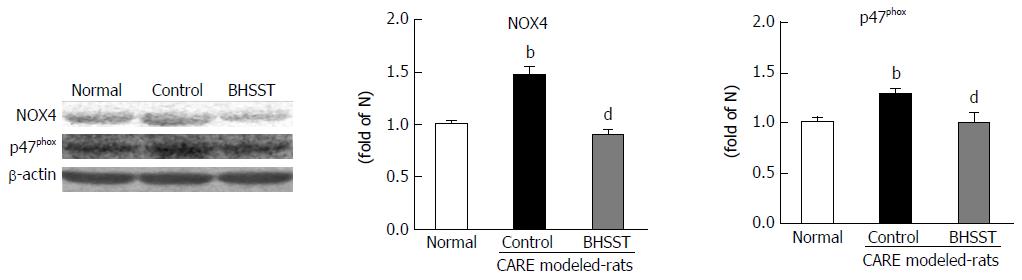
Figure 3 Expression of NOX4 and p47phox in chronic acid reflux esophagitis rats and effects of banhasasim-tang treatment.
Normal, normal rats; Control, untreated CARE modeled-rats; BHSST, BHSST-treated (1 g/kg body weight per day) CARE modeled rats. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 6). bP < 0.01 vs normal rats; dP < 0.01 vs untreated CARE modeled rats. CARE: Chronic acid reflux esophagitis; BHSST: Banhasasim-tang.
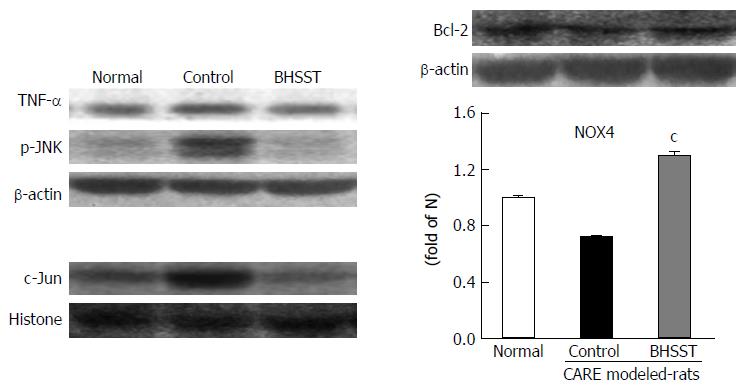
Figure 4 Detection of TNF-α, p-JNK, Bcl-2 and c-Jun in chronic acid reflux esophagitis rats and effects of banhasasim-tang treatment.
Normal, normal rats; Control, untreated CARE modeled-rats; BHSST, BHSST-treated (1 g/kg body weight per day) CARE modeled rats. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 6). cP < 0.05 vs untreated CARE modeled rats. CARE: Chronic acid reflux esophagitis; BHSST: Banhasasim-tang.
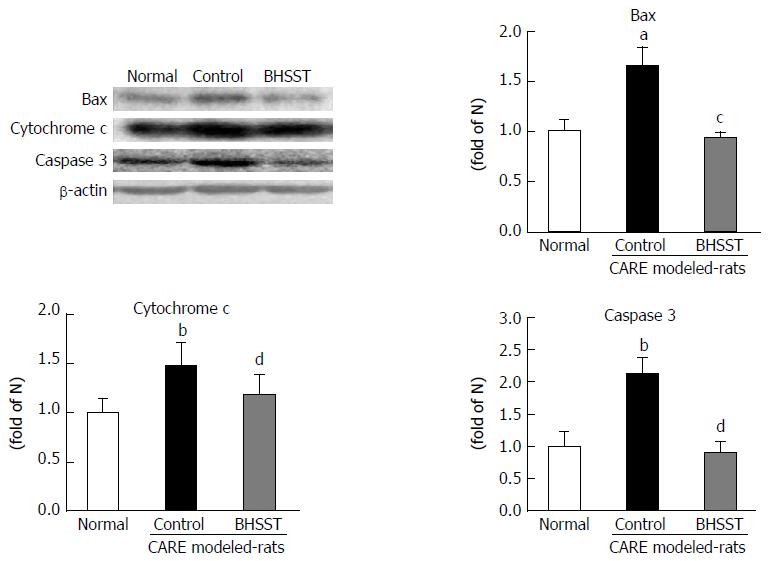
Figure 5 Expression of bax, cytochrome c and caspase 3 in chronic acid reflux esophagitis rats.
Normal, normal rats; Control, untreated CARE modeled rats; BHSST, BHSST, BHSST-treated (1 g/kg body weight per day) CARE modeled rats. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 6). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs normal rats; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs untreated CARE modeled-rats. CARE: Chronic acid reflux esophagitis; BHSST: Banhasasim-tang.
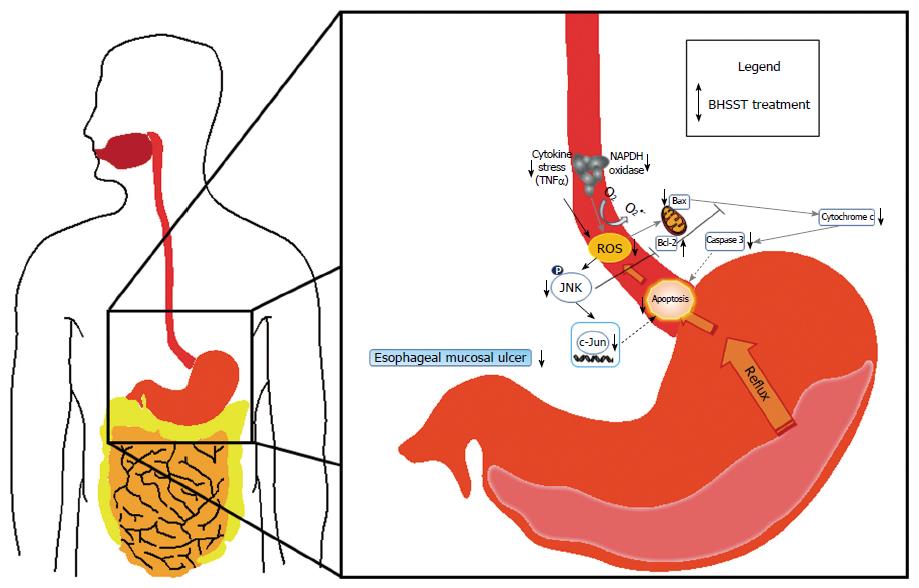
Figure 6 Possible mechanism of the banhasasim-tang protective mechanism in the esophagus of chronic acid reflux-induced esophageal ulcer in rats.
BHSST: Banhasasim-tang; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Shin MR, An HJ, Seo BI, Roh SS. Anti-apoptotic effect of banhasasim-tang on chronic acid reflux esophagitis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(25): 4644-4653
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i25/4644.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4644