©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2017; 23(22): 4039-4046
Published online Jun 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.4039
Published online Jun 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.4039
Figure 1 Systemic IL-9 in healthy individuals and patients with active and inactive inflammatory bowel disease.
Data presented as medians with 95%CI and analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis H test. 1Significantly different from other groups.
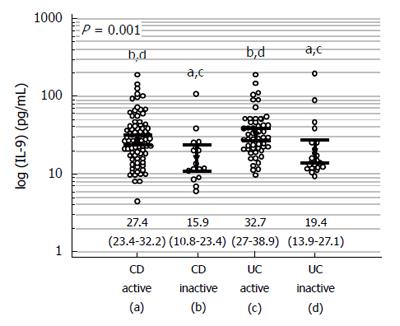
Figure 2 Systemic IL-9 in patients with active and inactive Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Data presented as geometric means with 95%CI and analyzed using one-way ANOVA. Small letters indicate statistical significance of between-group differences.
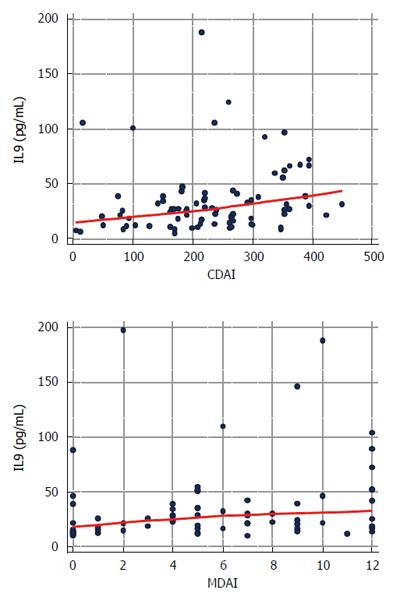
Figure 3 Correlation between the concentrations of circulating IL9 and the clinical activity of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Data analyzed using Spearman correlation test. CDAI: Crohn’s Disease Activity Index; MDAI: Mayo Disease Activity Index.
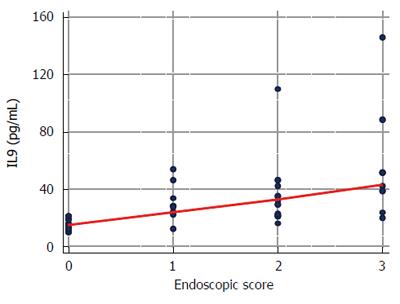
Figure 4 Correlation between the concentrations of circulating IL9 in patients with ulcerative colitis and endoscopic score.
Data analyzed using Spearman correlation test.
Figure 5 Comparison of IL9, hsCRP and IL6 as potential markers of mucosal non-healing.
Data presented as area under ROC curve (AUC) with 95%CI and P value. For an optimal cut-off value, markers sensitivity (sens.) and specificity (spec.) as well as Youden's J statistic (YI, where J = Sensitivity + Specificity - 1) were calculated.
- Citation: Matusiewicz M, Neubauer K, Bednarz-Misa I, Gorska S, Krzystek-Korpacka M. Systemic interleukin-9 in inflammatory bowel disease: Association with mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(22): 4039-4046
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i22/4039.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.4039