©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2017; 23(22): 3964-3977
Published online Jun 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3964
Published online Jun 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3964
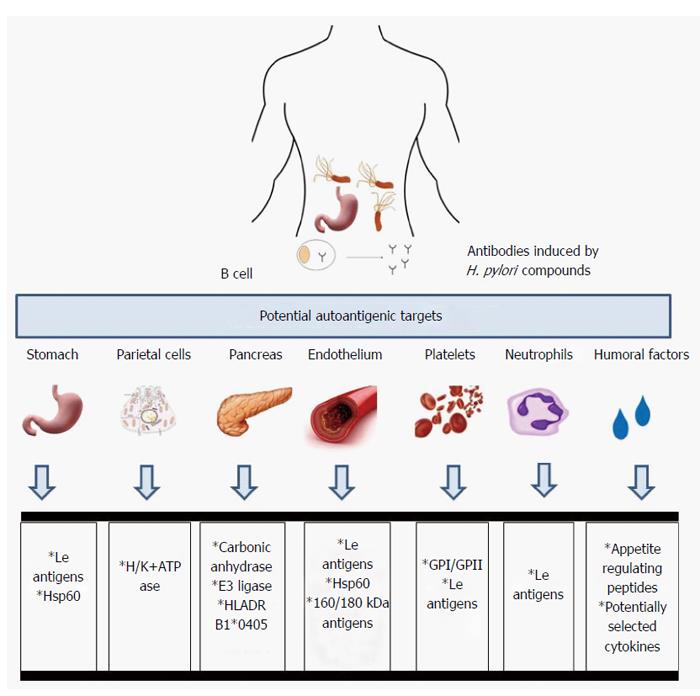
Figure 1 Hypothesis of autoimmune disorders due to molecular mimicry between Helicobacter pylori and the host components.
Chronic exposure of the host immune system to Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) components that have homologous sequences with the host cellular or soluble compounds may initiate the production of autoantibodies. However, how often the autoantibodies arising during H. pylori infection are involved in various post-infectious pathologies should be elucidated. The graph shows the examples of host targets for the antibodies induced by H. pylori components. GP: Glycoproteins; Hsp: Heat shock protein; H+/K+ ATPase: H+/K+-adenosine triphosphatase; HLA: Human leukocyte antigens; CCRL1: CC chemokine receptor-like 1; Le: Lewis antigens.
- Citation: Chmiela M, Gonciarz W. Molecular mimicry in Helicobacter pylori infections. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(22): 3964-3977
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i22/3964.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3964