©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2017; 23(2): 306-317
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.306
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.306
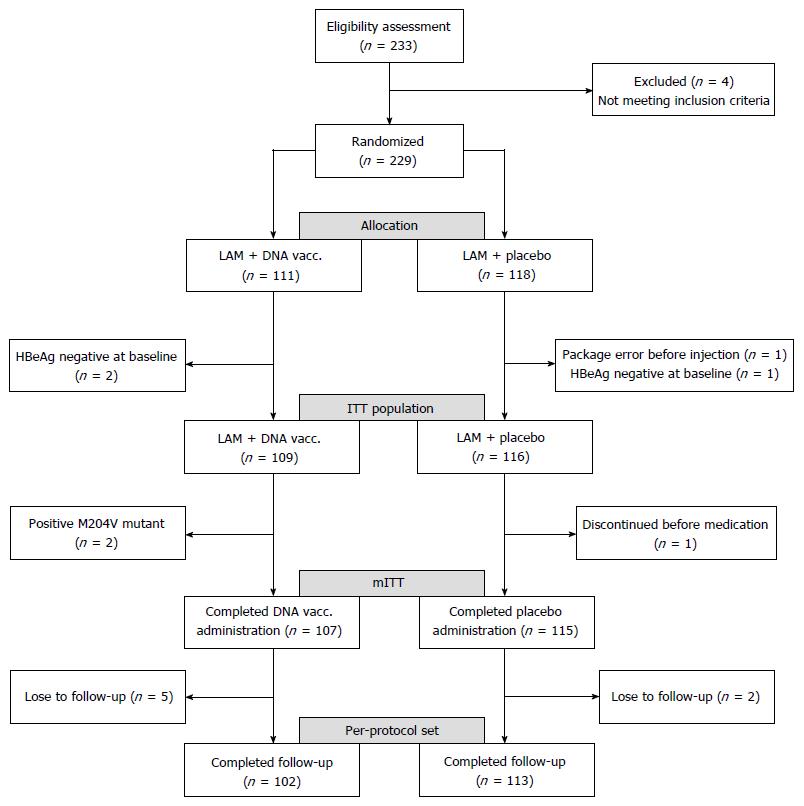
Figure 1 Patient disposition and different analysis populations.
M204V mutant: The lamivudine-resistant amino acid mutation of HBV; mITT: Modified intent-to-treat.
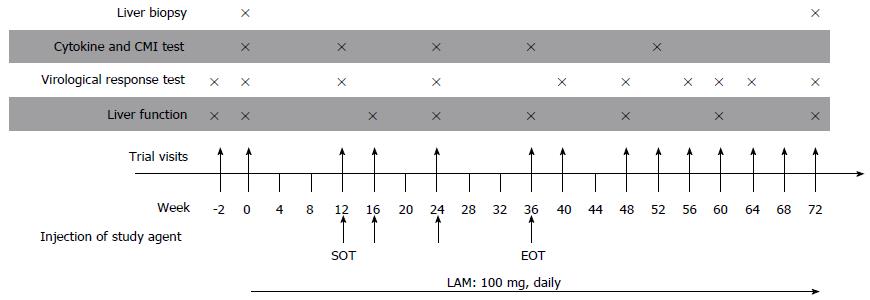
Figure 2 Study design.
Four intramuscular injections of either DNA vaccine (DNA Vacc.) or placebo mediated by in vivo electroporation were given to each patient. LAM: Lamivudine. SOT: Start of treatment (black arrow); EOT: End of treatment.
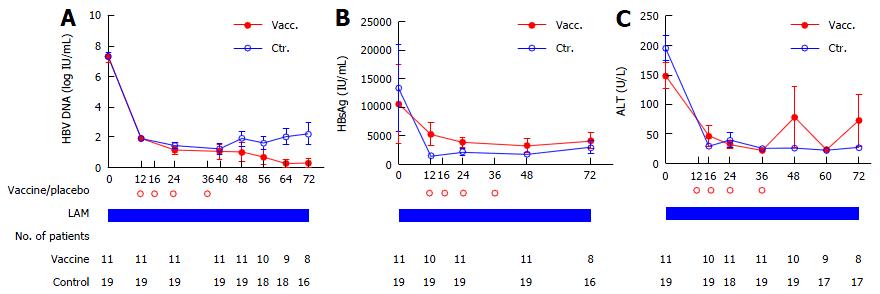
Figure 3 Serological kinetics of hepatitis B virus DNA (A), HBsAg (B) and alanine aminotransferase (C) in 30 patients with hepatitis B virus DNA < 1000 copies/mL at week 12 (1.
79 × 102 IU/mL). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Vacc.: Lamivudine (LAM) + DNA vaccine arm; Ctr.: LAM + placebo arm; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- Citation: Yang FQ, Rao GR, Wang GQ, Li YQ, Xie Y, Zhang ZQ, Deng CL, Mao Q, Li J, Zhao W, Wang MR, Han T, Chen SJ, Pan C, Tan DM, Shang J, Zhang MX, Zhang YX, Yang JM, Chen GM. Phase IIb trial of in vivo electroporation mediated dual-plasmid hepatitis B virus DNA vaccine in chronic hepatitis B patients under lamivudine therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(2): 306-317
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i2/306.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.306