©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2017; 23(17): 3043-3052
Published online May 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3043
Published online May 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3043
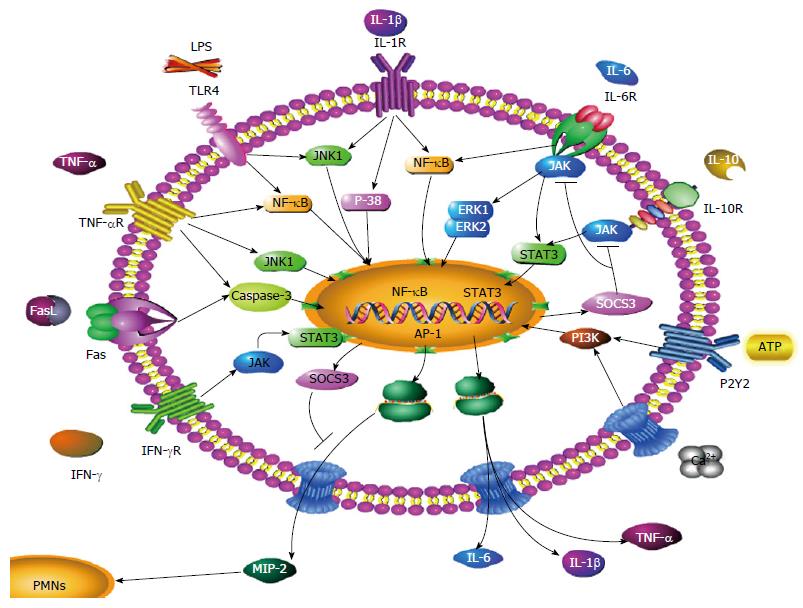
Figure 1 Molecular mechanisms involved in macrophage inflammatory protein-2 secretion of macrophages.
The Figure illustrates several reciprocal molecular pathways for the secretion of MIP-2. These include: LPS-mediated induction of MIP-2, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α through the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway; IL-6-mediated induction of MIP-2 through the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway; TNF-α-mediated induction of MIP-2 through the NF-κB/MAPK, caspase-3 signaling pathway; FasL-mediated induction of MIP-2 through the caspase-3 signaling pathway; Ca2+- and ATP-mediated induction of MIP-2 through the PI3K signaling pathway; IL-1β-mediated induction of MIP-2 through the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway; IFN-γ and IL-10-mediated inhibition of MIP-2, IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α through the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway; SOCS3-mediated inhibition of JAK/STAT3. MIP-2: Macrophage inflammatory protein-2; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; IL: Interleukin; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
- Citation: Qin CC, Liu YN, Hu Y, Yang Y, Chen Z. Macrophage inflammatory protein-2 as mediator of inflammation in acute liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(17): 3043-3052
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i17/3043.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3043