©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2016; 22(47): 10398-10405
Published online Dec 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i47.10398
Published online Dec 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i47.10398
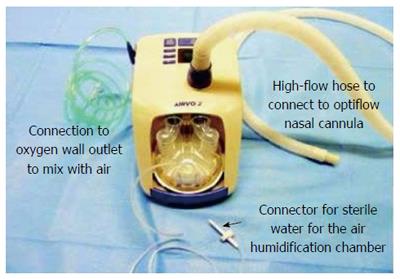
Figure 1 AIRVO™ 2 (Fisher and Paykel Healthcare Limited, Panmure, New Zealand).
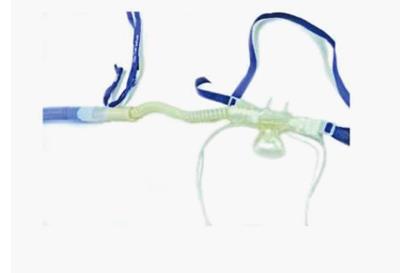
Figure 2 Modified nasal prongs.
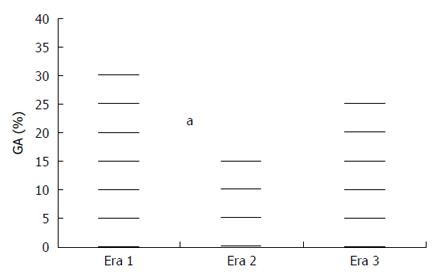
Figure 3 Use of general anesthesia during eras 1, 2 and 3.
During era 2 (HFNO available) significantly less cases were performed under GA compared to era 1, although this difference did not reach statistical significance between eras 2 and 3. HFNO: High-flow nasal oxygen; GA: General anesthesia. aP = 0.012 era 1 vs era 2.
- Citation: Schumann R, Natov NS, Rocuts-Martinez KA, Finkelman MD, Phan TV, Hegde SR, Knapp RM. High-flow nasal oxygen availability for sedation decreases the use of general anesthesia during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasound. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(47): 10398-10405
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i47/10398.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i47.10398