Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2016; 22(40): 8918-8928
Published online Oct 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i40.8918
Published online Oct 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i40.8918
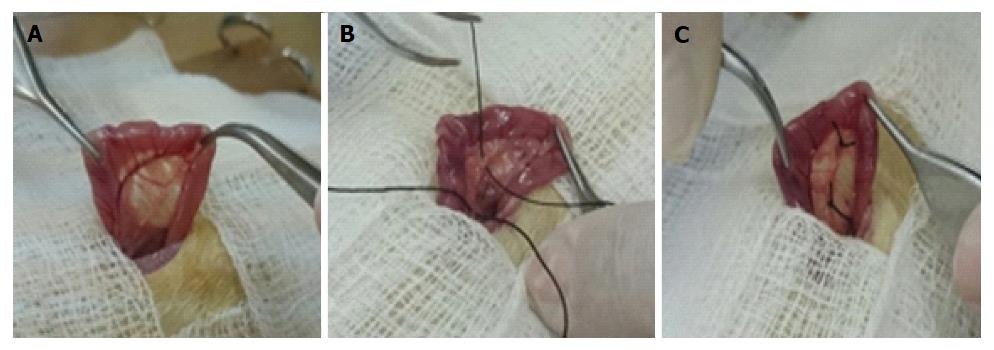
Figure 1 Bile duct ligation surgery.
A: Localization of the bile duct; B: Passage of silk thread for duct isolation; C: Resection of the bile duct.
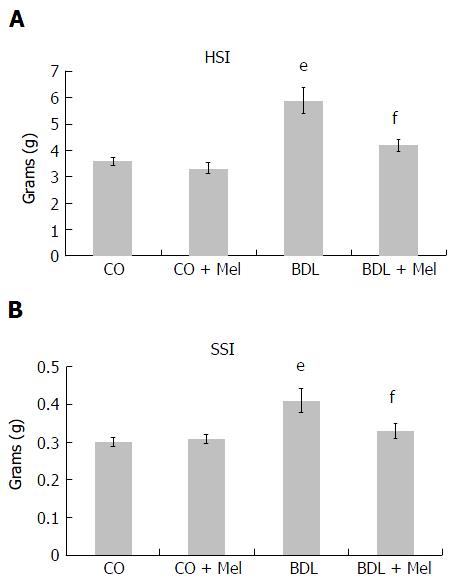
Figure 2 Mean hepatosomatic and splenosomatic index values in the different experimental groups.
All results are expressed as mean ± SD error. Significant difference existed between the BDL and control groups (CO and CO + Mel) (eP < 0.001). Significant difference existed between the BDL and BDL + Mel groups (fP < 0.001). CO: Control; CO + Mel: Control + melatonin; BDL: Bile duct ligation; BDL + Mel: Bile duct ligation + melatonin; HSI: Hepatosomatic index; SSI: Splenosomatic index.
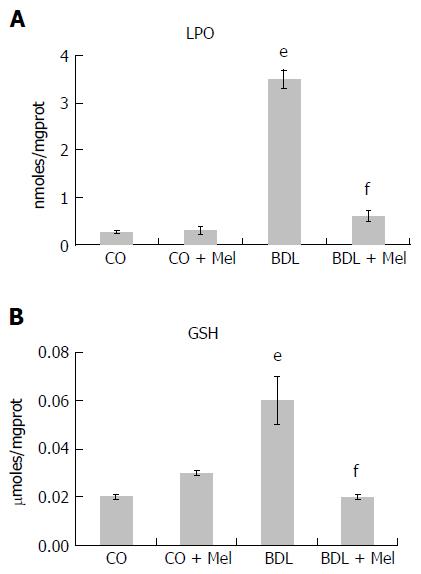
Figure 3 Lipoperoxidation markers and glutathione levels in the different experimental groups.
All results are expressed as mean ± SD error. Significant difference exists between the BDL and control groups (CO and CO + Mel) (eP < 0.001). Significant difference exists between the BDL and BDL + Mel groups (fP < 0.001). CO: Control; CO + Mel: Control + melatonin; BDL: Bile duct ligation; BDL + Mel: Bile duct ligation + melatonin; GSH: Glutathione; LPO: Lipid peroxidation.
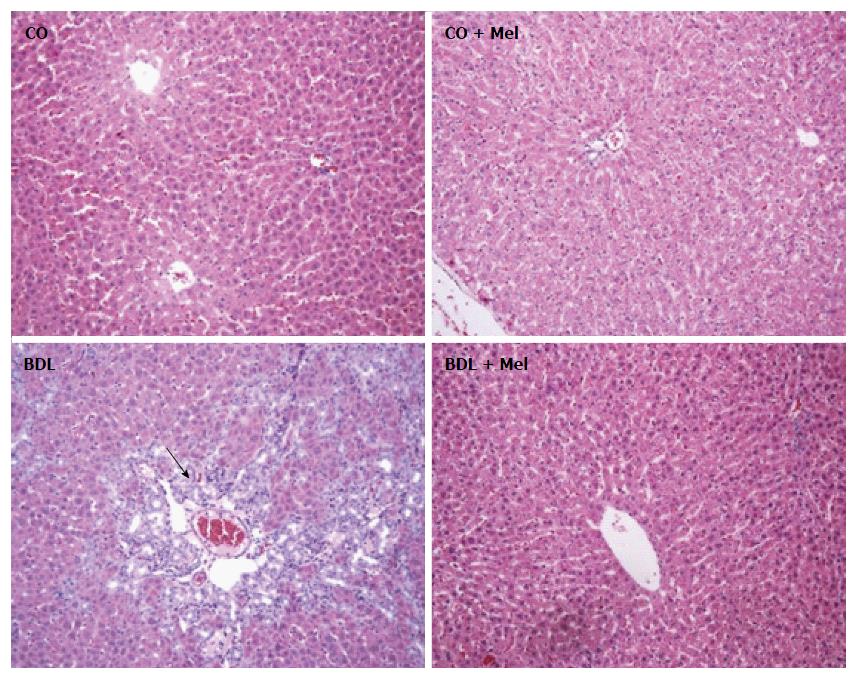
Figure 4 Histological analysis of liver tissue in the different experimental groups.
HE staining, 200 × magnification. The arrow indicates the presence of inflammatory infiltrate. CO: Control; CO + Mel: Control + melatonin; BDL: Bile duct ligation; BDL + Mel: Bile duct ligation + melatonin.
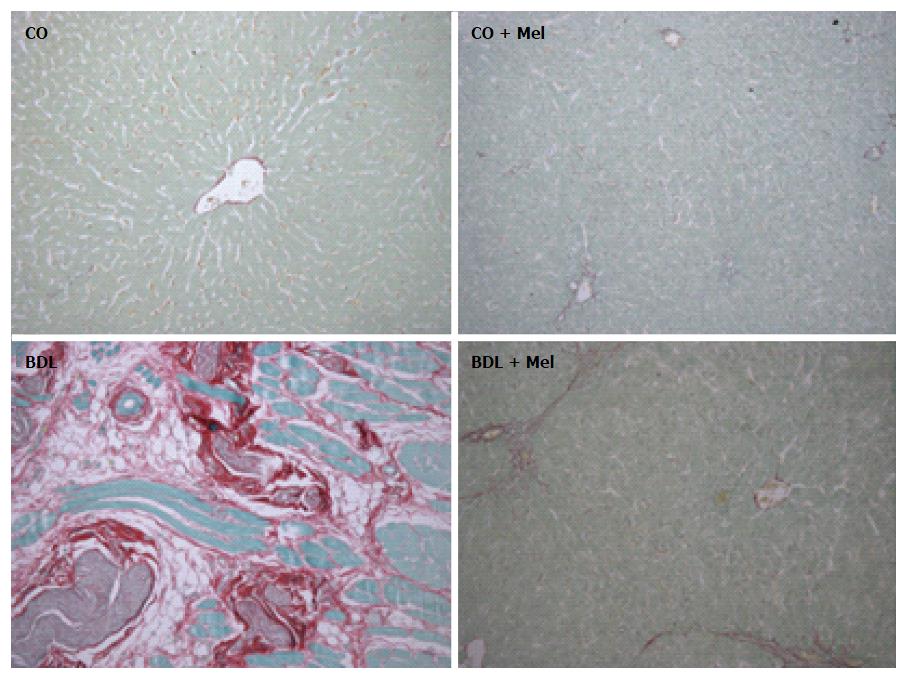
Figure 5 Histological analysis of liver tissue in the different experimental groups.
Picrosirius staining, 200 × magnification. CO: Control; CO + Mel: Control + melatonin; BDL: Bile duct ligation; BDL + Mel: Bile duct ligation + melatonin.
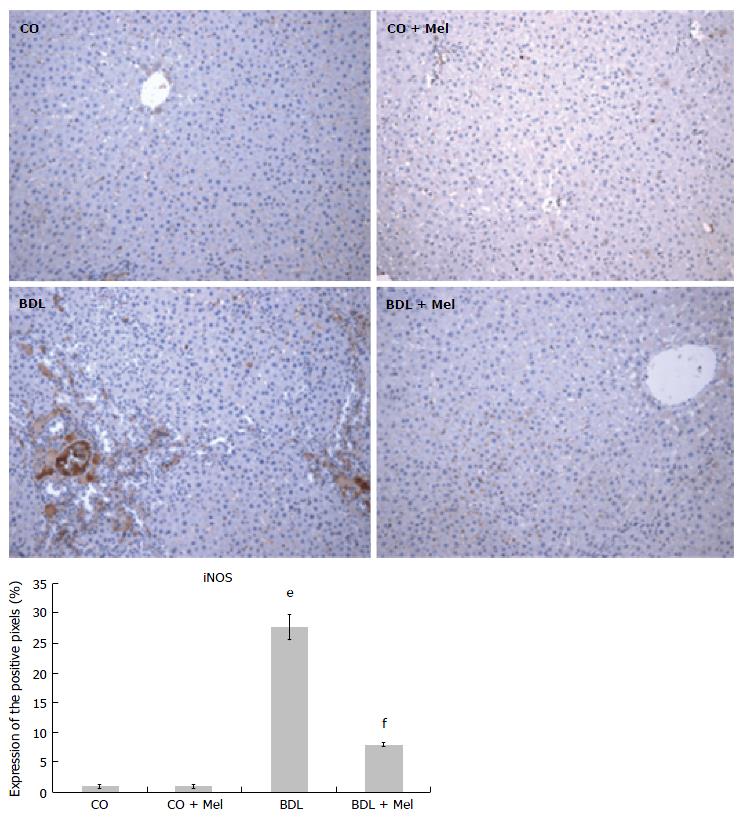
Figure 6 Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the different experimental groups.
Magnification 200 ×. All values are expressed as mean ± SD error. Significant difference exists between the BDL and control groups (CO and CO + Mel) (eP < 0.001). Significant difference exists between the BDL and BDL + Mel groups (fP < 0.001). CO: Control; CO + Mel: Control + melatonin; BDL: Bile duct ligation; BDL + Mel: Bile duct ligation + melatonin; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase.
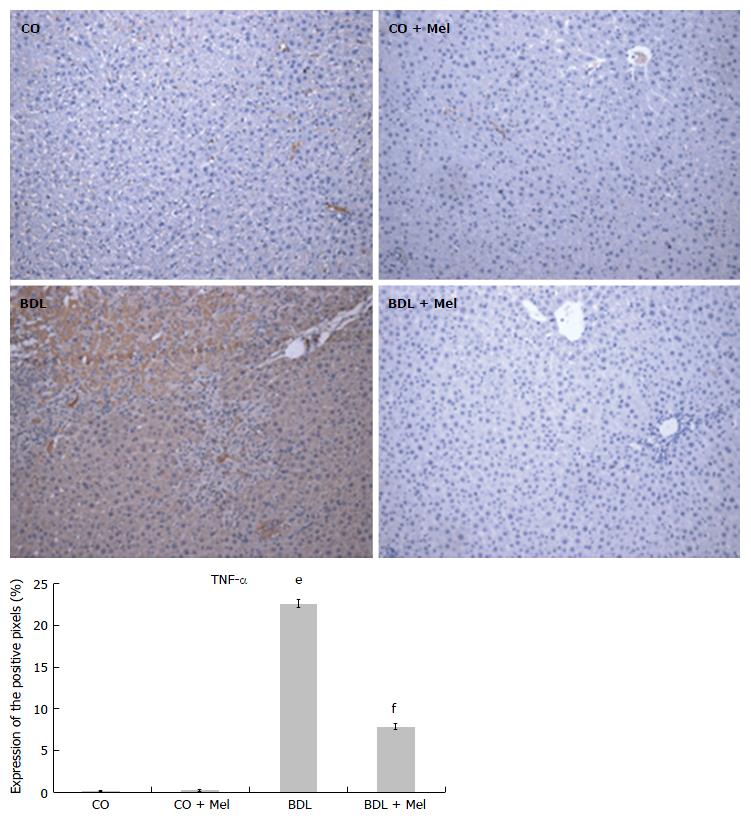
Figure 7 Expression of tumor necrosis factor in the different experimental groups.
Magnification 200 ×. All values are expressed as mean ± SD error. Significant difference exists between the BDL and control groups (CO and CO + Mel) (eP < 0.001). Significant difference exists between the BDL and BDL + Mel groups (fP < 0.001). CO: Control; CO + Mel: Control + melatonin; BDL: Bile duct ligation; BDL + Mel: Bile duct ligation + melatonin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
- Citation: Colares JR, Schemitt EG, Hartmann RM, Licks F, Soares MDC, Bosco AD, Marroni NP. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory action of melatonin in an experimental model of secondary biliary cirrhosis induced by bile duct ligation. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(40): 8918-8928
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i40/8918.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i40.8918