©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2016; 22(32): 7373-7382
Published online Aug 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i32.7373
Published online Aug 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i32.7373
Figure 1 Grade of mediastinal emphysema on computed tomography[9].
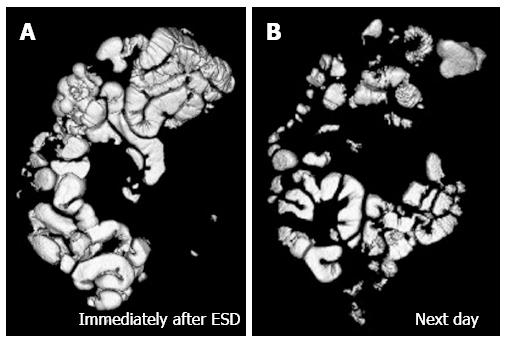
Figure 2 Volume-rendering image of bowel gas immediately after endoscopic submucosal dissection with CO2 insufflation (A) and that of the next day (B).
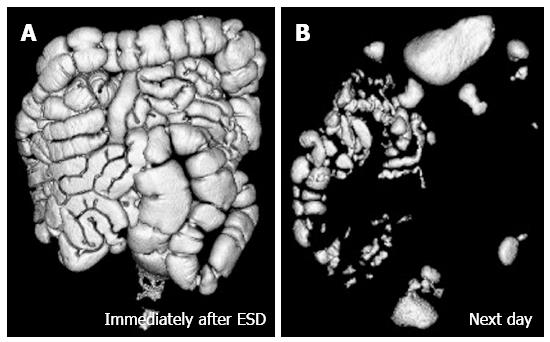
Figure 3 Volume-rendering image of bowel gas immediately after endoscopic submucosal dissection with air insufflation (A) and that of next day (B).
Figure 4 Patient flow chart.
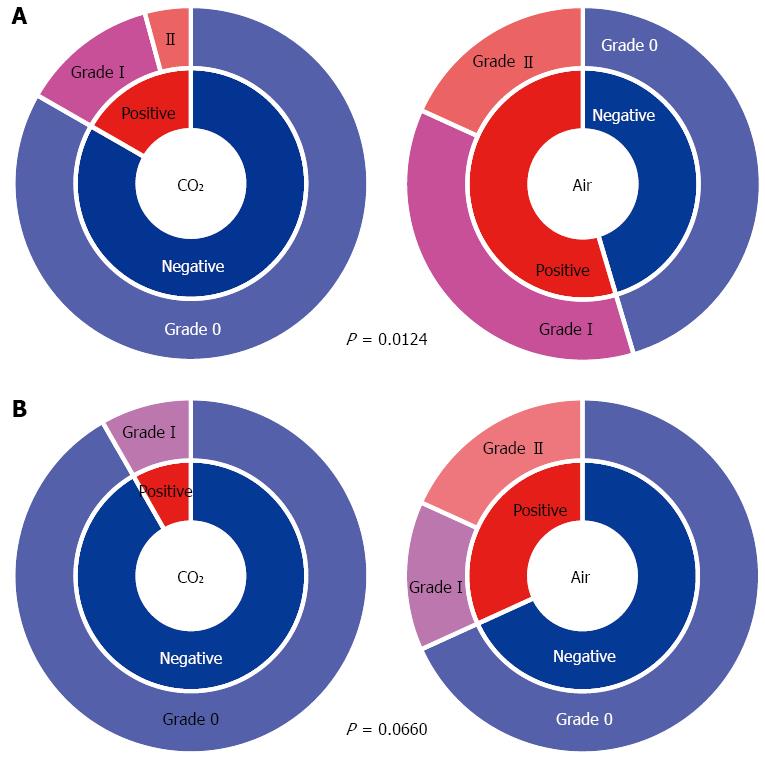
Figure 5 Incidence and degree of mediastinal emphysema immediately after endoscopic submucosal dissection (A) and on the day after endoscopic submucosal dissection (B).
P value for the incidence of ME. Grade-0 means negative for ME. ME: Mediastinal emphysema.
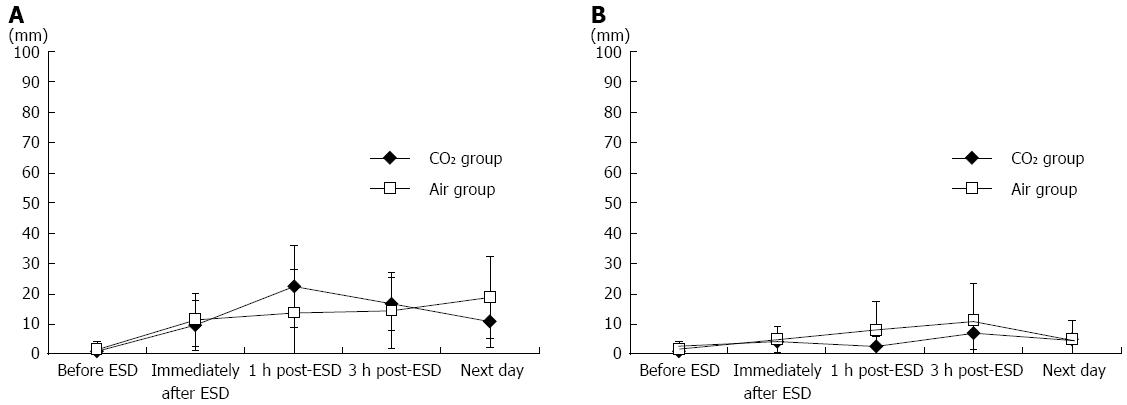
Figure 6 Mean pain score (A) and distension score (B) on the 100-mm visual analogue scale at different time points before and after endoscopic submucosal dissection in the CO2 and Air groups.
ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
- Citation: Maeda Y, Hirasawa D, Fujita N, Ohira T, Harada Y, Yamagata T, Koike Y, Suzuki K. Carbon dioxide insufflation in esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection reduces mediastinal emphysema: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(32): 7373-7382
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i32/7373.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i32.7373