©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2016; 22(30): 6757-6763
Published online Aug 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i30.6757
Published online Aug 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i30.6757
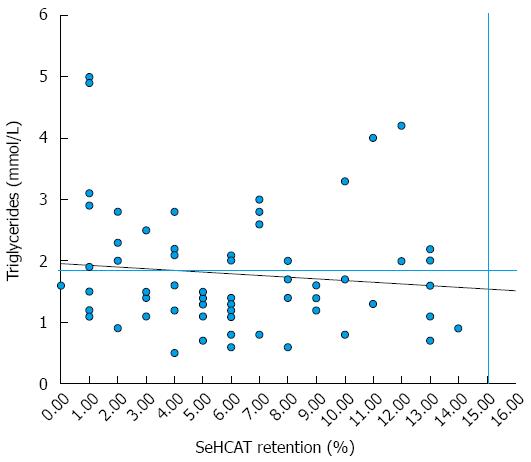
Figure 1 Relationship of triglycerides to selenium-75-homophoric acid taurine retention values in patients with primary and secondary bile acid diarrhoea.
The linear regression (R2 value 0.0129) and normal values for TGs (1.9 mmol/L) and selenium-75-homophoric acid taurine (SeHCAT) retention (15%) are shown.
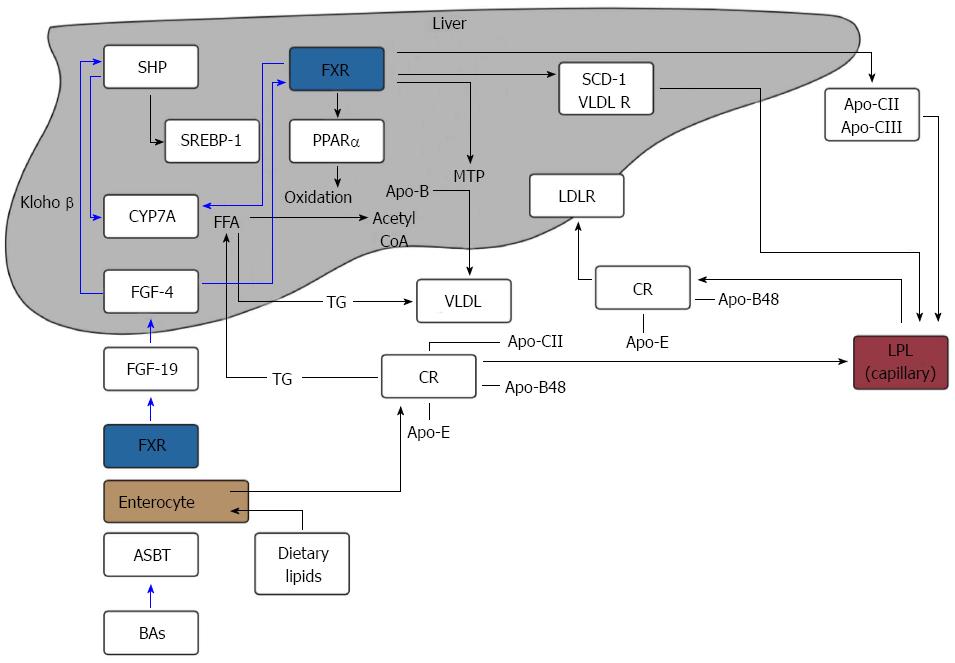
Figure 2 Overview of the farnesoid X receptor action on bile acid synthesis and triglyceride metabolism.
SHP: Small heterodimer primer; BA: Bile acid; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; FFA: Free fatty acid; LPL: Lipoprotein lipase; VLDL: Very low-density lipoproteins; CR: Chylomicron; ASBT: Apical ileal sodium dependant bile acid transporter; MTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; SREBP: Sterol regulatory element binding protein; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor.
- Citation: Sagar NM, McFarlane M, Nwokolo C, Bardhan KD, Arasaradnam RP. Mechanisms of triglyceride metabolism in patients with bile acid diarrhea. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(30): 6757-6763
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i30/6757.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i30.6757