Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2016; 22(3): 1236-1245
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1236
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1236
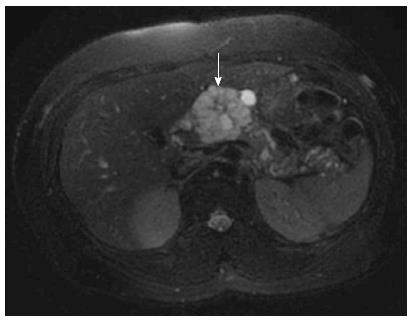
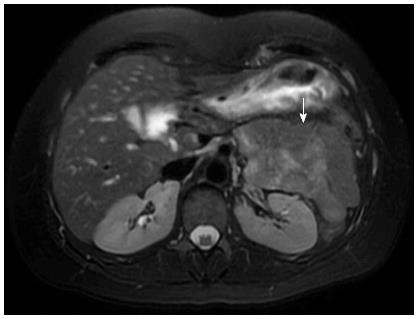
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging of microcystic serous cystadenoma (arrow) in body of pancreas.
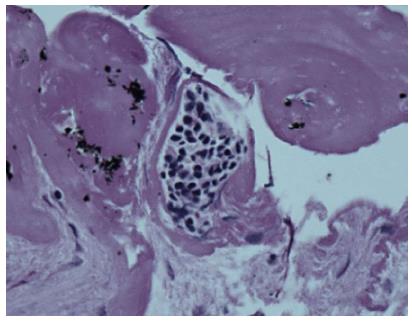
Figure 2 Cytology of serous cystadenoma with cuboidal epithelial cells containing glycogen staining for periodic acid-Schiff.
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography of main duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
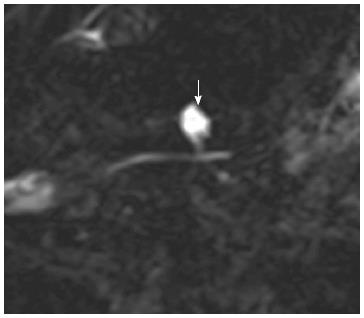
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (arrow) communicating with nondilated main pancreatic duct.
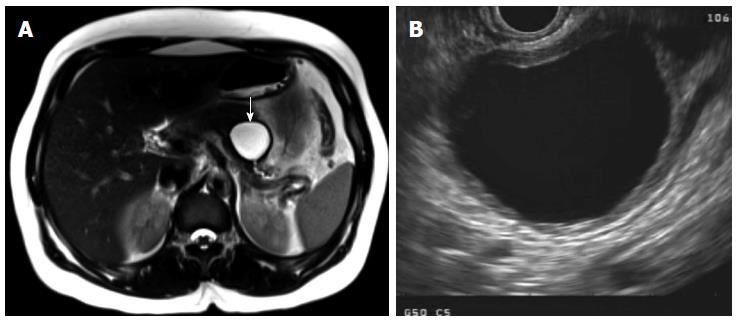
Figure 5 Mucinous cystic neoplasm seen on magnetic resonance imaging (A, arrow pointing to mucinous cystic neoplasm) and endoscopic ultrasound (B), with unilocular appearance and thick wall.
Figure 6 Magnetic resonance imaging of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (arrow).
- Citation: Chiang AL, Lee LS. Clinical approach to incidental pancreatic cysts. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(3): 1236-1245
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i3/1236.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1236