©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2016; 22(29): 6629-6637
Published online Aug 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6629
Published online Aug 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6629
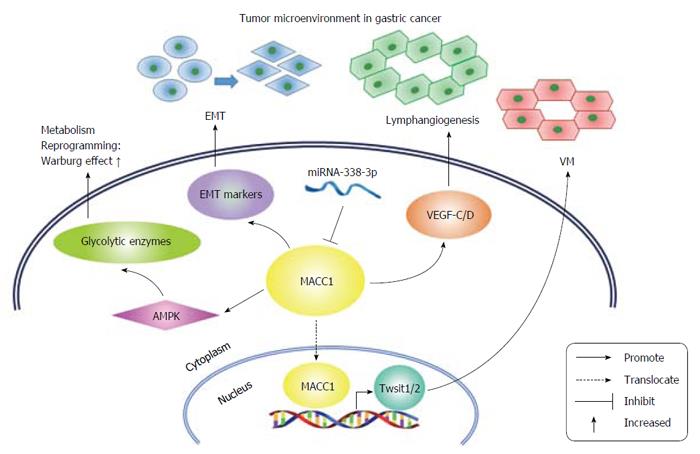
Figure 1 MACC1 participates in multiple biological processes inside and outside of gastric cancer cells, functioning as an important mediator of the tumor microenvironment.
MACC1 upregulates markers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to promote tumor metastasis. MACC1 facilitates lymphangiogenesis by increasing extracellular secretion of VEGF-C/D. MACC1 also serves as a transcription factor and increases TWIST1/2 transcription to prompt vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation. Additionally, MACC1 alters the expression of several glycolytic enzymes by activating the AMPK pathway to enhance the Warburg effect, leading to GC metabolic reprogramming. miRNA-338-3p, a tumor-suppressing microRNA, directly inhibits MACC1 and reverses some pro-tumorigenic properties of MACC1. GC: Gastric cancer.
- Citation: Wu ZZ, Chen LS, Zhou R, Bin JP, Liao YL, Liao WJ. Metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 in gastric cancer: Beyond metastasis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(29): 6629-6637
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i29/6629.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6629