©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2016; 22(14): 3845-3851
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3845
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3845
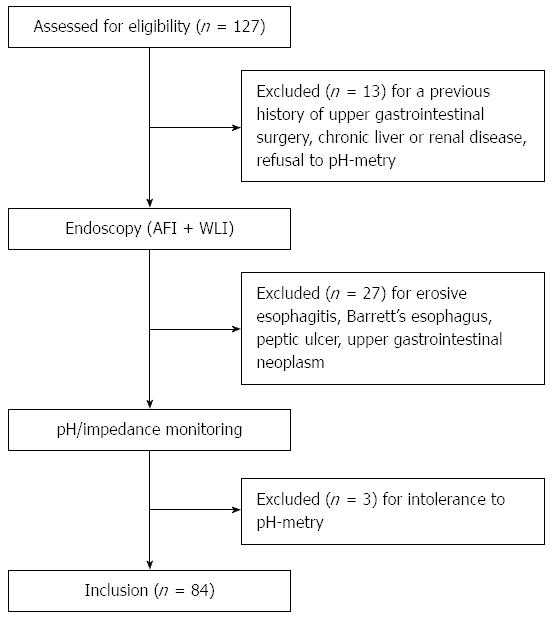
Figure 1 Flow diagram illustrating patients enrolled in the present study.
AFI: Autofluorescence imaging; WLI: White light imaging.
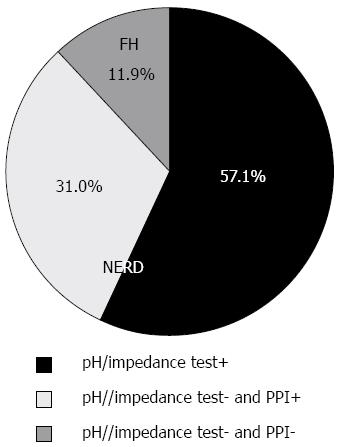
Figure 2 Categorization of patients by means of pH/impedance and proton-pump inhibitor test.
PPI: Proton-pump inhibitor; FH: Functional heartburn; NERD: Non-erosive reflux disease.
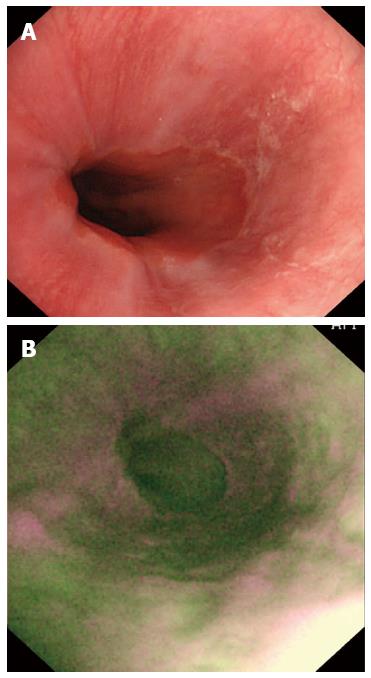
Figure 3 Images in a patient with non-erosive reflux disease.
A: A normal appearance of esophageal mucosa on WLI; B: Longitudinal purple lines on AFI. AFI: Autofluorescence imaging; WLI: White light imaging.
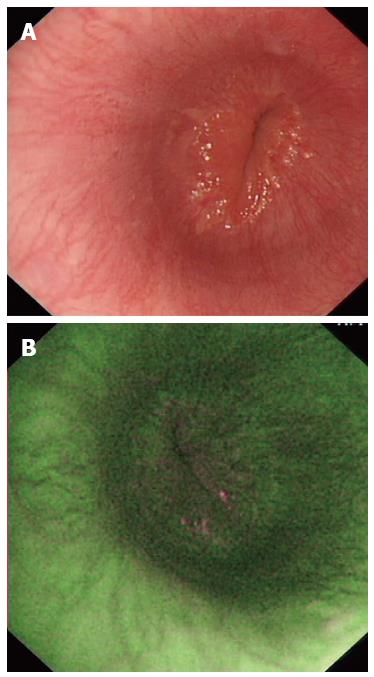
Figure 4 Images in a patient with functional heartburn.
A: A normal appearance of esophageal mucosa on WLI; B: A normal esophagus on AFI. AFI: Autofluorescence imaging; WLI: White light imaging.
- Citation: Luo X, Guo XX, Wang WF, Peng LH, Yang YS, Uedo N. Autofluorescence imaging endoscopy can distinguish non-erosive reflux disease from functional heartburn: A pilot study. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(14): 3845-3851
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i14/3845.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3845