©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2015; 21(8): 2568-2572
Published online Feb 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2568
Published online Feb 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2568
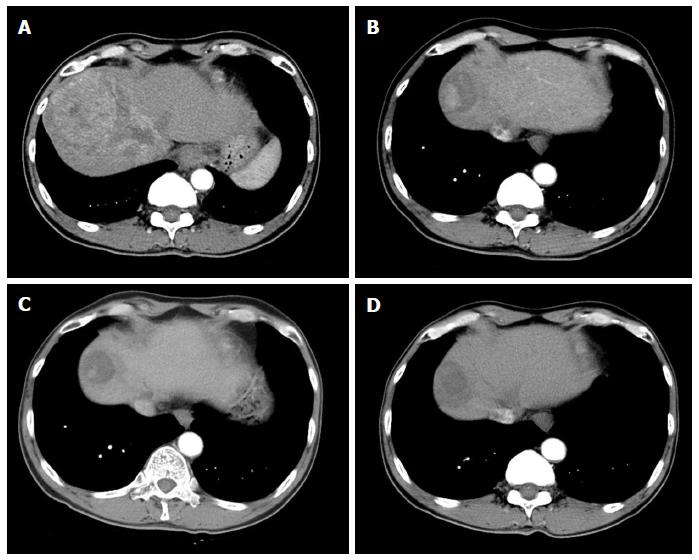
Figure 1 Arterial phase scans of contrast enhanced multiphase computed tomogram of abdomen.
A: Baseline abdominal computed tomogram (CT) scan showed 12.5 cm sized enhancing mass in segment 8 with tumor thrombus in middle, right hepatic vein extending to intrahepatic inferior vena cava; B: The size of tumor decreased to 4.8 cm with 2.7 cm sized enhancing nodule in tumor in 6 mo-follow-up CT scans; C: The tumor size further decreased to 3.0 cm with 1.5 cm sized enhancing nodule within tumor in 12 mo-follow-up CT scans with resolution of tumor thrombus in hepatic vein and portal vein. D: There was no arterial enhancing viable portion in ablated tumor in abdominal CT scans 6 mo after radiofrequency ablation.
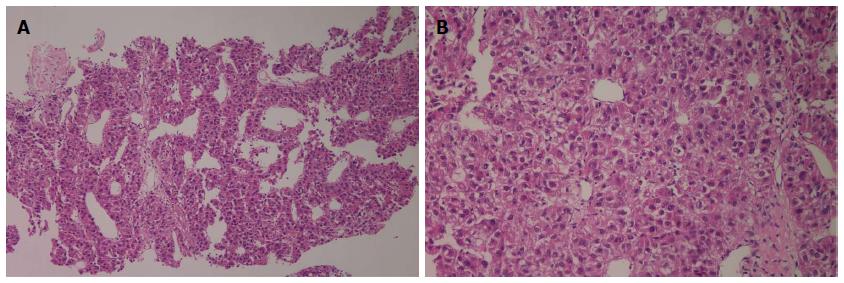
Figure 2 Liver biopsy revealed hepatocellular carcinoma with Edmonson-Steiner’s grade III showing psedoglandular or trabecular pattern.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, magnification × 100; B: HE staining, magnification × 200.
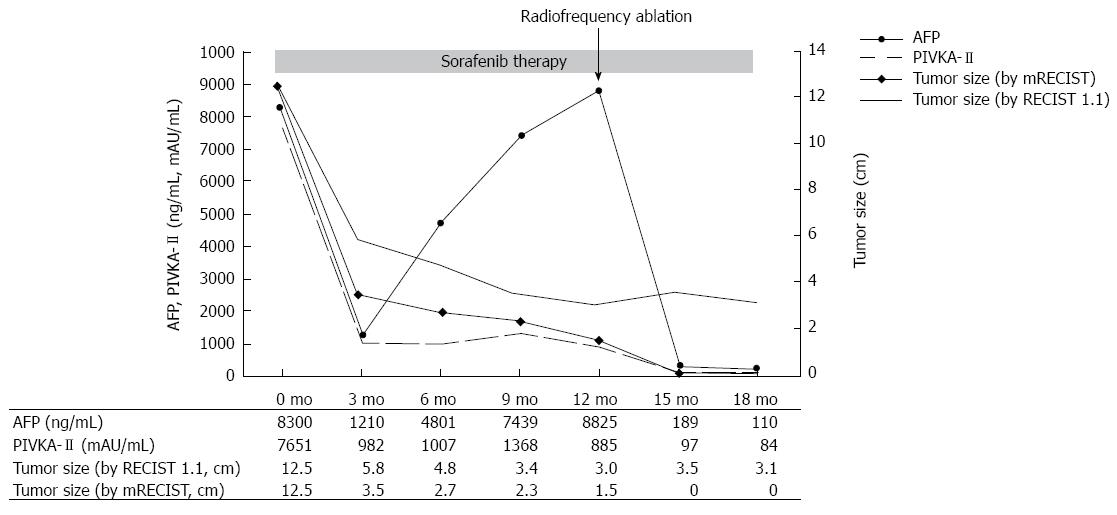
Figure 3 Clinical course and serial changes of patientâs serum level of alpha-fetoprotein, protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-â
¡ and tumor size accessed by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors 1.
1 and modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors. AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; PIVKA-â
¡: Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-â
¡; RECIST: Response evaluation criteria in solid tumors.
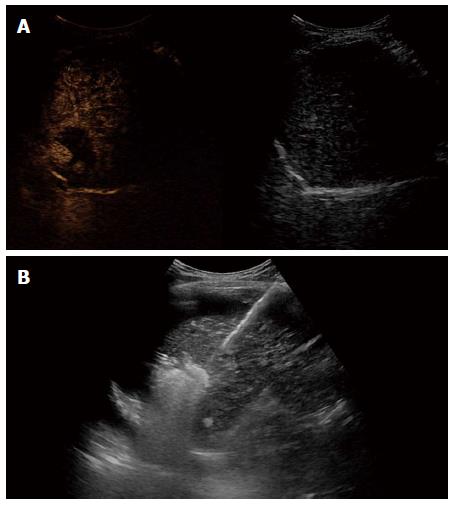
Figure 4 After confirming viable tumor by contrast enhanced ultrasound, radiofrequency ablation was performed.
A: Contrast enhanced ultrasound revealed two arterial enhancing nodules in tumor; B: Percutaneous ultrasound guided radiofrequency ablation was performed for residual viable tumor by inducing artificial ascites.
- Citation: Park JG, Park SY, Lee HW. Complete remission of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma by radiofrequency ablation after sorafenib therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(8): 2568-2572
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i8/2568.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2568