©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2015; 21(6): 1872-1879
Published online Feb 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1872
Published online Feb 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1872
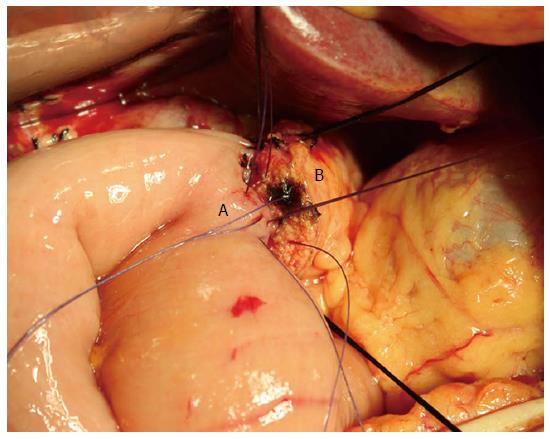
Figure 1 Pancreaticojejunal anastomosis.
This picture shows a two-layer end to side pancreatic duct to jejunal mucosa anastomosis. A: Jejunum; B: Pancreas.
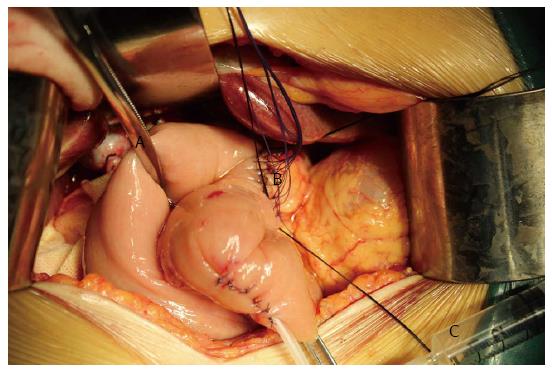
Figure 2 Air insufflation test to investigate the pancreaticojejunal anastomosis.
An intestinal clamp (A) was used to close the distal intestinal loop approximately 6 cm from the pancreaticojejunal anastomosis (B). Then, the anastomosis was submerged in irrigation fluid, and air was injected gently with a 1 or 5 mL syringe (C) through the pancreatic duct stent to determine whether there were bubbles generated.
- Citation: Yang H, Lu XF, Xu YF, Liu HD, Guo S, Liu Y, Chen YX. Application of air insufflation to prevent clinical pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(6): 1872-1879
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i6/1872.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1872