©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2015; 21(42): 12179-12189
Published online Nov 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12179
Published online Nov 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12179
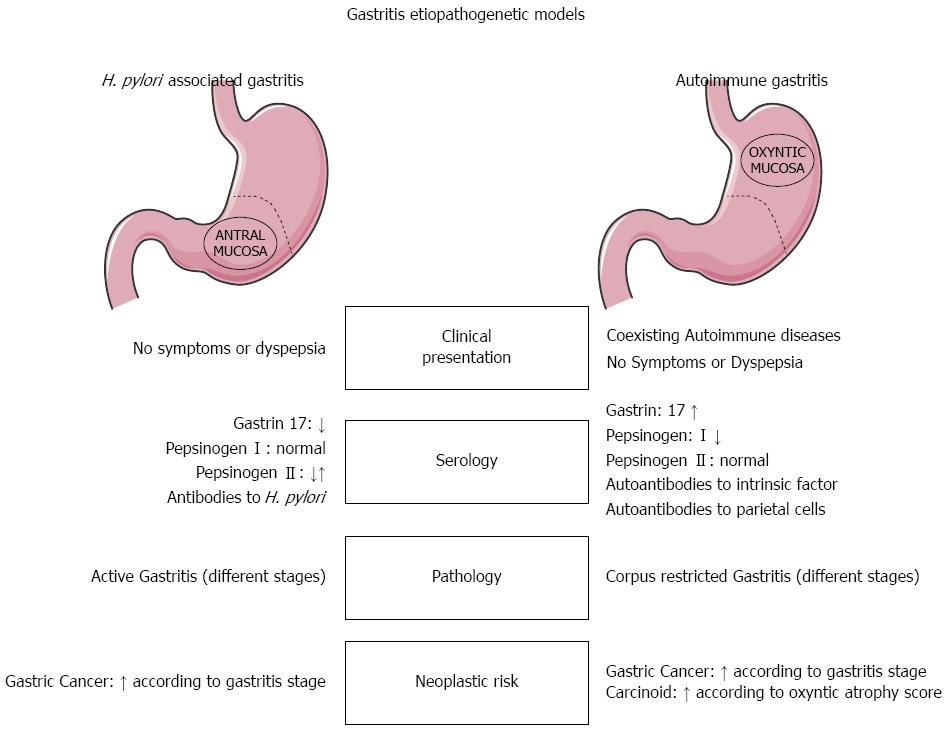
Figure 1 Helicobacter pylori-related vs autoimmune gastritis.
Main differences in clinical presentation, serology (immunological and functional profiles), pathology, and neoplastic risk. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
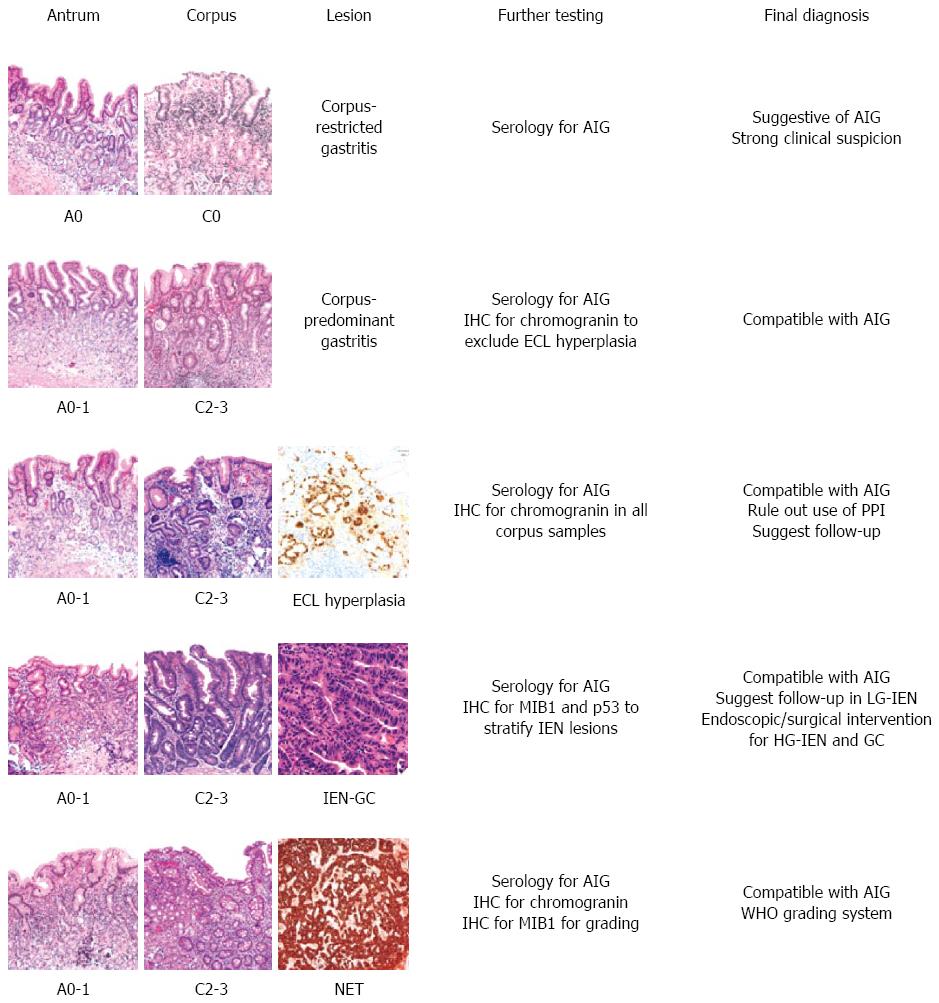
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the main diagnostic histological pictures seen in autoimmune gastritis.
Metaplastic changes in the antrum and corpus are staged using the OLGA system. IHC: Immunohistochemistry; ECL: Enterochromaffin-like; IEN: Intraepithelial neoplasia; LG-IEN: Low-grade IEN; HG-IEN: High-grade IEN; GC: Gastric carcinoma; OLGA: Operative link for gastritis assessment; AIG: Autoimmune gastritis; PPI: Proton pump inhibitor.
- Citation: Coati I, Fassan M, Farinati F, Graham DY, Genta RM, Rugge M. Autoimmune gastritis: Pathologist’s viewpoint. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(42): 12179-12189
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i42/12179.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12179