©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2015; 21(42): 12114-12124
Published online Nov 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12114
Published online Nov 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12114
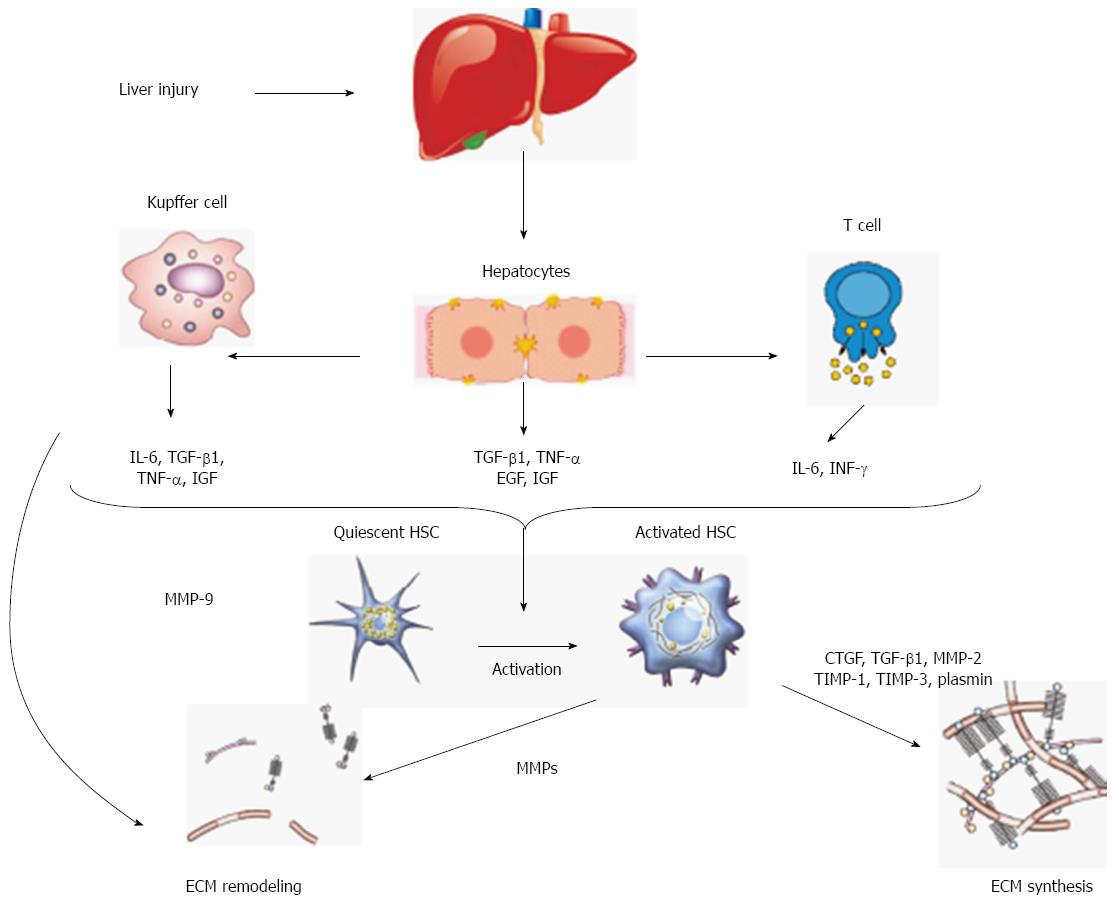
Figure 1 Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis.
IL-6: Interleukin-6; INF-γ: Interferon-γ; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-β1; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor; TIMP-1: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase Type1; TIMP-3: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase Type3; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; ECM: Extracellular matrix.
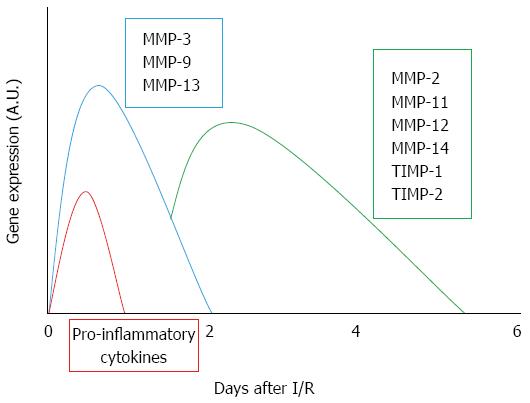
Figure 2 Time-course of matrix metalloproteinase expression following ischemia/reperfusion injury.
In response to injury, pro-inflammatory cytokines, which promptly increase, induce expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) expression by hepatic cells including hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). The MMPs secreted by HSCs degrade the normal extracellular matrix (ECM) in the space of Disse.
- Citation: Palladini G, Ferrigno A, Richelmi P, Perlini S, Vairetti M. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in cholestasis and hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury: A review. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(42): 12114-12124
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i42/12114.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12114