Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2015; 21(41): 11842-11853
Published online Nov 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11842
Published online Nov 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11842
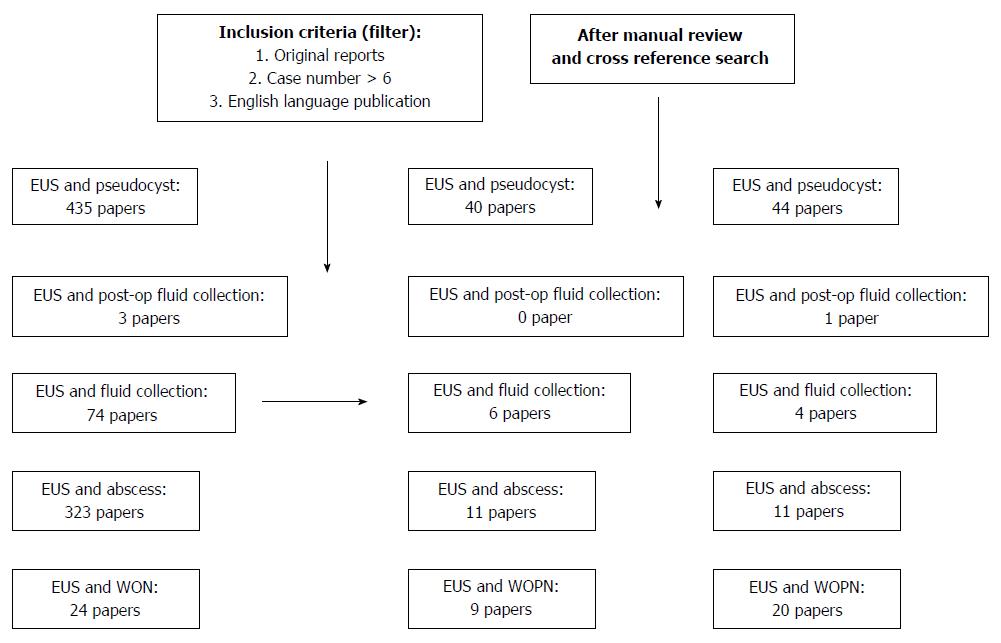
Figure 1 On November 15, 2014, the authors performed a PubMed search using following key word sets: endoscopic ultrasound in combination with terminologies related to pancreatic fluid collections such as pseudocyst, fluid collection, abscess, and walled off necrosis.
Each published paper was simultaneously reviewed by two authors who extracted important information related to this review. EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound; WON: Walled off necrosis.
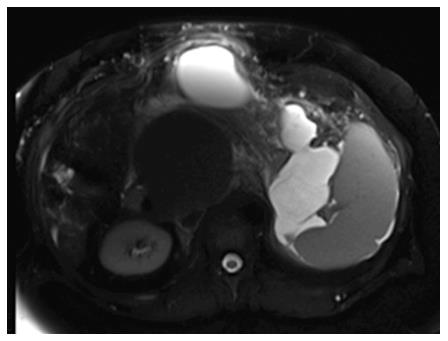
Figure 2 Selected magnetic resonance imaging frame showing a large peri-pancreatic pseudocyst extending from the pancreatic tail to the anterior abdominal wall in a patient with pancreatitis and splenic vein thrombosis.
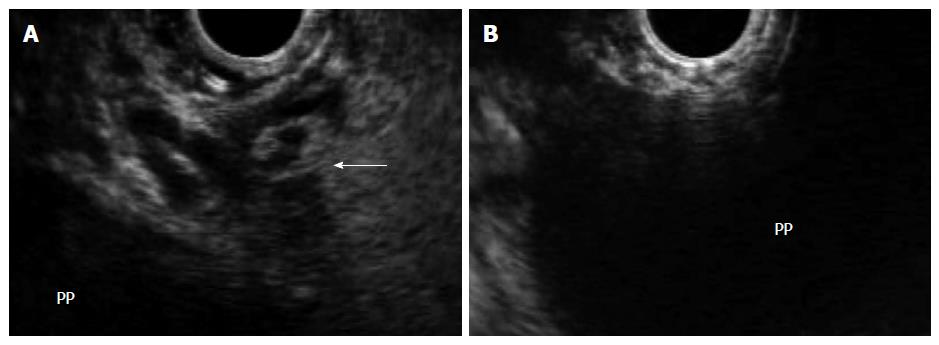
Figure 3 In the same patient, endoscopic ultrasound permits visualization of the pancreatic pseudocyst, assessment of wall maturity, determination of distance between the collection and the luminal wall, identification of intervening vessels or collaterals (arrow) (A), and selection of the optimal puncture site (B).
PP: Pancreatic pseudocyst.
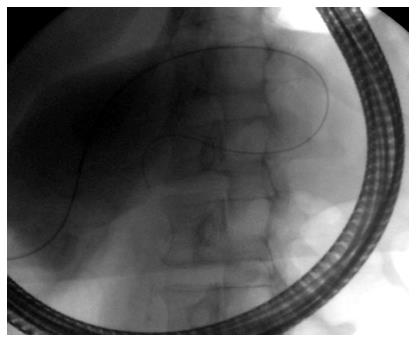
Figure 4 Fluoroscopic image showing transpapillary drainage of a pancreatic pseudocyst that is shared with the main pancreatic duct.
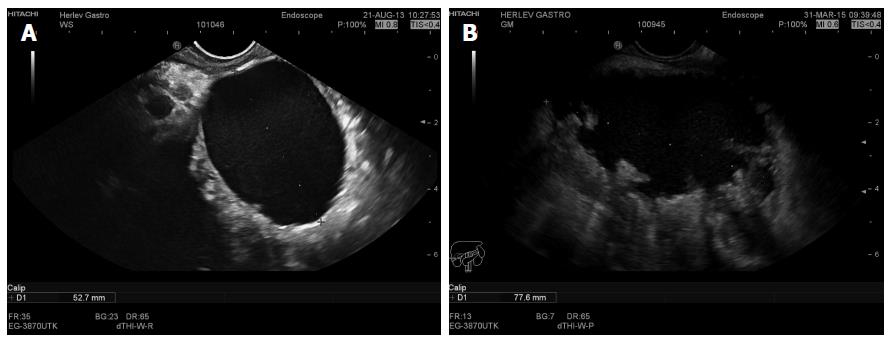
Figure 5 Endoscopic ultrasound image of a 5 cm chronic pseudocyst with a thin wall (A) or a 7.
8 cm irregular pseudocyst with walled off necrosis (B).
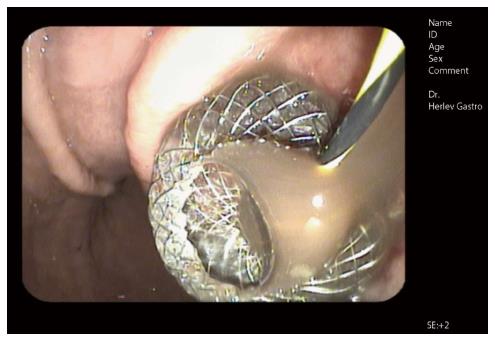
Figure 6 Endoscopic image of a self-expandable metal stent immediately after endoscopic ultrasound guided drainage (AXIOSTM system, Xlumina, Mountain View, CA, United States).
Note the fluid floating through the stent opening. A guidewire extending through the stent lumen is still visible.
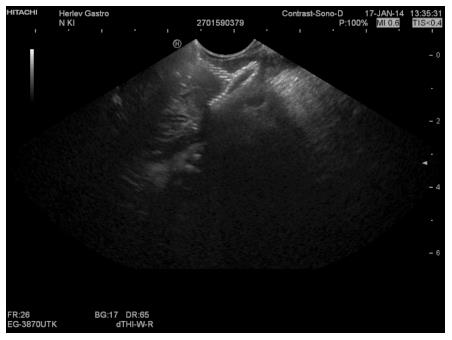
Figure 7 Corresponding endoscopic ultrasound image of a collapsed pancreatic pseudocyst immediately after drainage.
Note reflexions from the stent mesh inside the collapsed cyst.
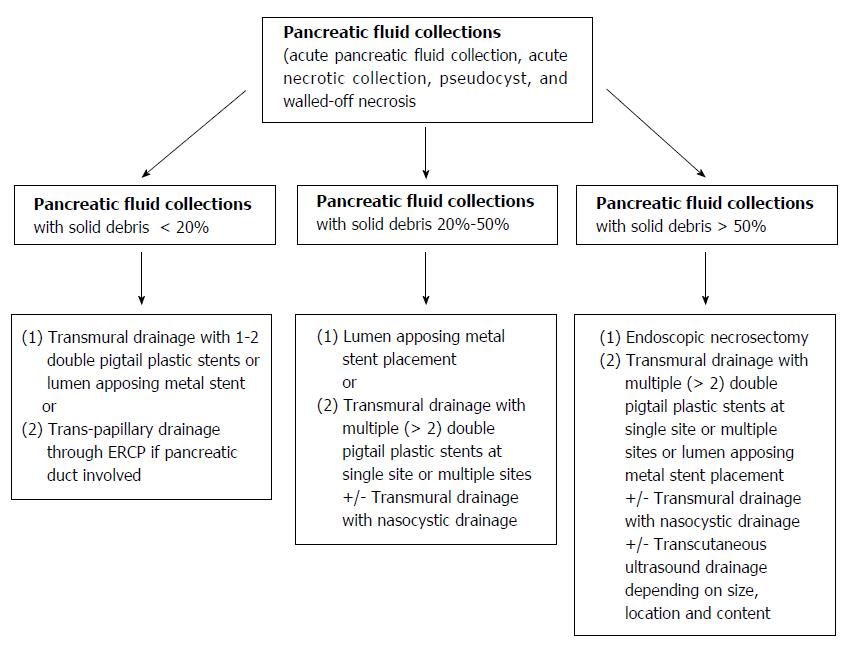
Figure 8 Authors' proposed endoscopic ultrasound-guided management algorithm based on the amount of internal debris inside a pancreatic fluid collection.
- Citation: Vilmann AS, Menachery J, Tang SJ, Srinivasan I, Vilmann P. Endosonography guided management of pancreatic fluid collections. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(41): 11842-11853
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i41/11842.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11842