©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2015; 21(39): 10931-10935
Published online Oct 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i39.10931
Published online Oct 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i39.10931
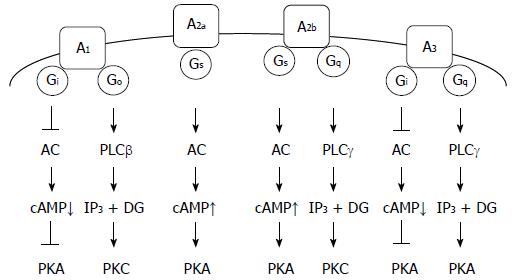
Figure 1 Adenosine receptors and their relevant signaling pathways.
A1: A1 adenosine receptor; A2a: A2a adenosine receptor; A2b: A2b adenosine receptor; A3: A3 adenosine receptor; PLC: Phospholipase C; IP3: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; DG: Diacylglycerol; PKA: Protein kinase A; PKC; Protein kinase C.
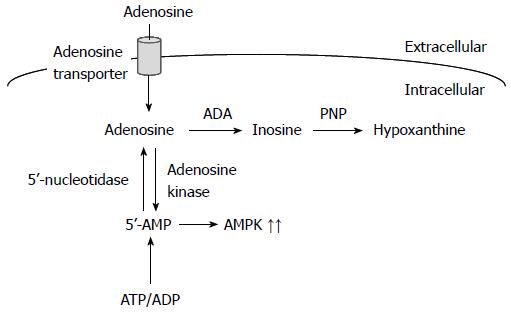
Figure 2 Intracellularly transported adenosine and the ensuing signaling pathways.
AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate.
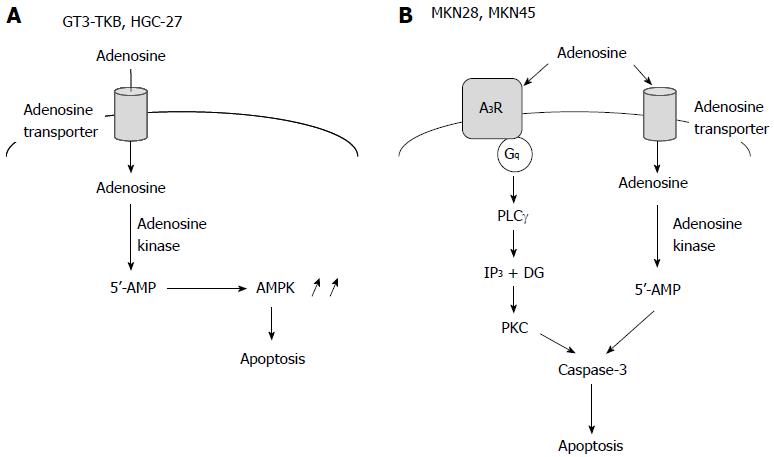
Figure 3 Extracellular adenosine-induced apoptosis of gastric cancer cells.
A: The adenosine-induced apoptotic pathway for GT3-TKB and HGC-27 cells; B: The adenosine-induced apoptotic pathway for MKN28 and MKN45 cells. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase.
-
Citation: Tsuchiya A, Nishizaki T. Anticancer effect of adenosine on gastric cancer
via diverse signaling pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(39): 10931-10935 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i39/10931.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i39.10931