©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2015; 21(38): 10776-10782
Published online Oct 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10776
Published online Oct 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10776
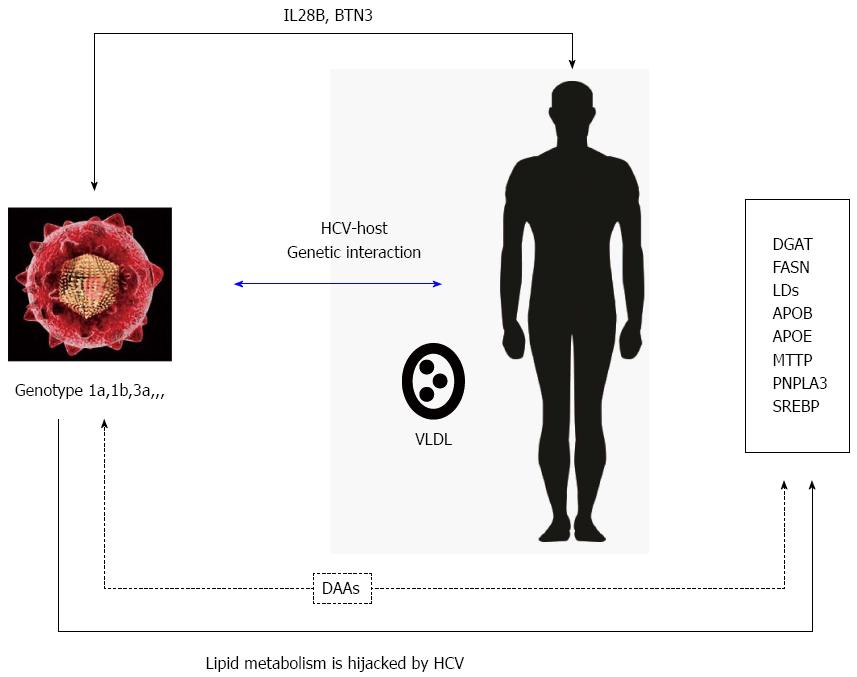
Figure 1 Schematic representation of hepatitis C virus and host interplay during hepatitis C virus infection.
Viral infection has a direct effect on lipid metabolism through two main mechanisms: first, by deregulating gene expression (FASN, DGAT, MTTP, SREBP). This effect can be modulated by certain SNPs in PNPLA3, among others. Secondly, VLDL synthesis is affected, since HCV replication takes place on lipid droplets. SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphisms; VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; DGAT: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase; LD: Lipid droplet; PNPLA3: patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3.
- Citation: Del Campo JA, Romero-Gómez M. Modulation of host lipid metabolism by hepatitis C virus: Role of new therapies. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(38): 10776-10782
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i38/10776.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10776