©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2015; 21(30): 9067-9078
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9067
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9067
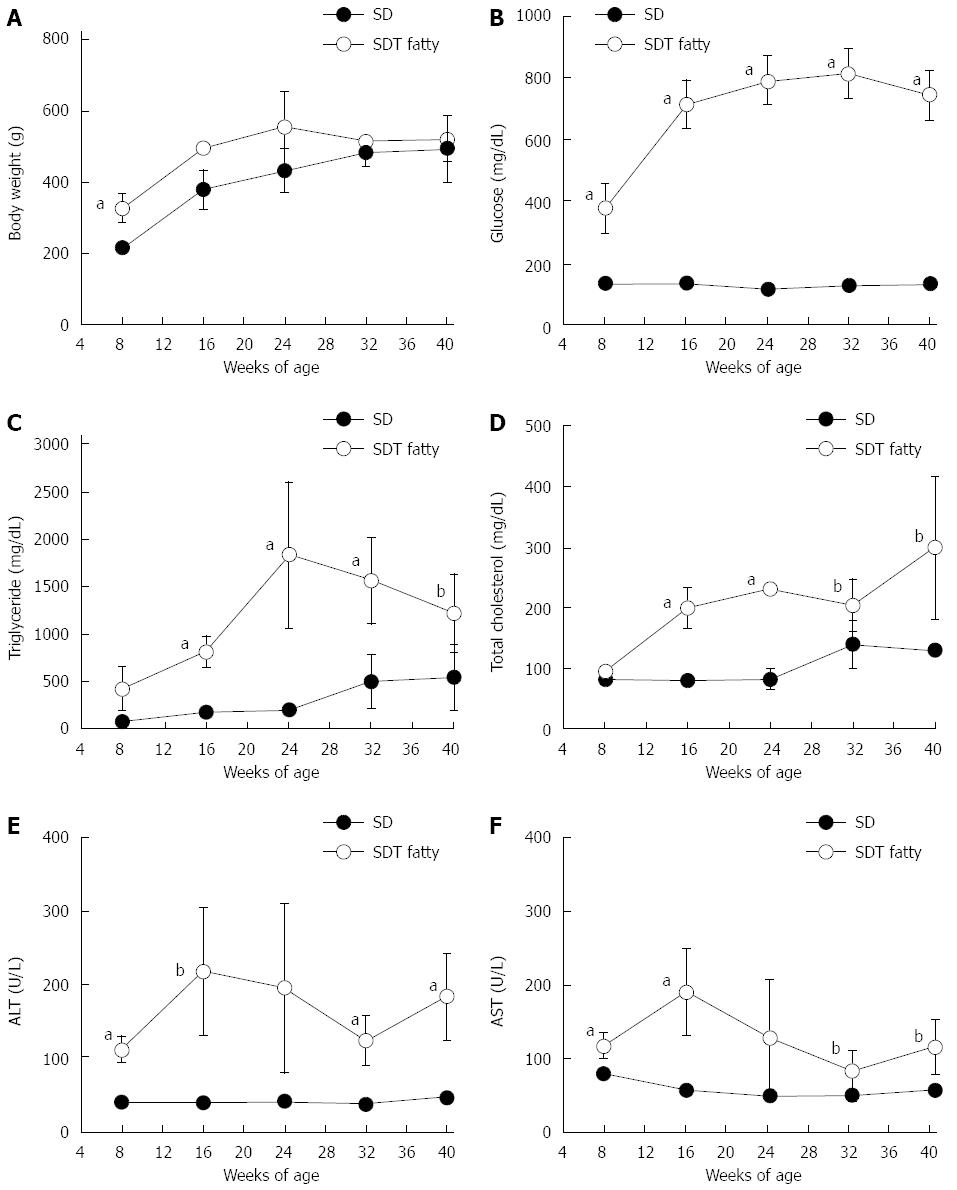
Figure 1 Changes in body weight and biological parameters in spontaneously diabetic Torii fatty rats and Sprague-Dawley rats.
A: Body weight; B: Glucose; C: Triglyceride; D: Total cholesterol; E: Alanine aminotransferase; F: Aspartate aminotransferase. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 4-5). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs Sprague-Dawley rats. SDT: spontaneously diabetic Torii; SD: Sprague-Dawley.
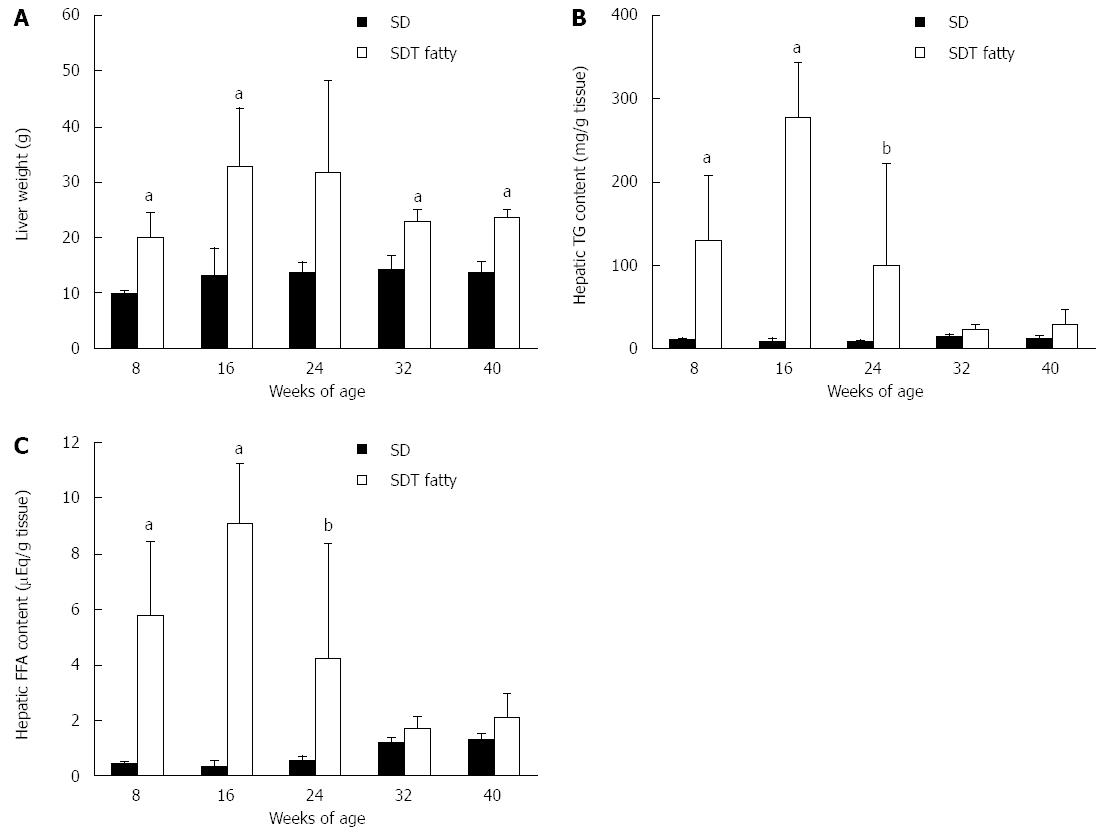
Figure 2 Changes in liver weight, hepatic triglyceride, and fatty acid contents in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii fatty rats and Sprague-Dawley rats.
A: Liver weight; B: Hepatic triglyceride content; C: Hepatic fatty acid content. Data are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 4-5). Data are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 4-5). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs SD rats. FFA: Free fatty acid; TG: Triglyceride.
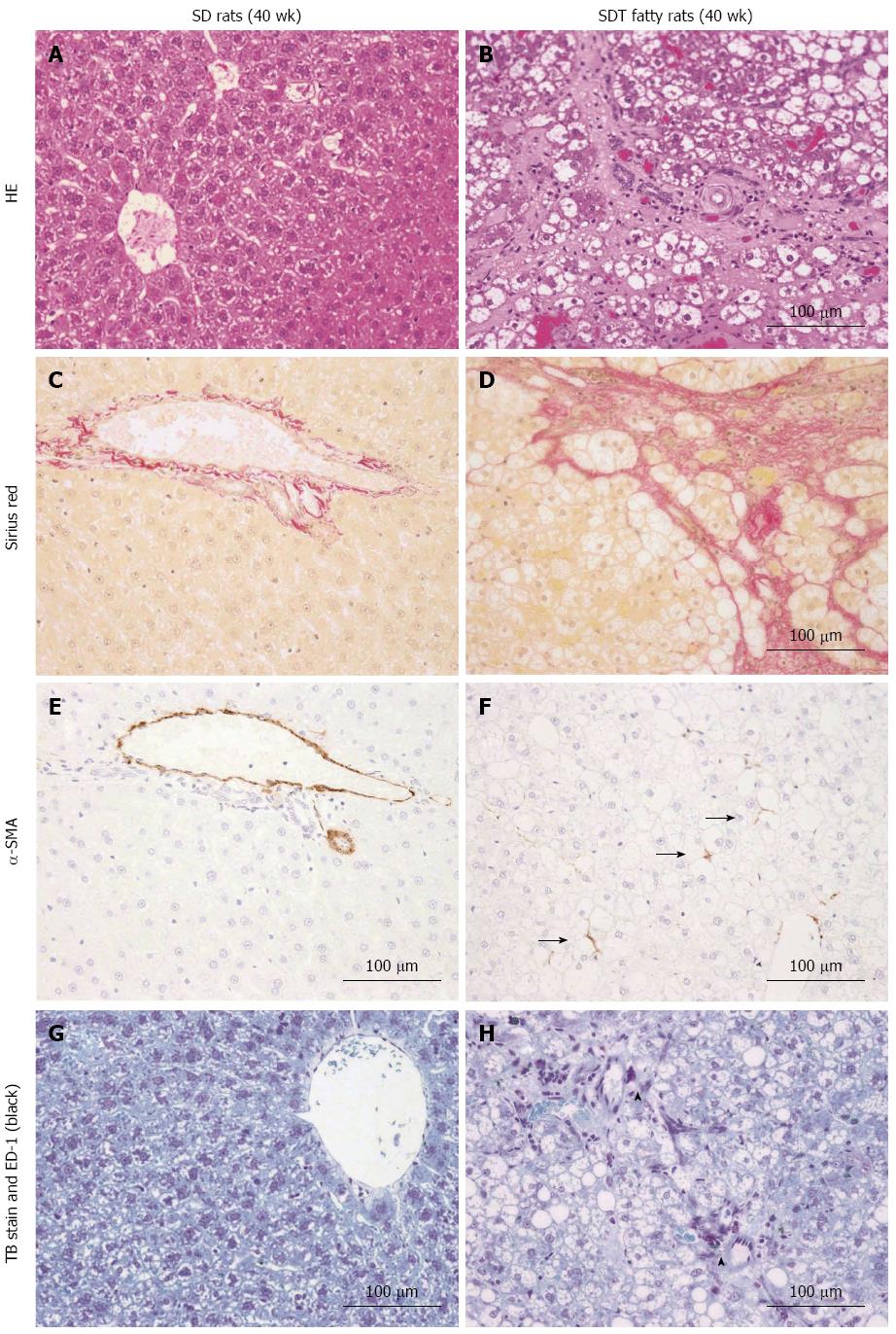
Figure 3 Liver histopathology at 40 wk of age.
A, C, E, G: SD rats; B, D, F, H: SDT fatty rats. A, B: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE); C, D: Sirius Red; E, F: Alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA); G, H: Toluidine blue staining and immunohistochemistry for ED-1.
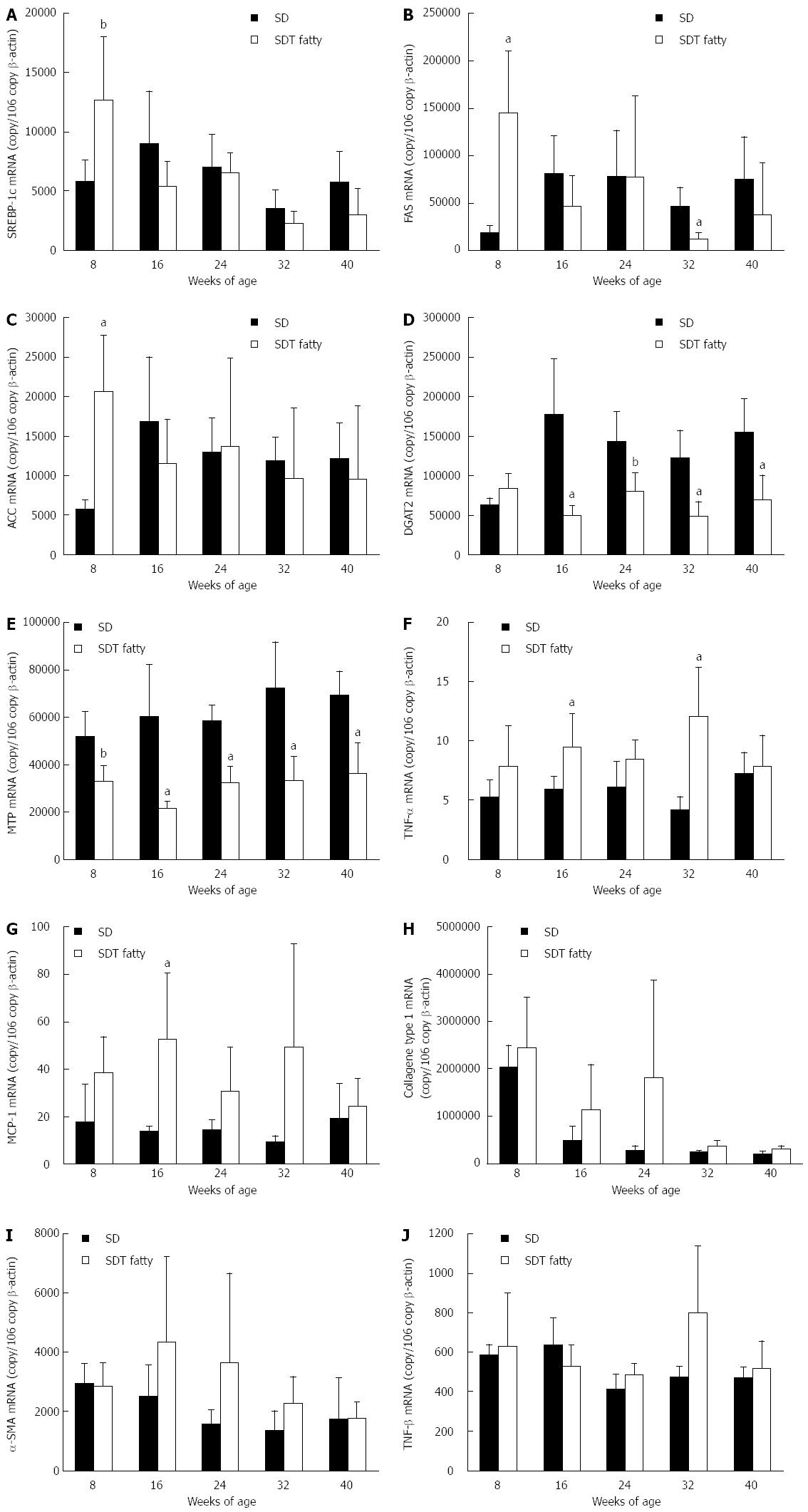
Figure 4 Expression of genes related to triglyceride synthesis, triglyceride secretion, inflammation, and fibrosis in spontaneously diabetic Torii fatty rats and SD rats.
A: SREBP-1c; B: FAS; C: ACC; D: DGAT2; E: MTP; F: TNF-α; G: MCP-1; H: Collagen type 1; I: α-SMA; J: TGF-β. Data are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 4-5). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs SD rats. SDT: Spontaneously diabetic Torii; SD: Sprague-Dawley.
- Citation: Ishii Y, Motohashi Y, Muramatsu M, Katsuda Y, Miyajima K, Sasase T, Yamada T, Matsui T, Kume S, Ohta T. Female spontaneously diabetic Torii fatty rats develop nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-like hepatic lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(30): 9067-9078
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i30/9067.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9067