©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2015; 21(27): 8227-8237
Published online Jul 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8227
Published online Jul 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8227
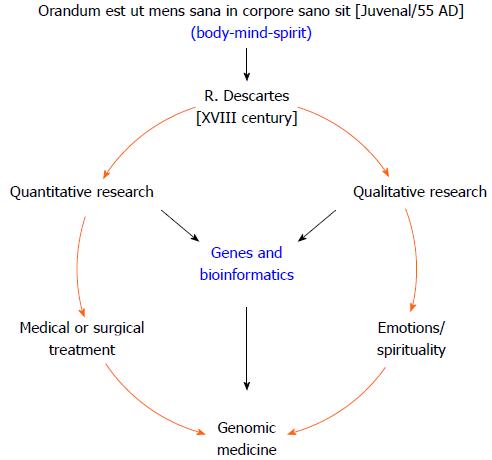
Figure 1 Esquematic representation of genomic medicine: a new paradigm shift or “back to the future”.
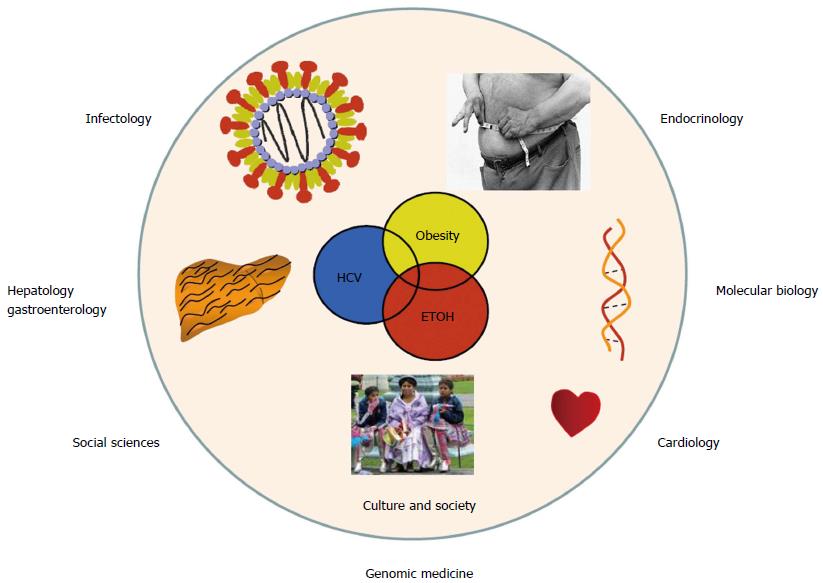
Figure 2 From medical specialties to genomic medicine.
The same patient usually requires consultation by different medical specialists. However, from a genomic medicine viewpoint, modern medicine should be integrative to prevent or halt chronic disease at an early stage of development.
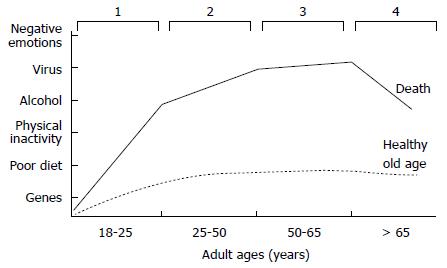
Figure 3 Four stages of the continuum of most chronic diseases.
1: Induction; 2: Disease progression; 3: Clinical complications; 4: Death. An individual with several risk factors may die at an earlier age (DARK LINE), in contrast, with an individual who has a healthier lifestyle (DASHED LINE).
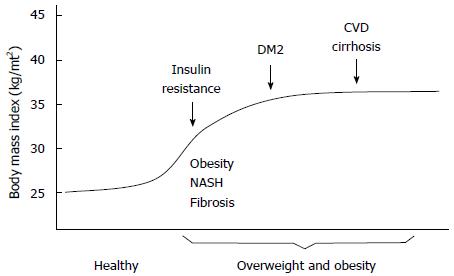
Figure 4 Overweight and obesity influence the onset of insulin resistance syndrome, a primary stage towards the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis fibrosis and cirrhosis.
DM2: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; CVD: Cardiovascular disease; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
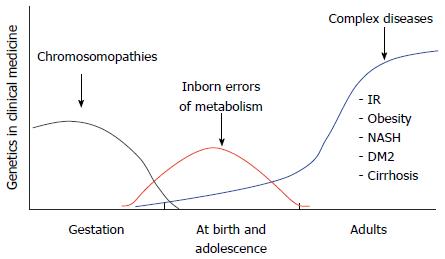
Figure 5 Impact of molecular biology in medicine: From cytogenetics to the study of complex diseases.
DM2: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; IR: Insulin resistance; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
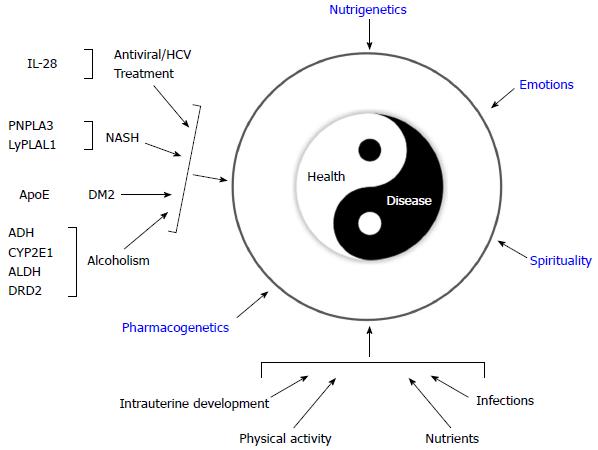
Figure 6 Genomic medicine: Interaction between specific polymorphisms with clinical implications and different environmental factors.
Disease-related gene polymorphisms: IL-28: Interleukin 28B; PNPLA3: Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3; LyPLAL1: lysophospholipase-like 1; ApoE: Apolipoprotein E; ADH: Alcohol dehydrogenase; CYP2E1: Cytochrome P450 2E1; ALDH: Aldehyde dehydrogenase; DRD2: Dopamine receptor D2. NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; DM2: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Citation: Roman S, Panduro A. Genomic medicine in gastroenterology: A new approach or a new specialty? World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(27): 8227-8237
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i27/8227.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8227