©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2015; 21(15): 4536-4546
Published online Apr 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4536
Published online Apr 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4536
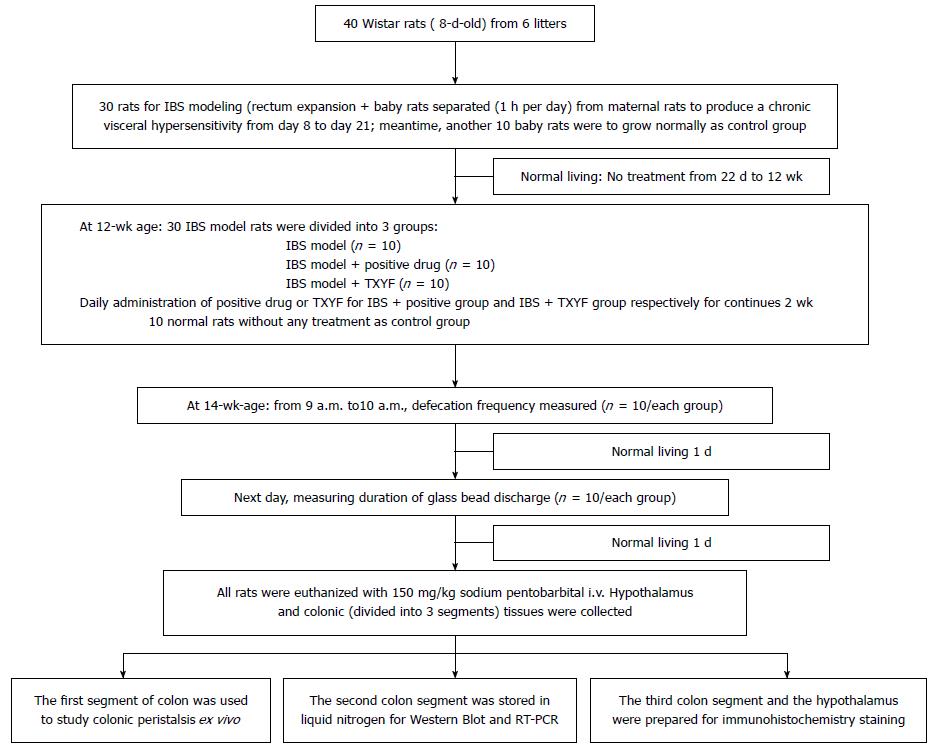
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study design and experiment procedure.
IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; TXYF: Tong Xie Yao Fang; RT-PCR: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
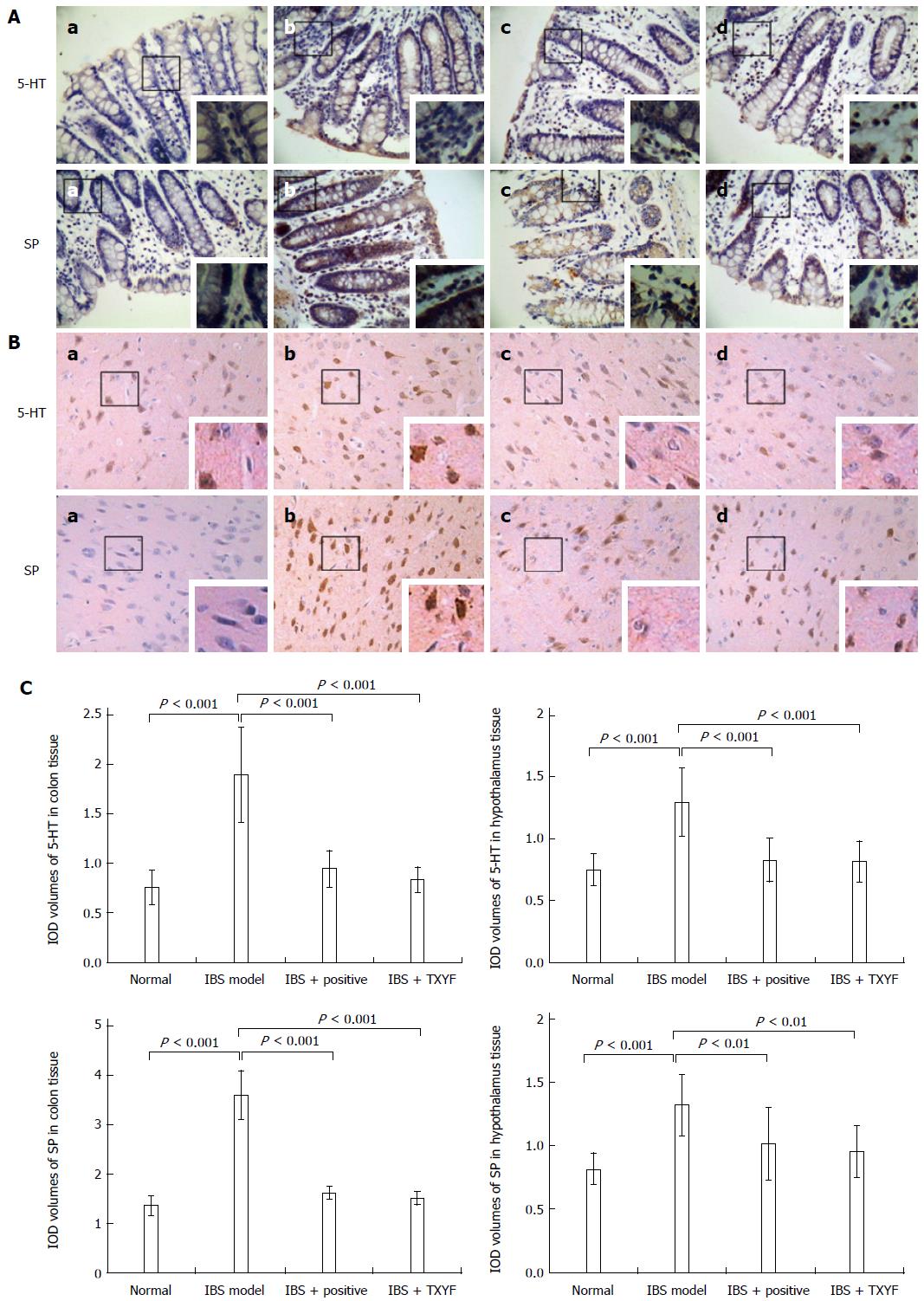
Figure 2 Tong Xie Yao Fang affects 5-hydroxytryptamine and substance P protein expression in colon (A) and hypothalamus (B) tissues in each group, as revealed by immunohistochemistry staining (× 400; inserted panel, × 1600); C: Quantitative measurements with Integral Optical Density data from A and B (n = 10 for each group).
a: Normal group; b: IBS model group; c: IBS model + positive group; d: IBS model + TXYF group. IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; TXYF: Tong Xie Yao Fang.
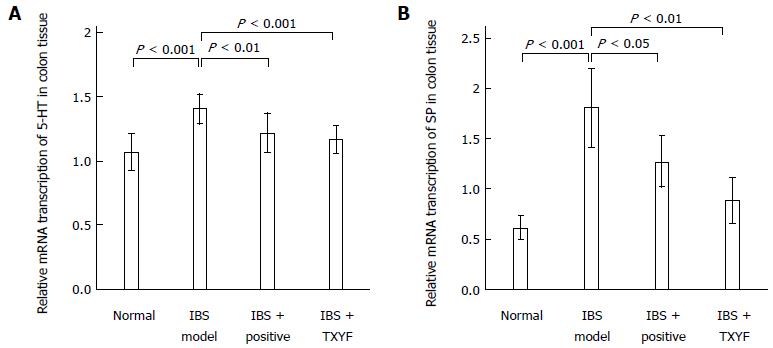
Figure 3 Quantitative data of 5-hydroxytryptamine (A) and substance P (B) mRNA expression via reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction detection in rat colon of the indicated groups.
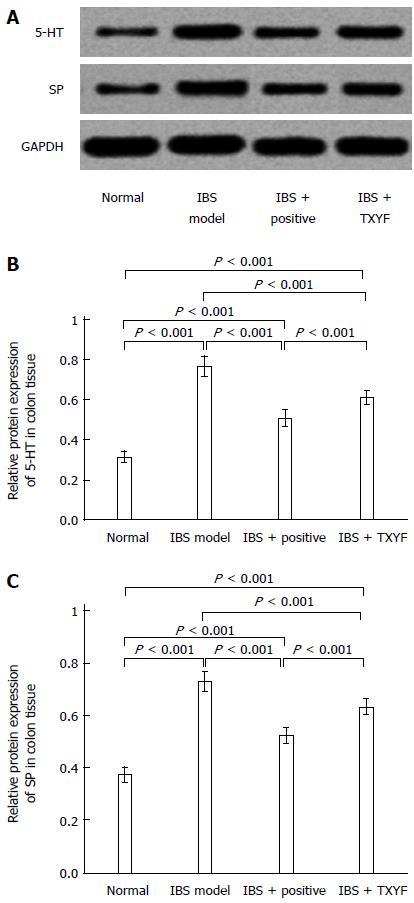
Figure 4 5-hydroxytryptamine and substance P protein expression in rat colon tissues of the indicated groups.
A: Representative Western blot image; B, C: Quantitative data from collected Western blot image. IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; TXYF: Tong Xie Yao Fang.
-
Citation: Yin Y, Zhong L, Wang JW, Zhao XY, Zhao WJ, Kuang HX. Tong Xie Yao Fang relieves irritable bowel syndrome in rats
via mechanisms involving regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine and substance P. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(15): 4536-4546 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i15/4536.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4536