©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2015; 21(12): 3657-3662
Published online Mar 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3657
Published online Mar 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3657
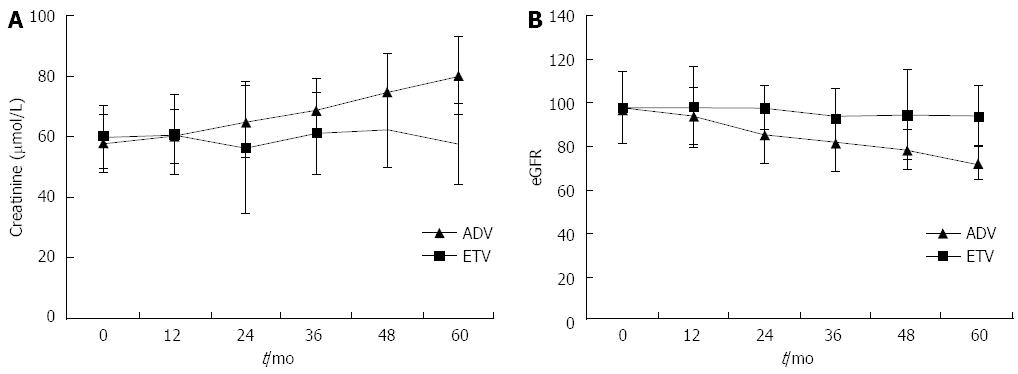
Figure 1 Time course after treatment with adefovir dipivoxil with or without lamivudine and entecavir for chronic hepatitis B patients.
A: Changes in mean creatinine level; B: Mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) with adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) and entecavir (ETV) administration.
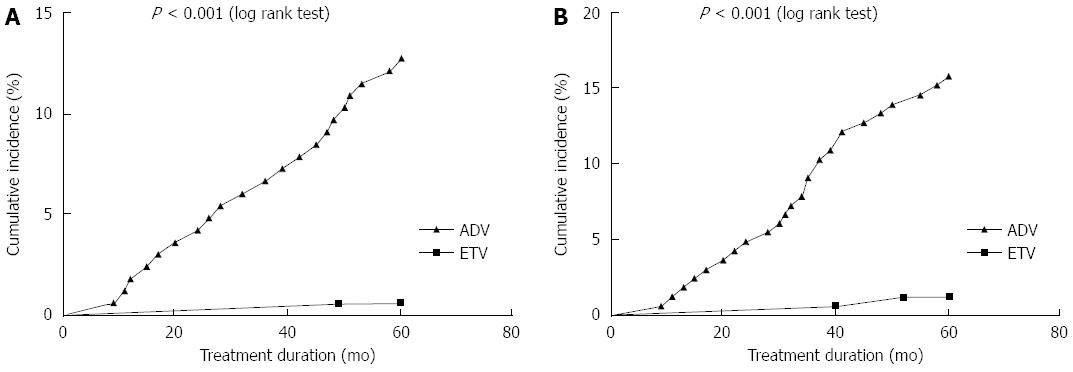
Figure 2 Cumulative incidence of urine microprotein abnormalities after treatment with adefovir dipivoxil with or without lamivudine or entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients.
Cumulative incidence of A: Urine β2-microglobulin abnormality; and B: Retinol-binding protein abnormality with long-term adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) or entecavir (ETV) treatment.
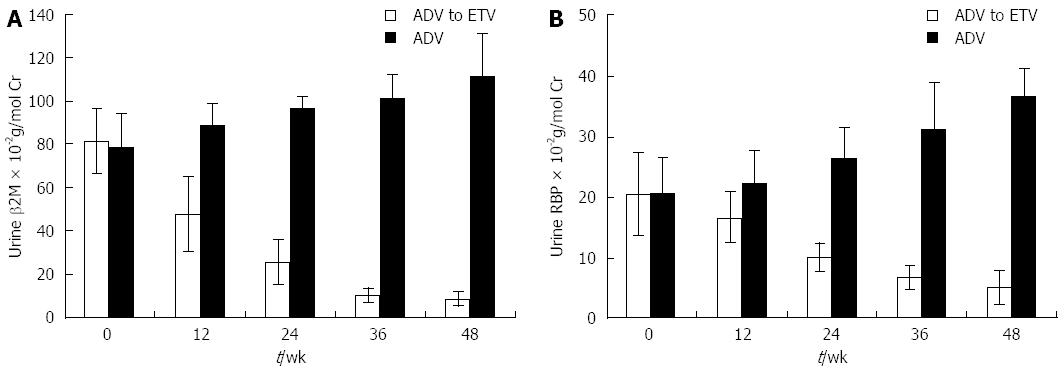
Figure 3 Changes in urine microproteins after modification of adefovir dipivoxil treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients.
A: Mean urine β2-microglobulin (β2-M); B: Mean urine retinol-binding protein (RBP) after switching to entecavir treatment [adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) to entecavir (ETV)] or with continued ADV treatment.
- Citation: Jia HY, Ding F, Chen JY, Lian JS, Zhang YM, Zeng LY, Xiang DR, Yu L, Hu JH, Yu GD, Cai H, Lu YF, Zheng L, Li LJ, Yang YD. Early kidney injury during long-term adefovir dipivoxil therapy for chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(12): 3657-3662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i12/3657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3657