©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2015; 21(10): 3139-3145
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.3139
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.3139
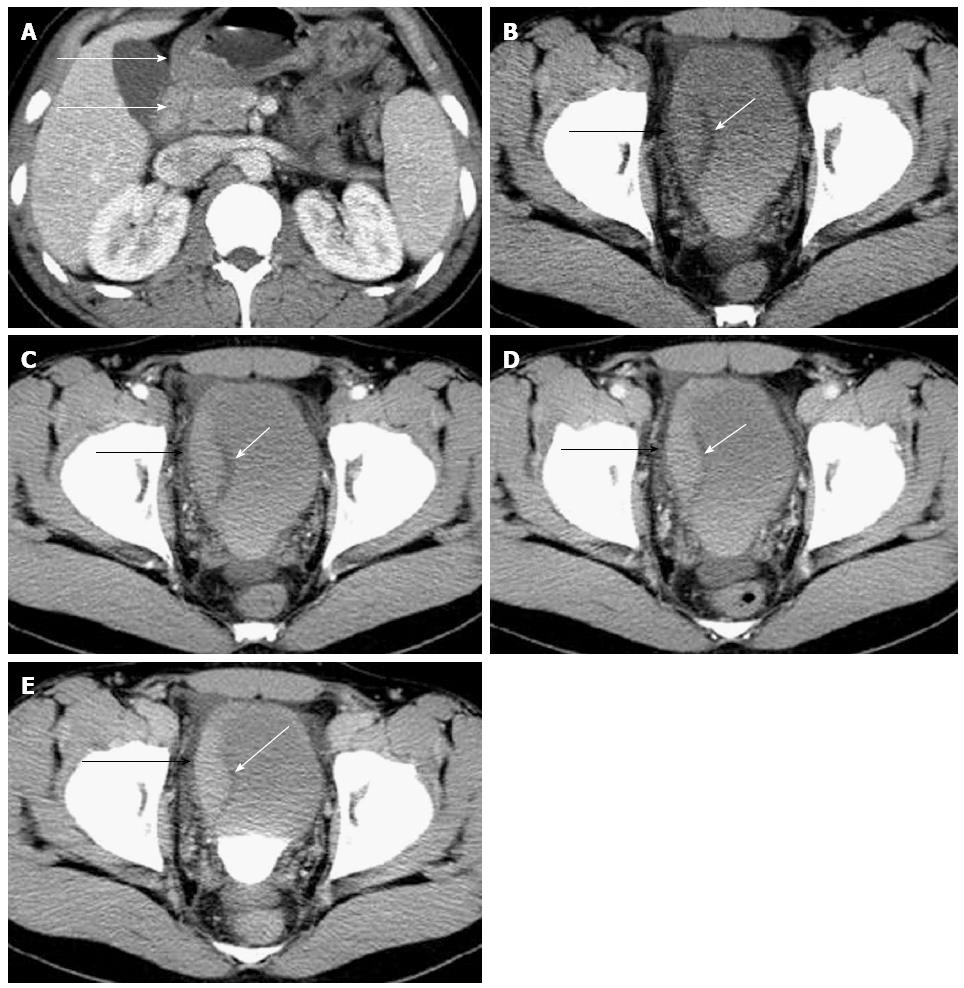
Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography of case 1.
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) showed the wall thickening of gastric antrum (white arrow) and duodenum (white arrow) with inhomogeneous reinforcement (A). Contrast-enhanced CT examination also showed coexistent right lateral bladder wall asymmetrical thickening with progressive enhancement (black arrow) on the plain (B), arterial (C), portal (D), and delayed phase (E) scans, with preservation of the low-density mucosal line (white arrow).
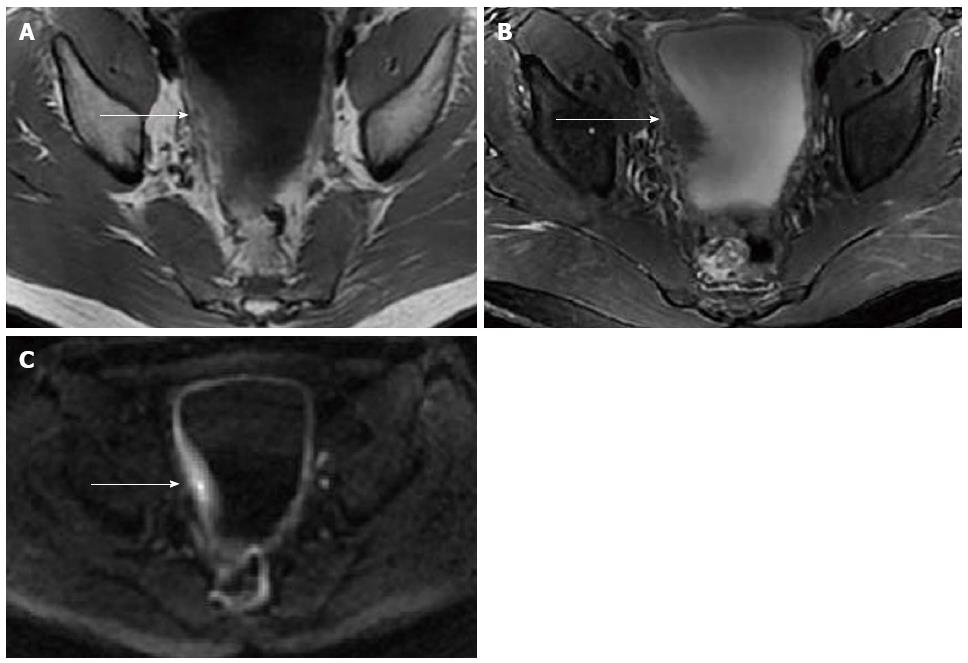
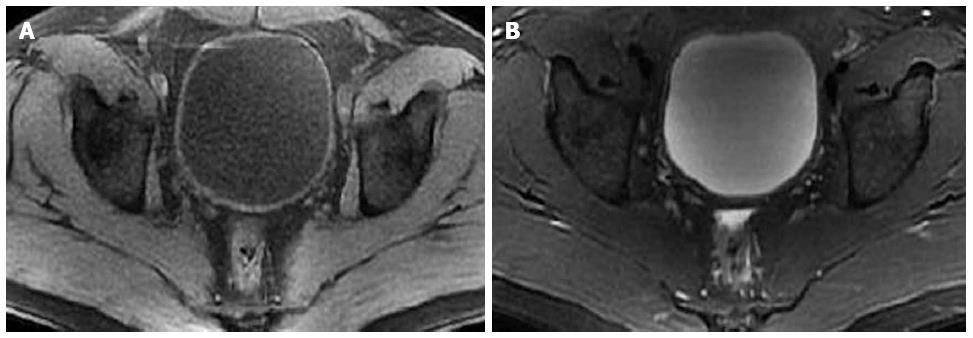
Figure 2 Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging of case 1.
Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging revealed thickening of the bladder wall measuring 18 mm in thickness of the right part of the bladder wall (arrow). The thickened bladder wall exhibited mildly homogeneous hyper-intensity relative to muscle on T1WI (A), hypo-intensity on fat-suppressed T2WI (B), and slight hyper-intensity on DWI (b-value = 1000) (C).
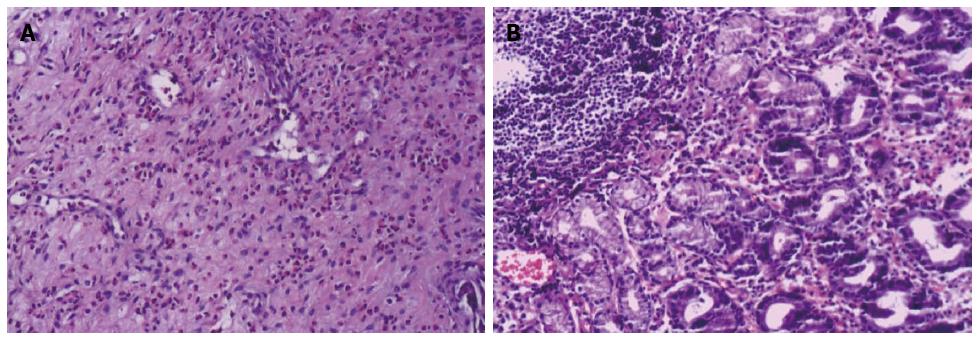
Figure 3 Histopathological examination of case 1.
A: Histopathological examination of the specimen obtained by cystoscopy showed infiltration of the bladder wall mucosa and submucosa by numerous eosinophils (HE staining, × 200); B: Extensive subserosal eosinophilic infiltration was also demonstrated by gastric and duodenal biopsies (HE staining, × 400).
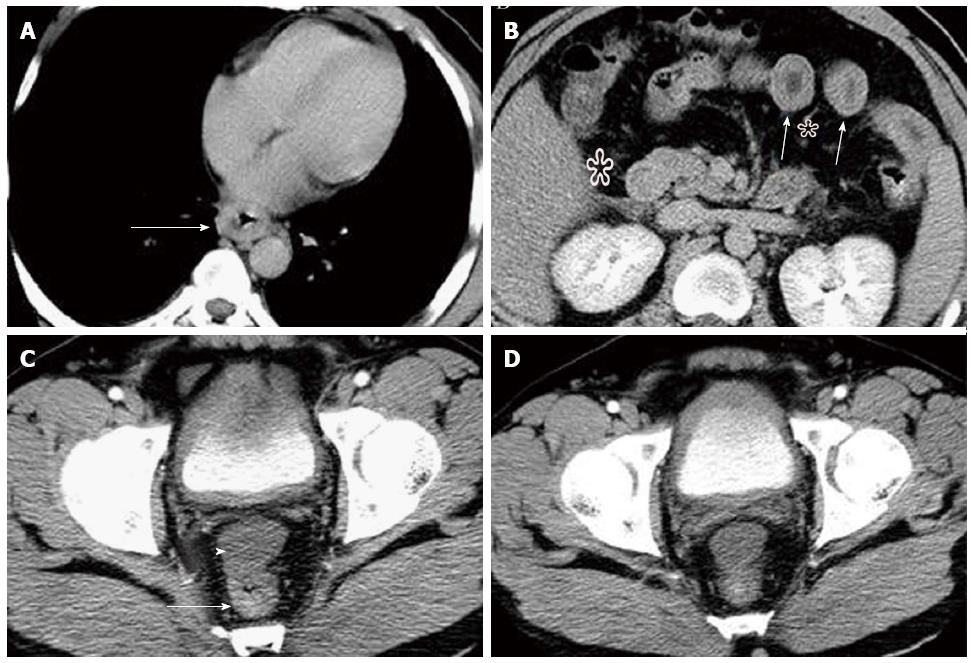
Figure 4 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography of case 2.
A-C: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) showed multifocal segmental gastroenterocolic tract wall thickening (arrow) from the lower esophagus to rectum, with fat surrounding stratification (star), and moderate ascites in the abdominopelvic cavity (arrowhead); D: Contrast-enhanced CT also showed diffuse, marked, nearly circumferential bladder wall thickening with clear margins and preservation of the mucosa.
Figure 5 Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging of case 2.
After hormonal therapy, the pelvic magnetic resonance imaging scan revealed the bladder wall was smooth with no evident thickening on fat-suppressed T1WI (A) and T2WI (B).
- Citation: Han SG, Chen Y, Qian ZH, Yang L, Yu RS, Zhu XL, Li QH, Chen Q. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis associated with eosinophilic cystitis: Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(10): 3139-3145
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i10/3139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.3139