©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2014; 20(8): 2120-2126
Published online Feb 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2120
Published online Feb 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2120
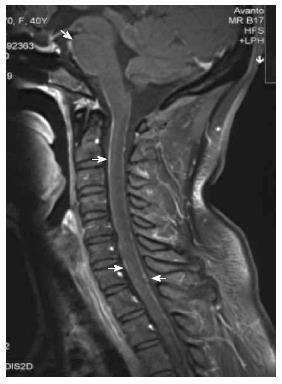
Figure 1 Sagittal magnetic resonance imaging with a T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced sequence.
Arrows show linear and punctiform contrast enhancement along the spine.
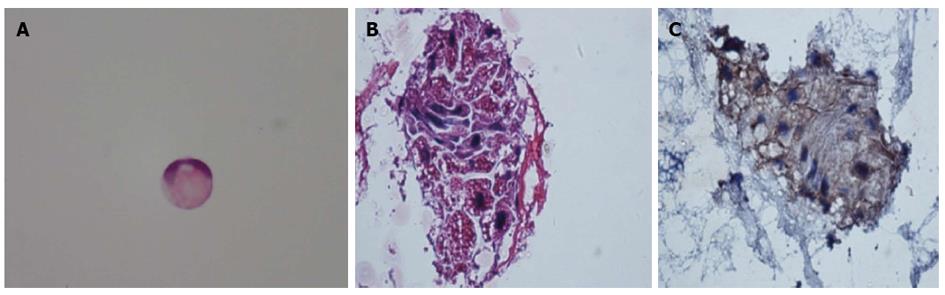
Figure 2 Detection of malignant cells and expression of creatine kinase in the patient’s cerebral spinal fluid specimen.
A: Signet-ring cells (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 20); B: Malignant epithelial cells (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 40); C: Positive expression of creatine kinase in carcinoma cells (immunohistochemistry staining, × 40).
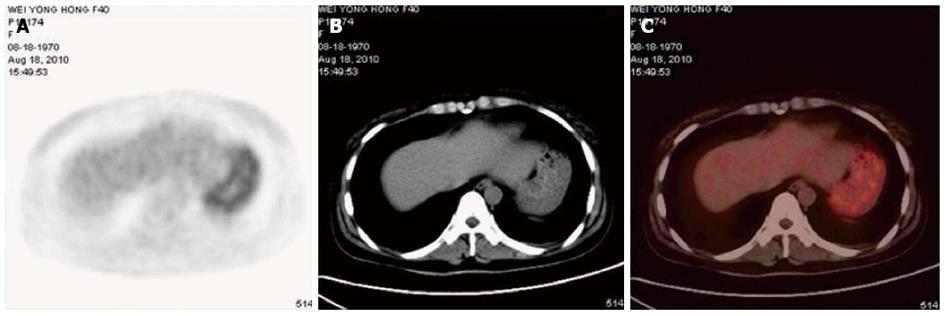
Figure 3 Position emission tomography/computed tomography finding.
An increased 18F-FDG uptake in a diffuse manner, with a maximum standardized uptake value of 4.3 (mean 3.7) in the stomach. A: A cross-section image of position emission tomography (PET) scan; B: A cross-section image of computed tomography (CT) scan; C: PET/CT fusion image.
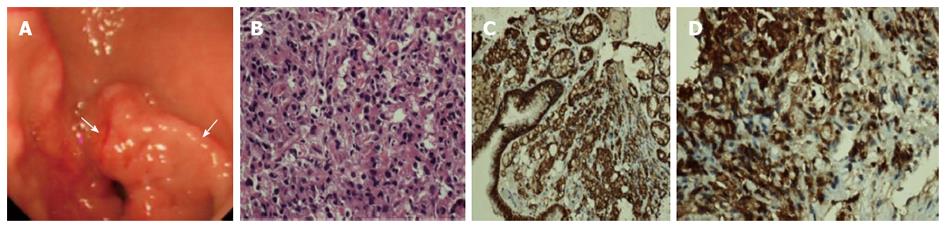
Figure 4 Gastroscopic view and histopathological findings of the tumor.
A: 1/2 circle convex tumor (arrow) in the gastric antrum found by gastroscopy (Bormann class I); B: Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma, diffused type, in biopsy of the gastric antrum sampled during gastroscopy (hematoxylin and eosin; × 40); C: Positive expression of creatine kinase; D: Carcinoembryonic antigen in biopsy specimen of gastric adenocarcinoma (immunohistochemical staining × 40).
- Citation: Guo JW, Zhang XT, Chen XS, Zhang XC, Zheng GJ, Zhang BP, Cai YF. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis as the initial manifestation of gastric adenocarcinoma: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(8): 2120-2126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i8/2120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2120