©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2014; 20(48): 18330-18337
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18330
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18330
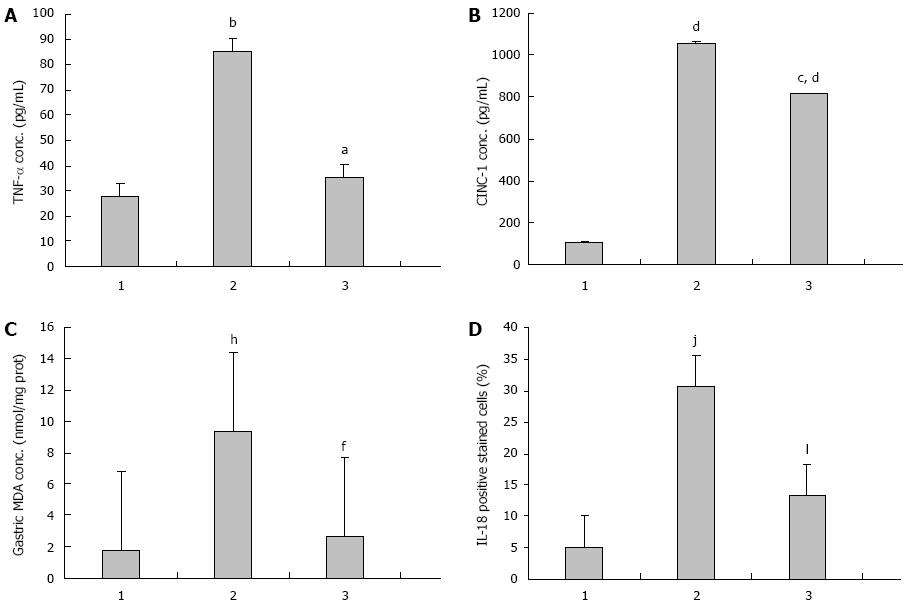
Figure 1 Effects of Aloe vera on serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha, serum cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1, gastric malondialdehyde, interleukin-18 gastric epithelial positive stained cells in rats with indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer.
A: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), aP < 0.05 vs indomethacin (IMN) group, bP < 0.01 vs control group; B: Cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1 (CINC-1), cP < 0.05 vs IMN group, dP < 0.01 vs control group; C: Gastric malondialdehyde (MDA), fP < 0.01 vs IMN group, hP < 0.01 vs control group; D: Interleukin (IL)-18, jP < 0.01 vs IMN group, lP < 0.01 vs control group. 1: Control; 2: IMN; 3: Aloe vera-treated.
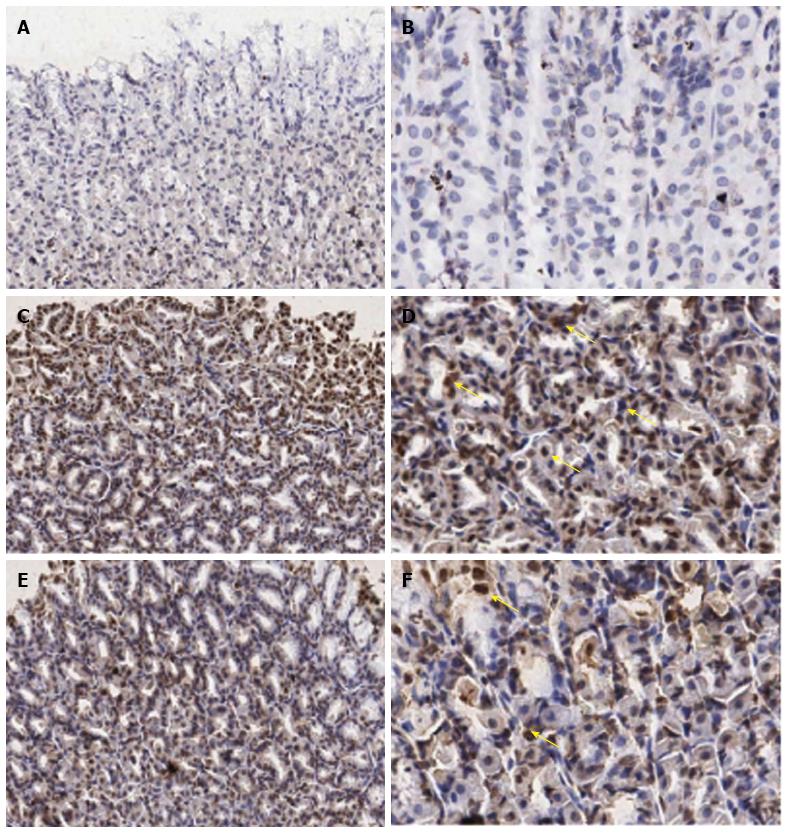
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical staining of interleukin-18 antibody in the representative tissue specimens.
A, B: Control; C, D: Indomethacin; E, F: Aloe vera-treated. Images were obtained at × 20 (A, C, and E) and × 40 (B, D, and F). DAB staining was used to highlight gastric epithelial cells in each section (dark brown stain, yellow arrows).
-
Citation: Werawatganon D, Rakananurak N, Sallapant S, Prueksapanich P, Somanawat K, Klaikeaw N, Rerknimitr R.
Aloe vera attenuated gastric injury on indomethacin-induced gastropathy in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(48): 18330-18337 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i48/18330.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18330