©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2014; 20(44): 16518-16528
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16518
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16518
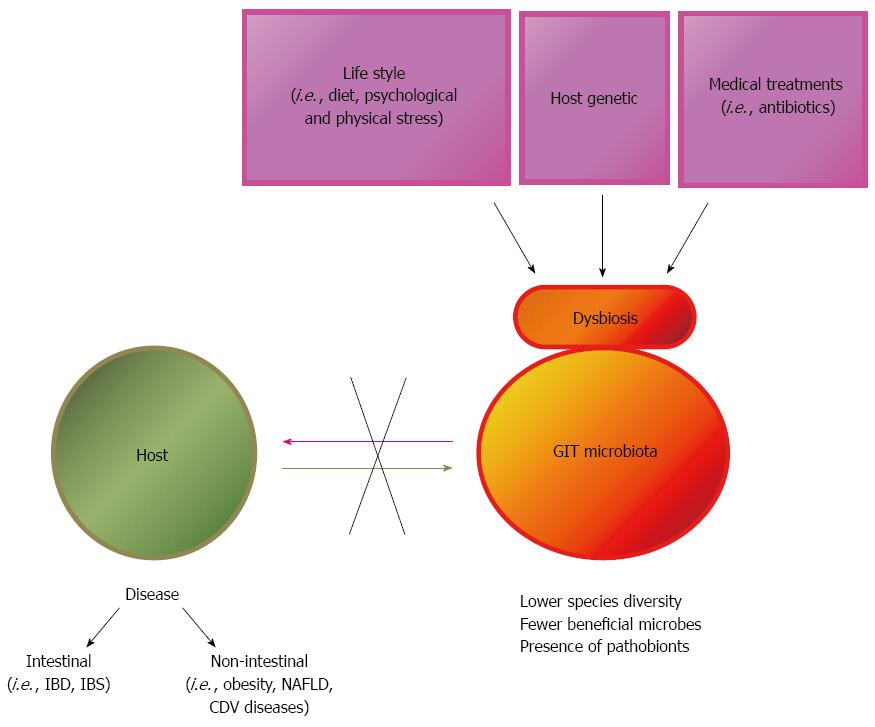
Figure 1 Causes of gastrointestinal tract microbiota dysbiosis and effect on host health.
GIT: Gastrointestinal tract; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; IBD: Inflammatory bowel diseases; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; CDV: Canine distemper virus.
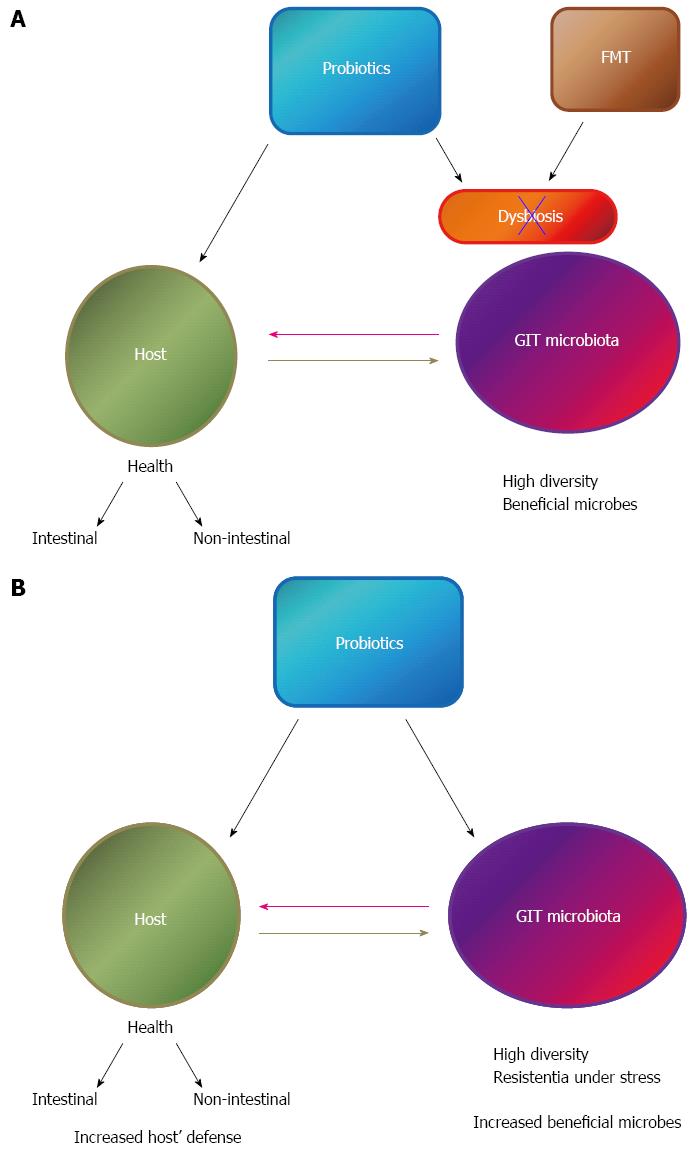
Figure 2 Effect of probiotic administration on gastrointestinal tract dysbiosis (A) or healthy individuals (B) and the interaction of the gastrointestinal tract microbiota with the host.
GIT: Gastrointestinal tract; FMT: Fecal microbial transplantation.
- Citation: LeBlanc AM, LeBlanc JG. Effect of probiotic administration on the intestinal microbiota, current knowledge and potential applications. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(44): 16518-16528
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i44/16518.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16518