©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2014; 20(41): 15253-15261
Published online Nov 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15253
Published online Nov 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15253
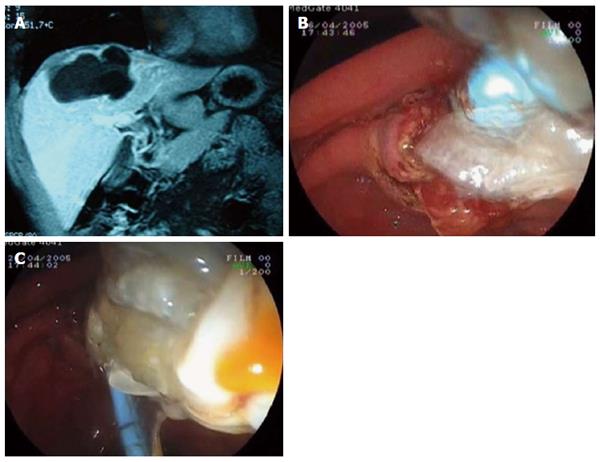
Figure 1 Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
A: Magnetic resonance image of a hydatid cyst with major rupture; B: Emptying of hydatid membranes with endoscopic sphincterotomy and a biliary occlusion balloon; C: Extraction of hydatid materials.
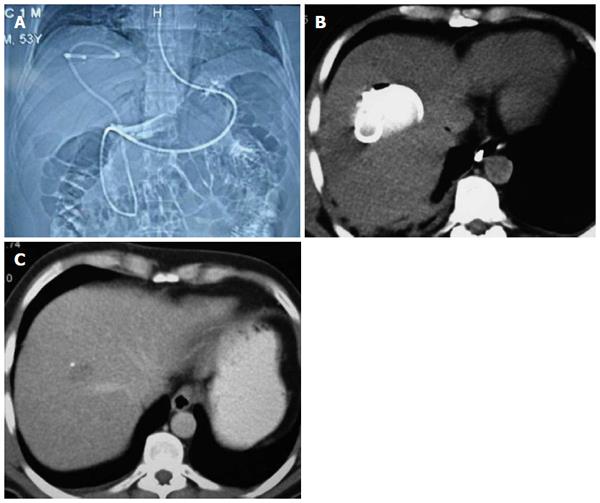
Figure 2 Nasocystic-biliary drainage procedure.
A: Topographic images of hydatid cyst with major rupture by nasocystic drainage; B: Drainage catheter within the cystic cavity; C: Computed tomography of the same patient taken at the three-month follow-up.
- Citation: Dolay K, Akbulut S. Role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in the management of hepatic hydatid disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(41): 15253-15261
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i41/15253.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15253