©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2014; 20(38): 14063-14067
Published online Oct 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.14063
Published online Oct 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.14063
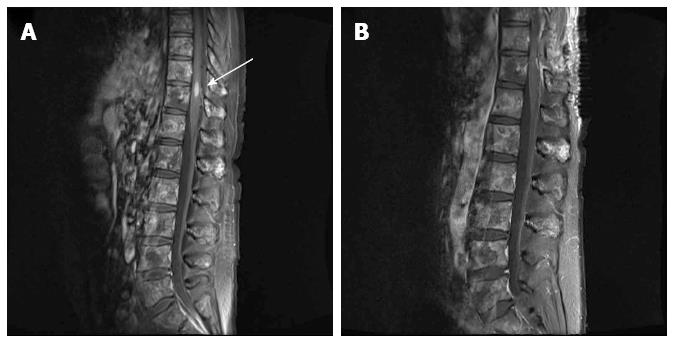
Figure 1 T1-weighted magnetic resonance image of the spine.
A: The 5.9 mm × 5.3 mm × 14.8 mm metastatic tumor was observed in the T10/11 level (arrow). Diffuse vertebral metastases were also observed in almost the entire spine; B: The intramedullary tumor was removed by surgical treatment.
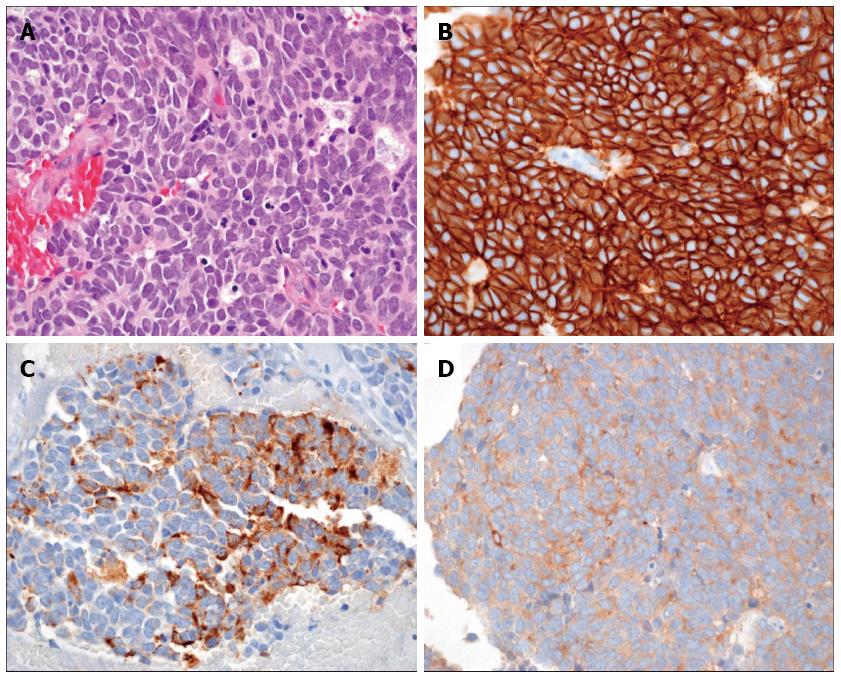
Figure 2 Pathologic findings of surgically removed tissue.
A: High-power view of the tumor shows medium to large sized tumor cells with scanty cytoplasm, prominent nucleoli, and coarse “salt and pepper” chromatin. The tumor cells exhibited intense mitosis greater than 10/10 HPF (HE × 400); B-D: Immunohistochemically, tumor cells showed a diffuse and strong membranous positivity for CD56 (B), as well as cytoplasmic positivity for chromogranin (C) and synaptophysin (D) (immunohistochemical staining × 400).
- Citation: Kim JH, Hyun CL, Han SH. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis from pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(38): 14063-14067
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i38/14063.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.14063