Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2014; 20(37): 13620-13624
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13620
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13620
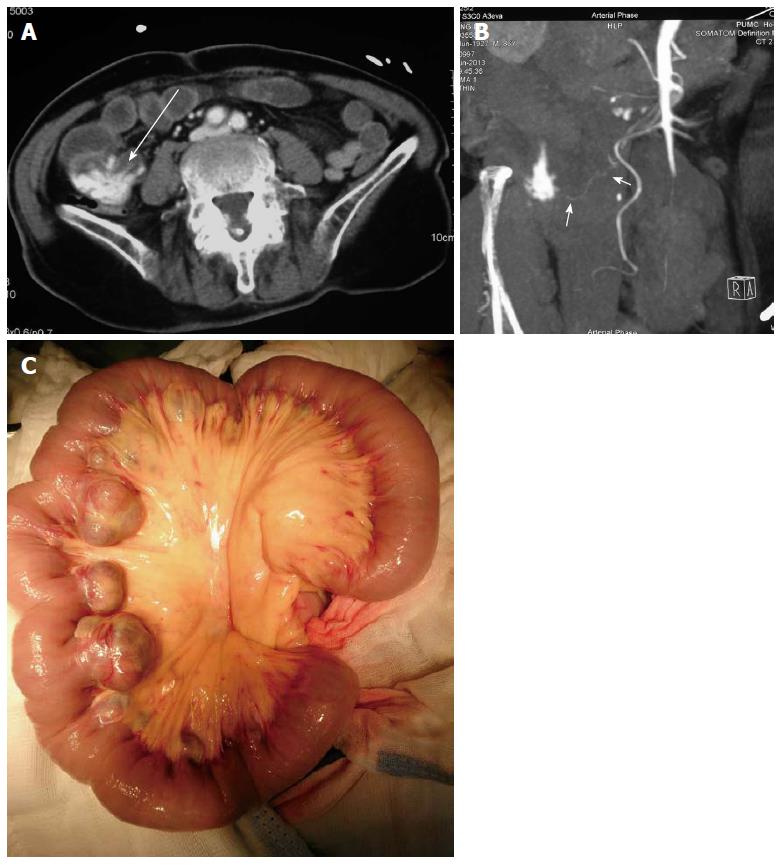
Figure 1 Imaging of case 1.
A: Computed tomography (CT) angiography revealed contrast extravasation in a jejunal diverticulum (arrow); B: CT angiography showed the blood supply for the jejunal diverticulum source was from a branch of the superior mesenteric artery (arrow); C: Multiple diverticula in a 30 cm segment of the jejunum.
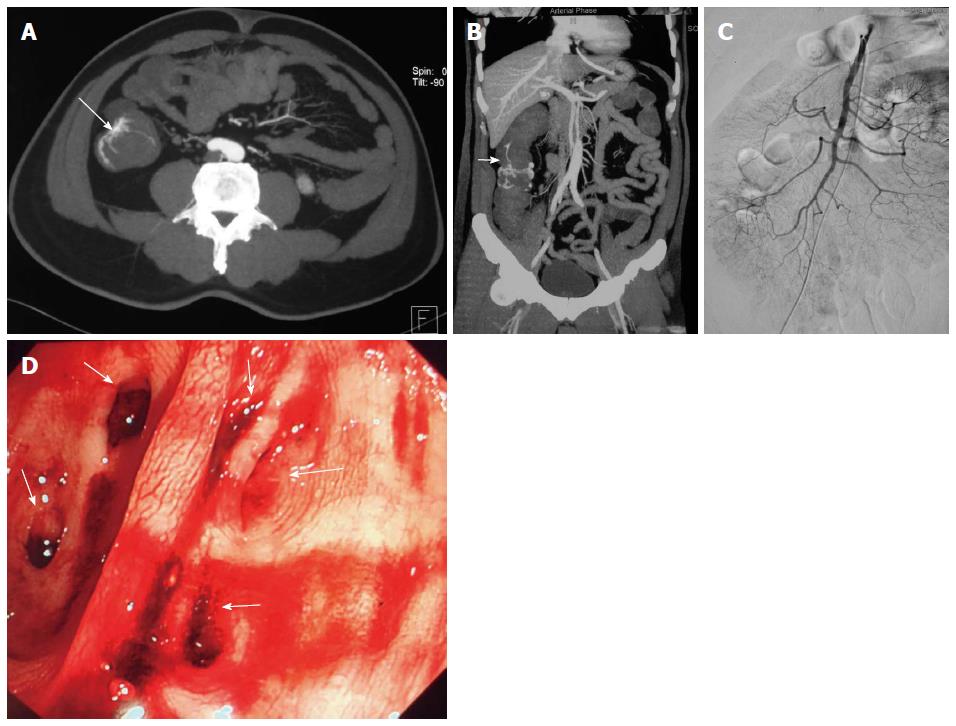
Figure 2 Imaging of case 2.
A: Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed contrast extravasation in the ascending colon (arrow); B: CT angiography revealed bleeding from the intramural branches of the marginal artery supplying the ascending colon (arrow); C: Angiography failed to reveal the precise location of the bleeding; D: Emergent colonoscopy revealed multiple diverticula in the middle part of the ascending colon without definite bleeding vessels identified (arrow).
- Citation: Xu XQ, Hong T, Li BL, Liu W. Active gastrointestinal diverticulum bleeding diagnosed by computed tomography angiography. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(37): 13620-13624
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i37/13620.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13620