©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2014; 20(37): 13573-13581
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13573
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13573
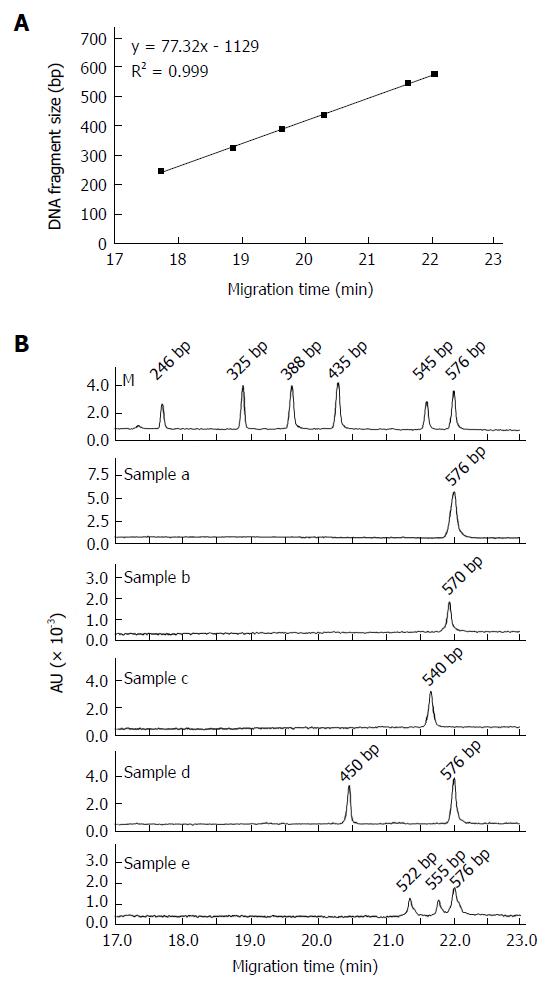
Figure 1 Establishment of a rapid method based on capillary gel electrophoresis to detect HBV pre-S deletions.
A: A DNA marker was applied to construct the standard curve. CGE was used to detect the size of DNA fragments with a linear range of 246 bp to 576 bp and a regression coefficient (R2) of 0.999; B: Representative CGE profiles of the pre-S DNA amplification products from the serum samples of 5 HBV-infected subjects. Sample a: wild-type HBV; Sample b: 6 bp deletion mutant alone; Sample c: 36 bp deletion mutant alone; Sample d: mixture of wild-type virus and a 126 bp deletion mutant; Sample e: mixture of wild-type virus and 21 bp and 54 bp deletion mutants. M: Maker (246 bp, 325 bp, 388 bp, 435 bp, 545 bp, and 576 bp); AU: Absorbance units.
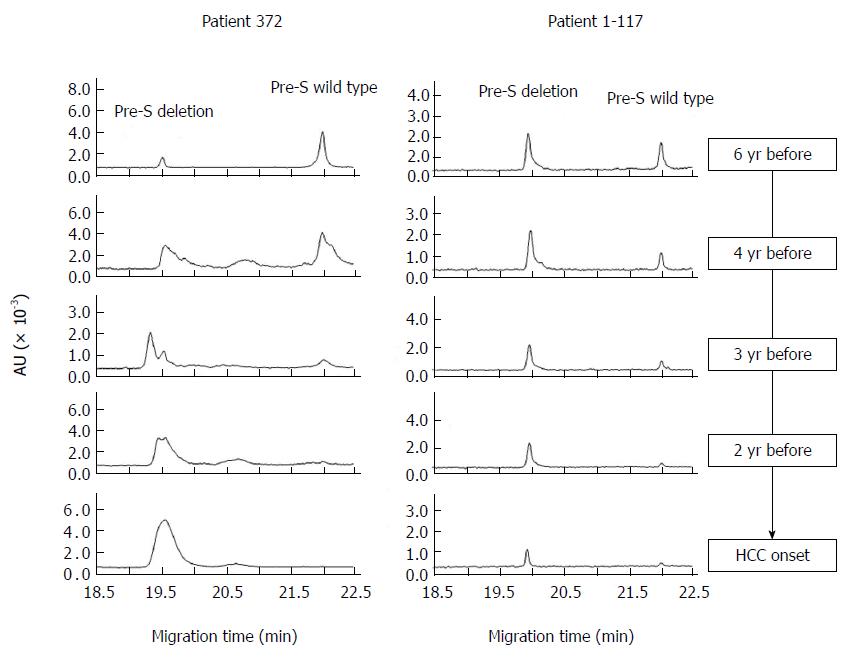
Figure 2 Longitudinal observation of hepatocellular carcinoma-related pre-S deletions during the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
Figure 3 Longitudinal observation of hepatocellular carcinoma-related pre-S deletions in Qidong hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
Black: Pre-S deletion; Grey: Wild type; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Zhao ZM, Jin Y, Gan Y, Zhu Y, Chen TY, Wang JB, Sun Y, Cao ZG, Qian GS, Tu H. Novel approach to identifying the hepatitis B virus pre-S deletions associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(37): 13573-13581
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i37/13573.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13573