©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2014; 20(35): 12501-12508
Published online Sep 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12501
Published online Sep 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12501
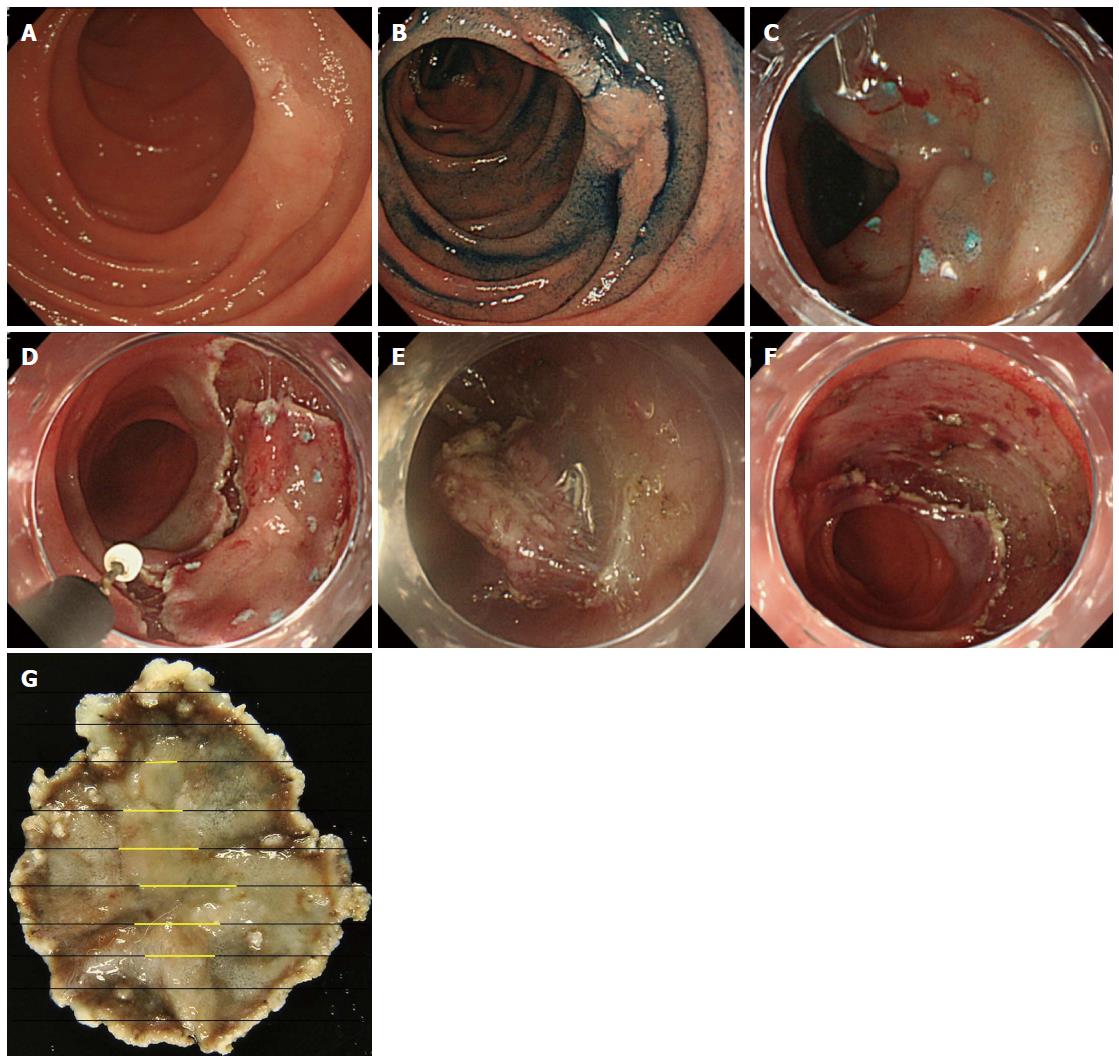
Figure 1 Images in endoscopic submucosal dissection.
A: A superficial elevated type (IIa) lesion is observed in the second portion of the duodenum; B: Chromoendoscopy with indigocarmine was used to clarify the border of the tumor; C: After marking with argon plasma coagulation, submucosal injection was performed; D: Circumferential cutting was performed using an insulated-tipped knife [ITknife nano (KD-612); Olympus, Tokyo, Japan]; E: Submucosal dissection was performed; F: The lesion was successfully removed en bloc without complications; G: Histopathological analysis revealed a mucosal adenocarcinoma of 16 mm in diameter (yellow lines).
- Citation: Kakushima N, Kanemoto H, Tanaka M, Takizawa K, Ono H. Treatment for superficial non-ampullary duodenal epithelial tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(35): 12501-12508
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i35/12501.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12501