©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2014; 20(34): 12330-12340
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12330
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12330
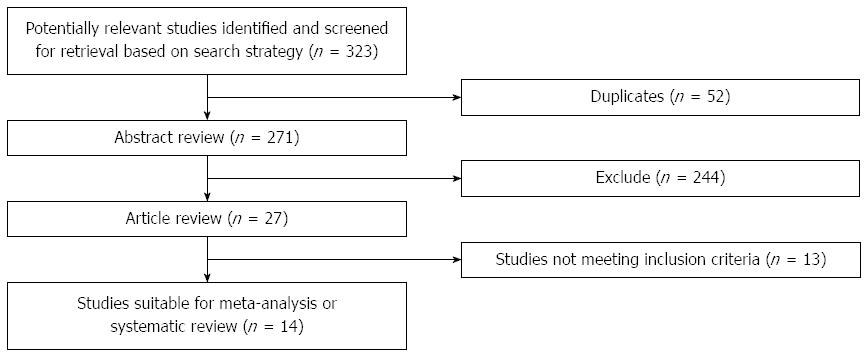
Figure 1 Selection of studies.
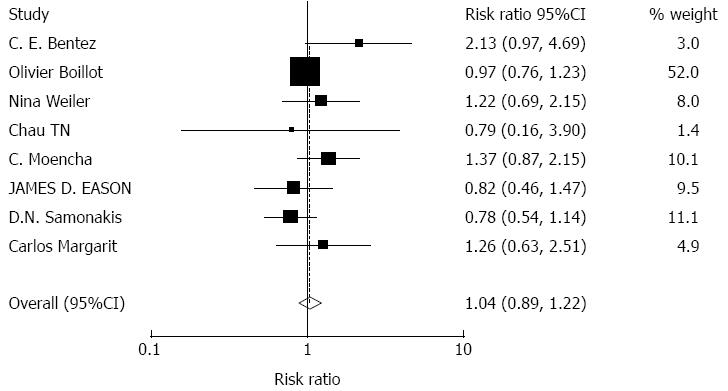
Figure 2 Meta-analysis of randomized cohort studies comparing the effect of tacrolimus monotherapy on graft acute rejection.
Heterogeneity was tested and was found to be not statistically significant (χ2 = 8.58, P = 0.284).
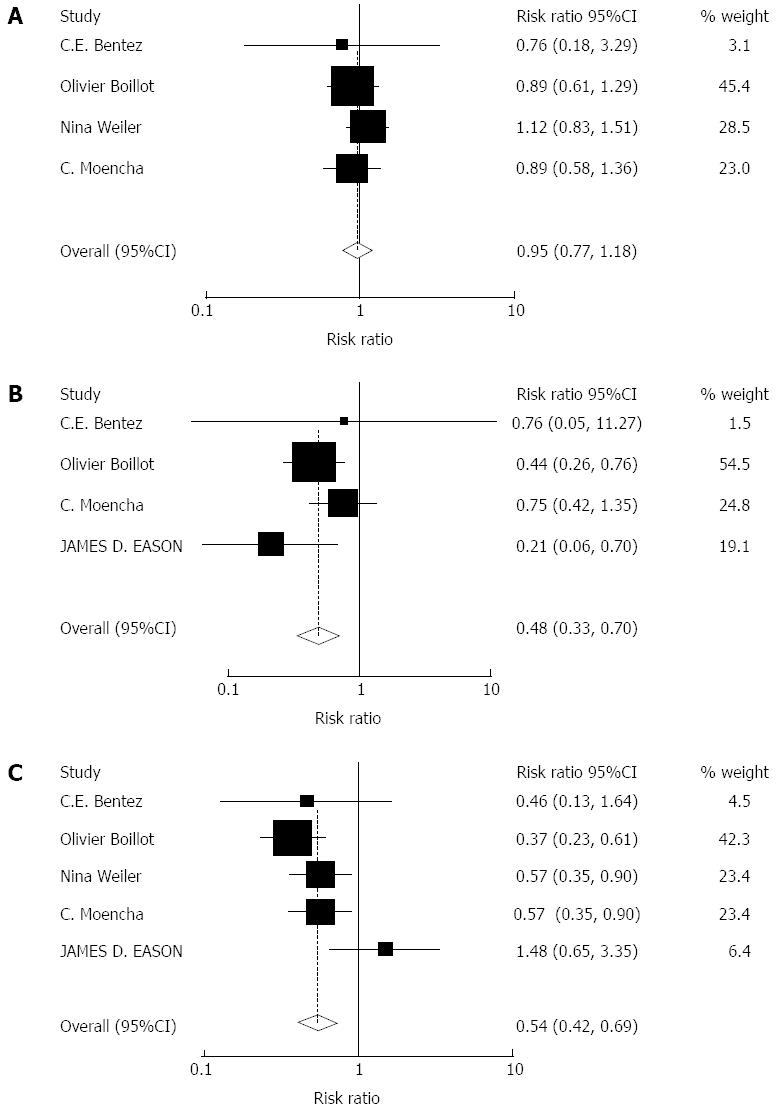
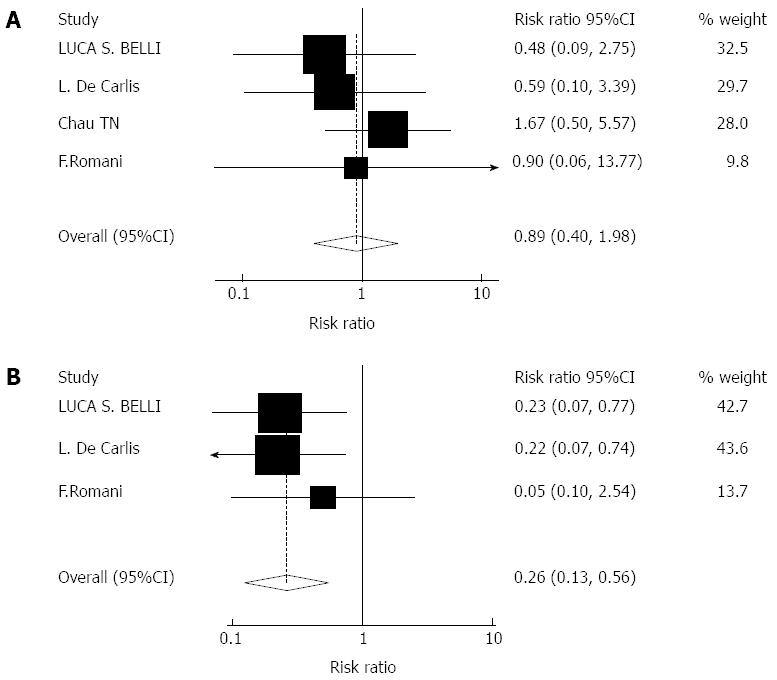
Figure 3 Meta-analysis of andomized cohort studies comparing the effect of tacrolimus monotherapy.
A: Drug-related hypertension. Heterogeneity was tested and was found to be not statistically significant (χ2 = 4.21, P = 0.240); B: Cytomegalovirus infection. Heterogeneity was tested and was found to be not statistically significant (χ2 = 1.44, P = 0.696). C: Drug-related diabetes mellitus. Heterogeneity was tested and was found to be not statistically significant (χ2 = 8.10, P = 0.088).
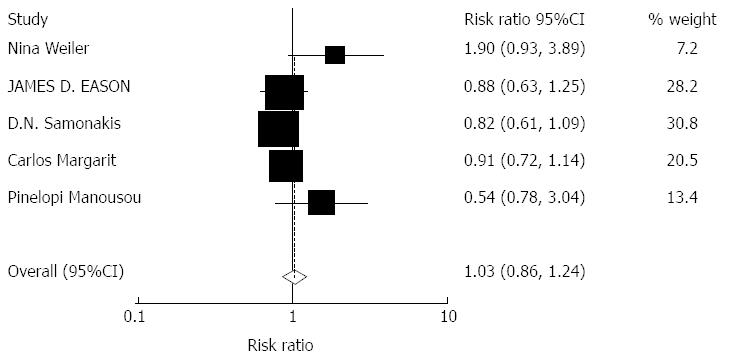
Figure 4 Meta-analysis of andomized cohort studies comparing the effect of tacrolimus monotherapy on hepatitis C virus recurrence.
Heterogeneity was tested and was not statistically significant (χ2 = 8.63, P = 0.071).
Figure 5 Meta-analysis of randomized cohort studies comparing the effect of cyclosporine monotherapy.
A: Graft rejection. Heterogeneity was tested and was found to be not statistically significant (χ2 = 1.72, P = 0.632); B: Drug-related diabetes mellitus. Heterogeneity was tested and was found to be not statistically significant (χ2 = 1.72, P = 0.697).
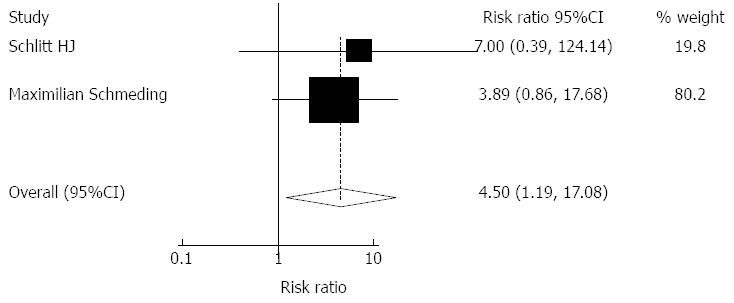
Figure 6 Meta-analysis of randomized cohort studies comparing the effect of mycophenolate mofetil monotherapy on acute rejection.
Heterogeneity was tested and was found to be not statistically significant (χ2 = 0.13, P = 0.77).
- Citation: Lan X, Liu MG, Chen HX, Liu HM, Zeng W, Wei D, Chen P. Efficacy of immunosuppression monotherapy after liver transplantation: A meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(34): 12330-12340
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i34/12330.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12330