Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 9976-9989
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9976
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9976
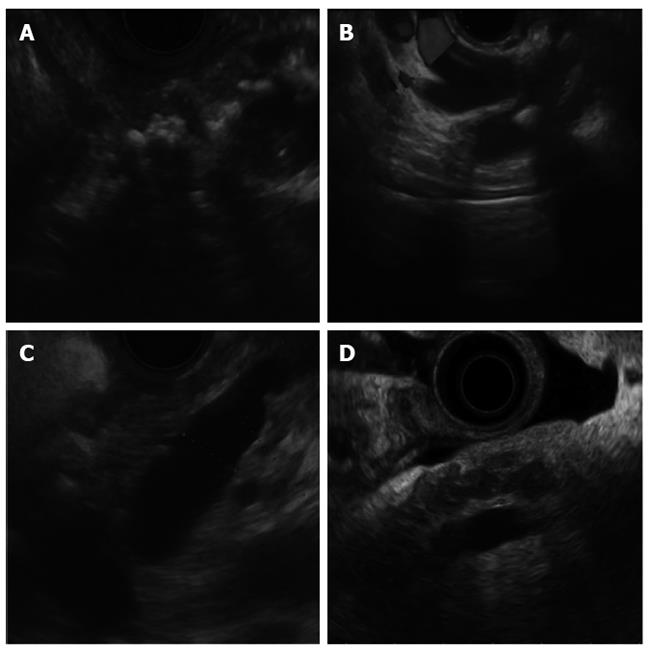
Figure 1 Endoscopic ultrasound features of chronic pancreatitis.
A: Calcification; B: Pancreatic duct (PD) stone; C: PD dilation; D: Lobularity.
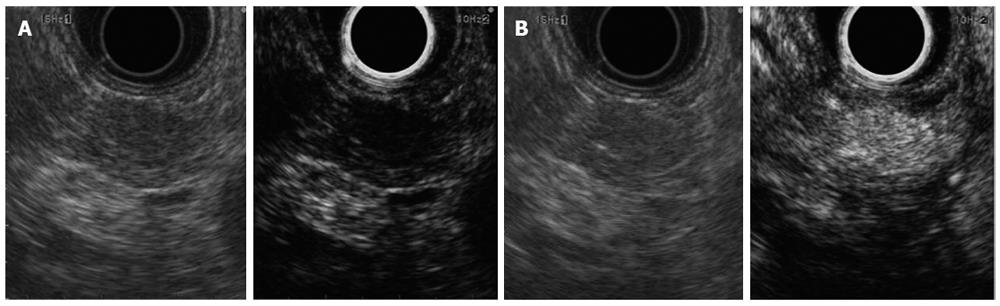
Figure 2 Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor.
A: Appearing as a hypoechoic lesion prior to the administration of contrast; B: Demonstrating hyperenhancement after contrast injection with Sonovue.
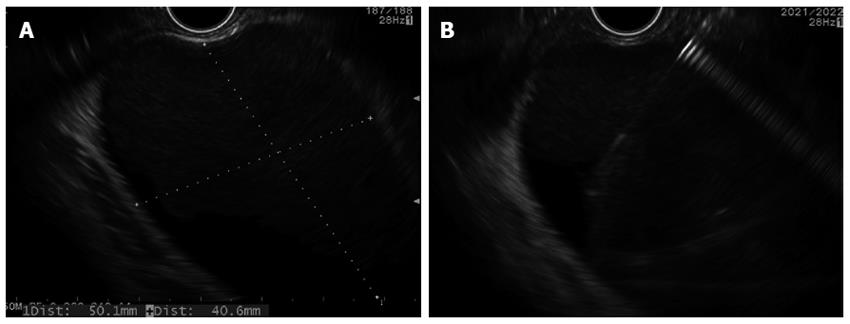
Figure 3 Pancreatic fluid collection.
A: Internal debris; B: Fine needle aspiration using 19 guage needle.
Figure 4 Direct endoscopic necrosectomy.
A: Balloon dilation of fistula tract to 20 mm; B: Necrotic debris apparent within the walled-off necrosis.
- Citation: Teshima CW, Sandha GS. Endoscopic ultrasound in the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 9976-9989
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/9976.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9976