©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2014; 20(18): 5389-5395
Published online May 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5389
Published online May 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5389
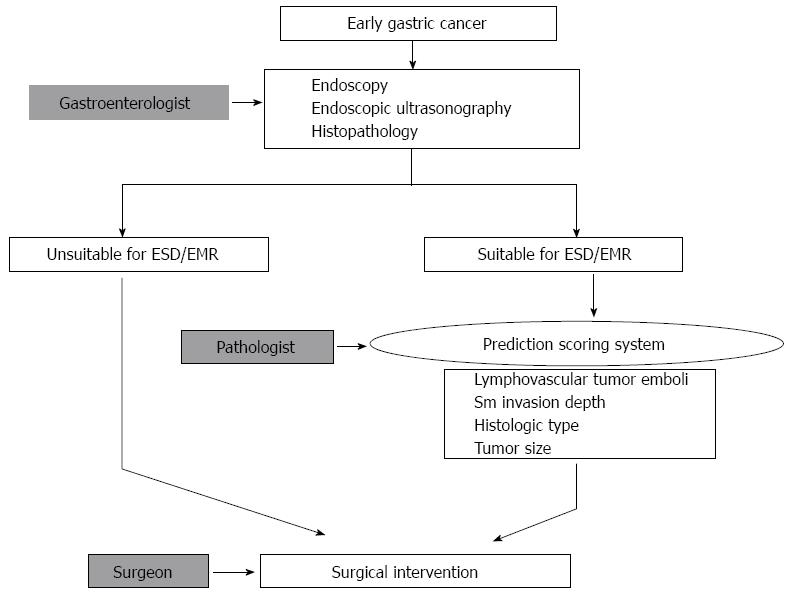
Figure 1 Workflow for deciding on a therapeutic method for cases of early gastric cancer.
The first step is the selection of suitable patients for endoscopic resection, based on endoscopic and histopathologic findings. After endoscopic resection, additional surgical intervention could be determined on the basis of a comprehensive review of the EMR/ESD specimen, including lymphovascular tumor emboli, tumor size, histologic type, and depth of invasion. ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; EMR: Endoscopic mucosal resection; Sm: Submucosal.
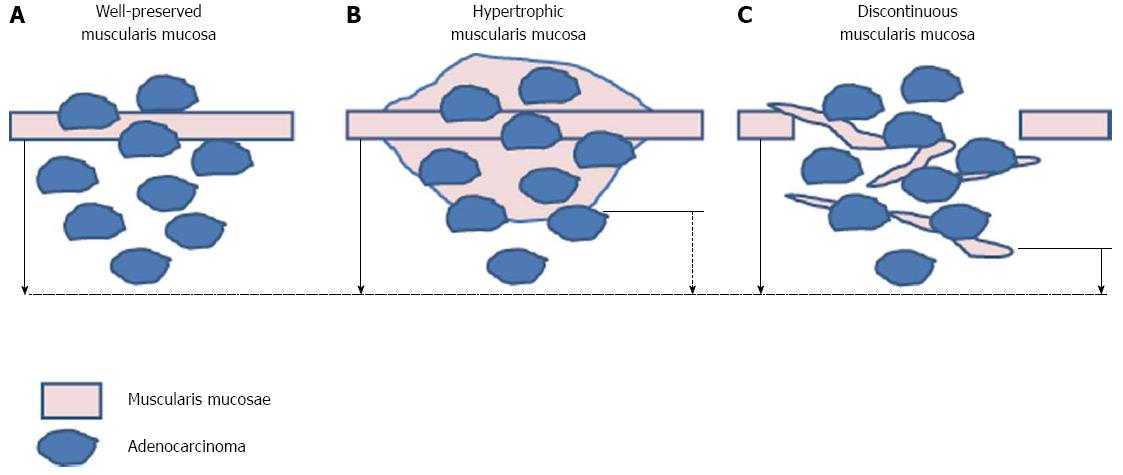
Figure 2 Recommendation of measurement of the submucosal depth of invasion.
Measuring from the bottom of muscularis mucosa in patients with normal muscularis mucosa (A) and from imaginary line of the muscularis mucosae in patients with irregular muscularis mucosa [hypertrophic (B), discontinuoud (C)] (solid arrow) is recommended rather than measuring from bottom of muscularis mucosae (broken arrow).
- Citation: Shin N, Jeon TY, Kim GH, Park DY. Unveiling lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(18): 5389-5395
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i18/5389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5389