©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4626-4635
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4626
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4626
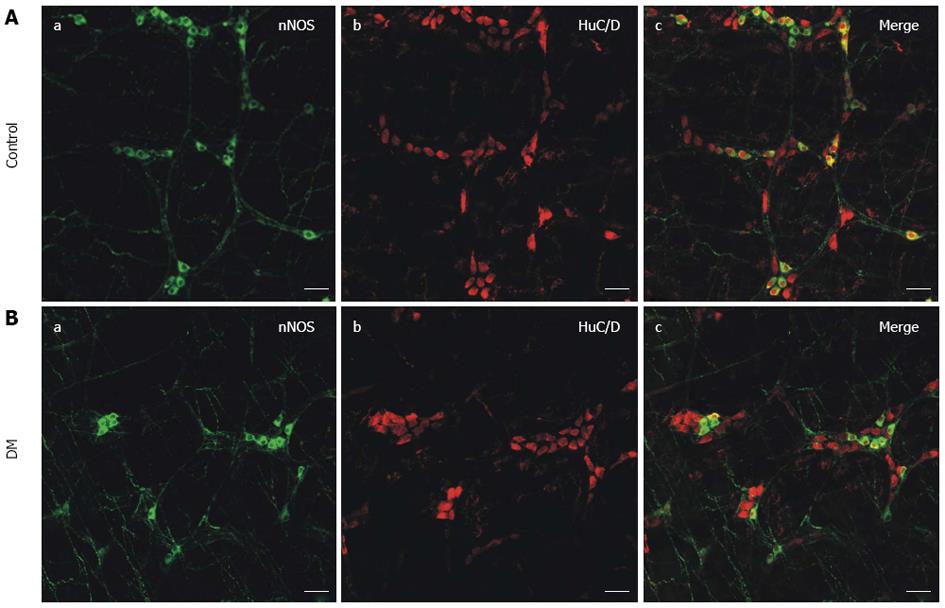
Figure 1 Whole mount immunostaining of nitric oxide synthase and HuC/D in gastric fundus smooth muscle tissue.
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) staining is used to show NOS neurons, while HuC/D staining is used to label all enteric neurons in the control and diabetic mice (DM) groups. Bar = 50 μm.
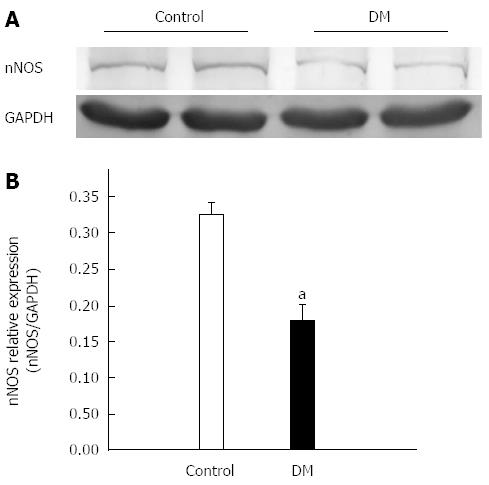
Figure 2 Expression of nitric oxide synthase in gastric fundus smooth muscles tissues.
A: Representative bands of nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) protein expression in control and diabetic mice (DM) groups; B: The nNOS expression level in gastric fundus smooth muscle tissue was significantly decreased in the DM group (n = 7, aP < 0.05 vs control).
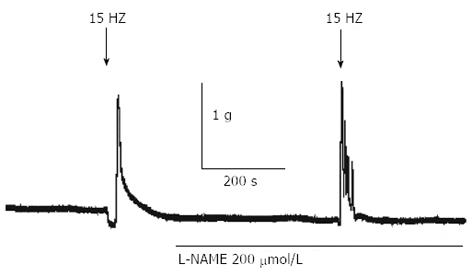
Figure 3 Electric field stimulation-induced relaxation and contraction in gastric fundus smooth muscle of normal mice.
A typical raw trace showing that electric field stimulation EFS (15 Hz)-induced relaxation was completely blocked by L-NAME (n = 5).
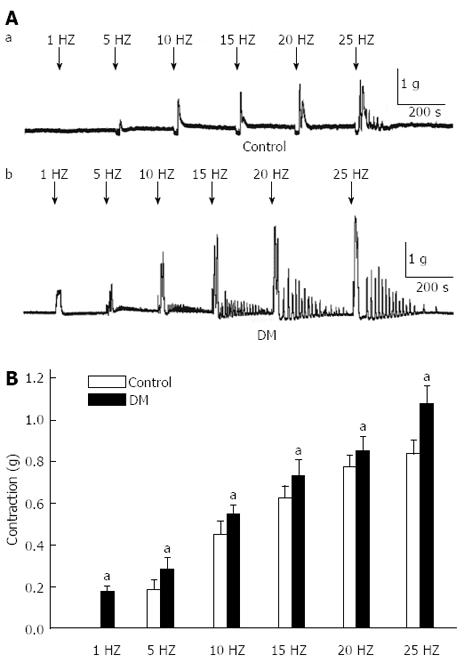
Figure 4 Electric field stimulation-induced contraction of gastric fundus smooth muscle was recorded in control and diabetic mice.
A: Typical raw traces of fundus smooth contractions induced by electric field stimulation (EFS) at different frequencies in control and diabetic groups; B: The amplitude of contraction from two groups and the smooth muscle contraction was more sensitive to EFS in the diabetic mice (DM) group (n = 8, aP < 0.05 vs control).
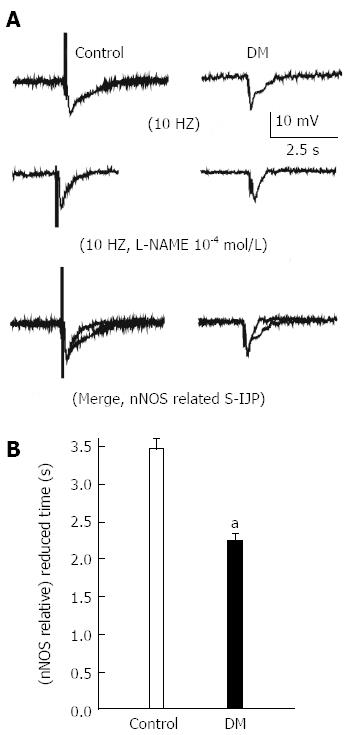
Figure 5 Slow inhibitory junction potentials of gastric fundus smooth muscle were recorded in normal and diabetic mice.
A: Representative raw traces of slow inhibitory junction potentials (sIJP) elicited by electric field stimulation in control and diabetic mice (DM) groups; B: Summarized data showing that the NO-mediated duration of sIJP was significantly decreased in the DM group (n = 9, aP < 0.05 vs control).
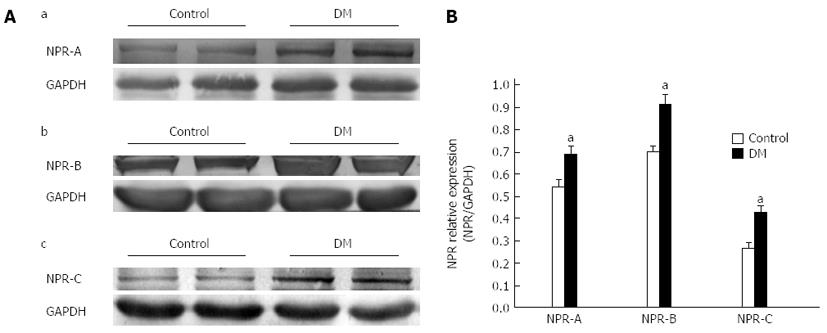
Figure 6 Natriuretic peptide receptors expression in gastric fundus smooth muscle tissues in control and diabetic mice.
A: Representative bands of natriuretic peptide receptors (NPRs) protein expression in control and diabetic mice (DM) groups; B: Summarized data showing that the levels of NPRs expression in the DM group were significantly decreased (n = 8, aP < 0.05 vs control).
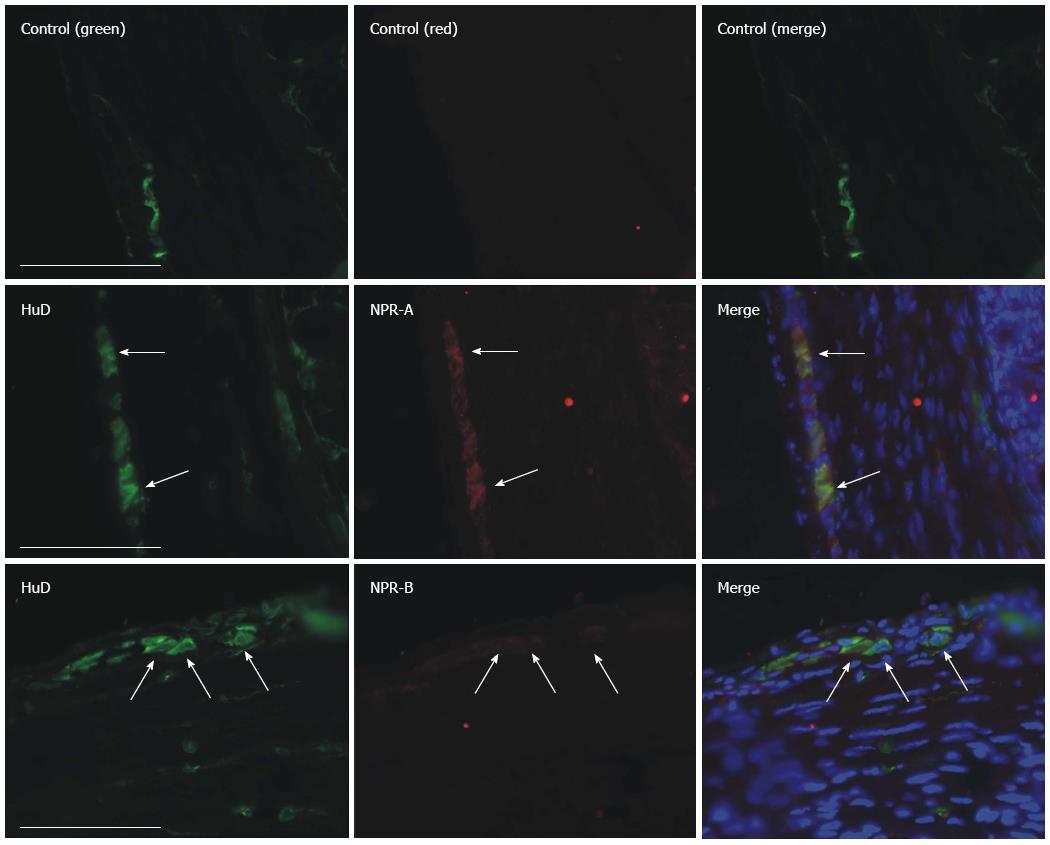
Figure 7 Natriuretic peptide receptors-A and B immunofluorescence staining in gastric fundus smooth muscle tissue of normal mice.
Myenteric neurons were labeled by an anti-HuD antibody and natriuretic peptide receptors (NPRs) were labeled by an anti-NPR-A, B antibody. Bar = 100 μm.
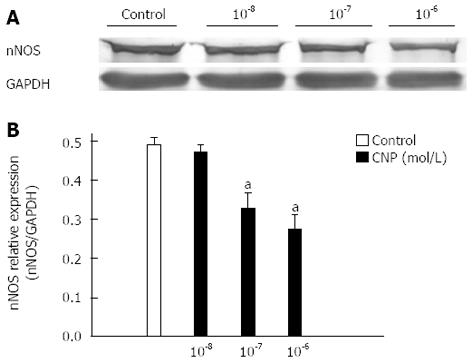
Figure 8 Effects of C-type natriuretic peptide on the nitric oxide synthase expression in gastric fundus smooth muscle tissues of normal mice.
A: Representative bands of nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) protein expression in control and C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) groups; B: Summarized data shows that CNP significantly inhibited nNOS expression in a dose-dependent manner in cultured gastric fundus smooth muscle tissue (n = 7, aP < 0.05 vs control).
- Citation: Lu HL, Huang X, Wu YS, Zhang CM, Meng XM, Liu DH, Kim YC, Xu WX. Gastric nNOS reduction accompanied by natriuretic peptides signaling pathway upregulation in diabetic mice. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4626-4635
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4626.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4626