Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2014; 20(14): 4076-4084
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4076
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4076
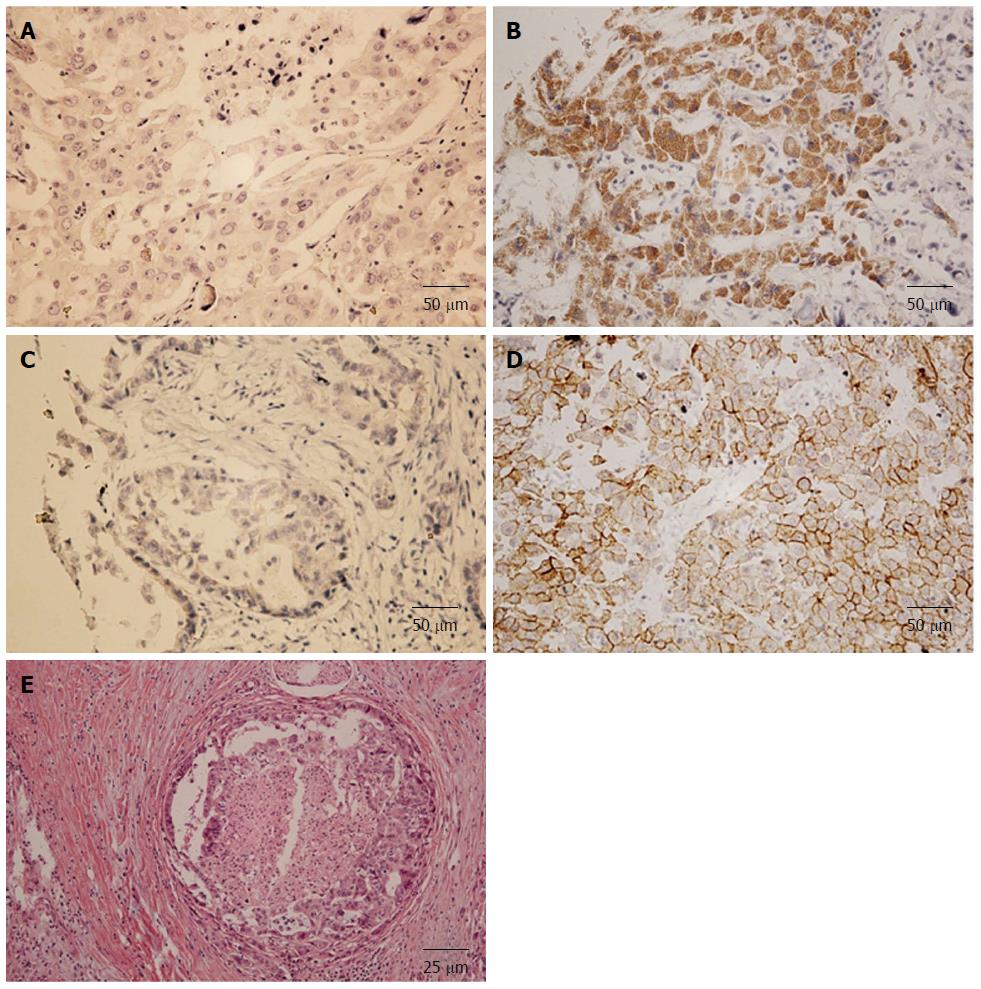
Figure 1 Nerve growth factor and tropomyosin-receptor-kinase expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Representative figures showing lower NGF expression (A), higher NGF expression (B), lower TrkA expression (C), higher TrkA expression (D), intraneural invasion by CCA cells (E). NGF: Nerve growth factor; CCA: Cholangiocarcinoma; TrkA: Tropomyosin-receptor-kinase.
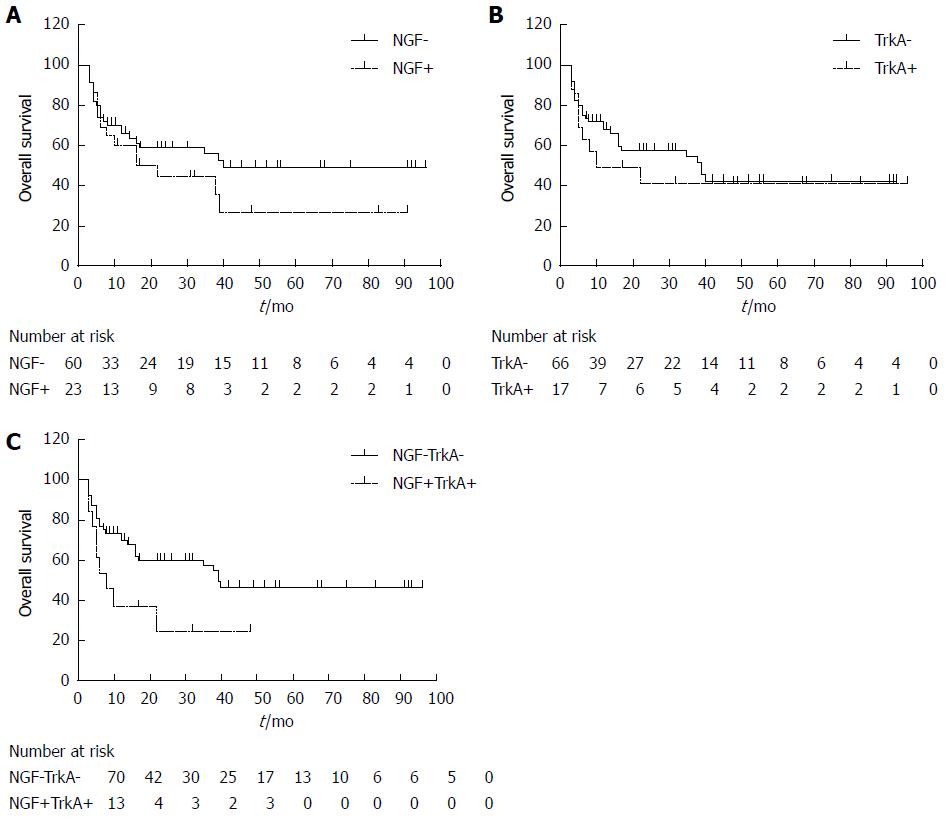
Figure 2 Correlations between overall survival rate and detected proteins.
Expressions of NGF (A) and TrkA (B) have no significant association with prognosis of IHCC (P = 0.201 and 0.483, respectively). The group with NGF and TrkA double higher expression had poorer prognosis than the non-NGF/TrkA double higher group (C) (including both lower expression, only NGF higher and only TrkA higher, P = 0.003). NGF: Nerve growth factor; IHCC: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; TrkA: Tropomyosin-receptor-kinase.
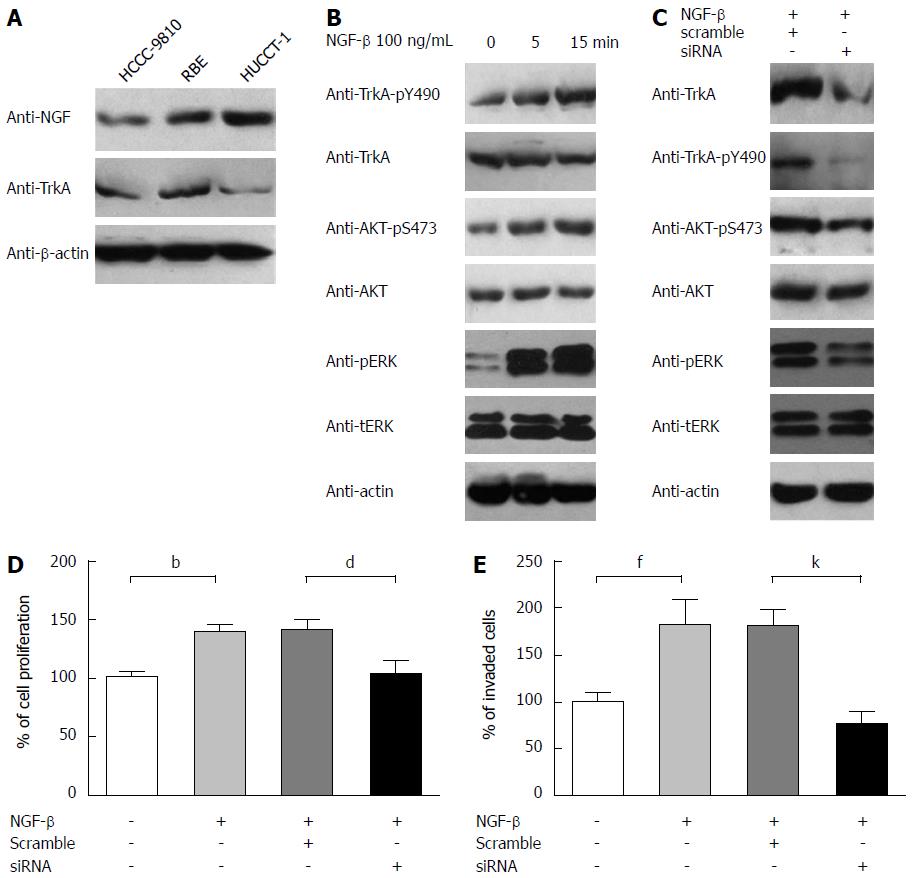
Figure 3 Nerve growth factor-tropomyosin-receptor-kinase signaling pathway can promote cholangiocarcinoma proliferation and invasion.
A: NGF and TrkA expression in IHCC cell line HCCC9810, RBE and HUCCT-1; B: Phosphorylation level of TrkA, AKT and ERK notably elevated with NGF stimulation for different time (0, 5 or 15 min); C: After TrkA knocked down, phosphorylation level of TrkA, AKT and ERK decreases significantly; D: Proliferation of RBE was tested by MTT 48 h after siRNA transfection. NGF-β can promote RBE proliferation and TrkA knockdown reduces this tendency. Data were from three independent experiments and statistical analysis was performed by student t test, bP < 0.01 between control and HCCC9810; dP < 0.01 vs RBE and HUCCT-1; E: Invasive activity of RBE cells. RBE invasion is accelerated by NGF-β stimulation and reversed by TrkA knockdown. Cell numbers were counted under 200 × magnification. Data were from at least three independent experiments and statistical significance was measured by student t test, fP < 0.01 between control and HCCC9810; kP < 0.01 vs RBE and HUCCT-1. NGF: Nerve growth factor; IHCC: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; TrkA: Tropomyosin-receptor-kinase.
- Citation: Yang XQ, Xu YF, Guo S, Liu Y, Ning SL, Lu XF, Yang H, Chen YX. Clinical significance of nerve growth factor and tropomyosin-receptor-kinase signaling pathway in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(14): 4076-4084
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i14/4076.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4076