©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3680-3692
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3680
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3680
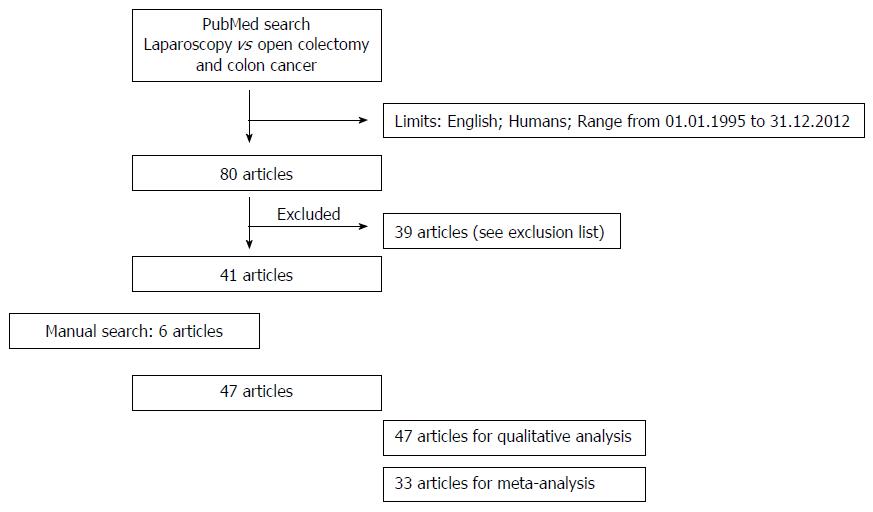
Figure 1 Study design.
Study design according to the PRISMA statement for systematic reviews and meta-analysis.
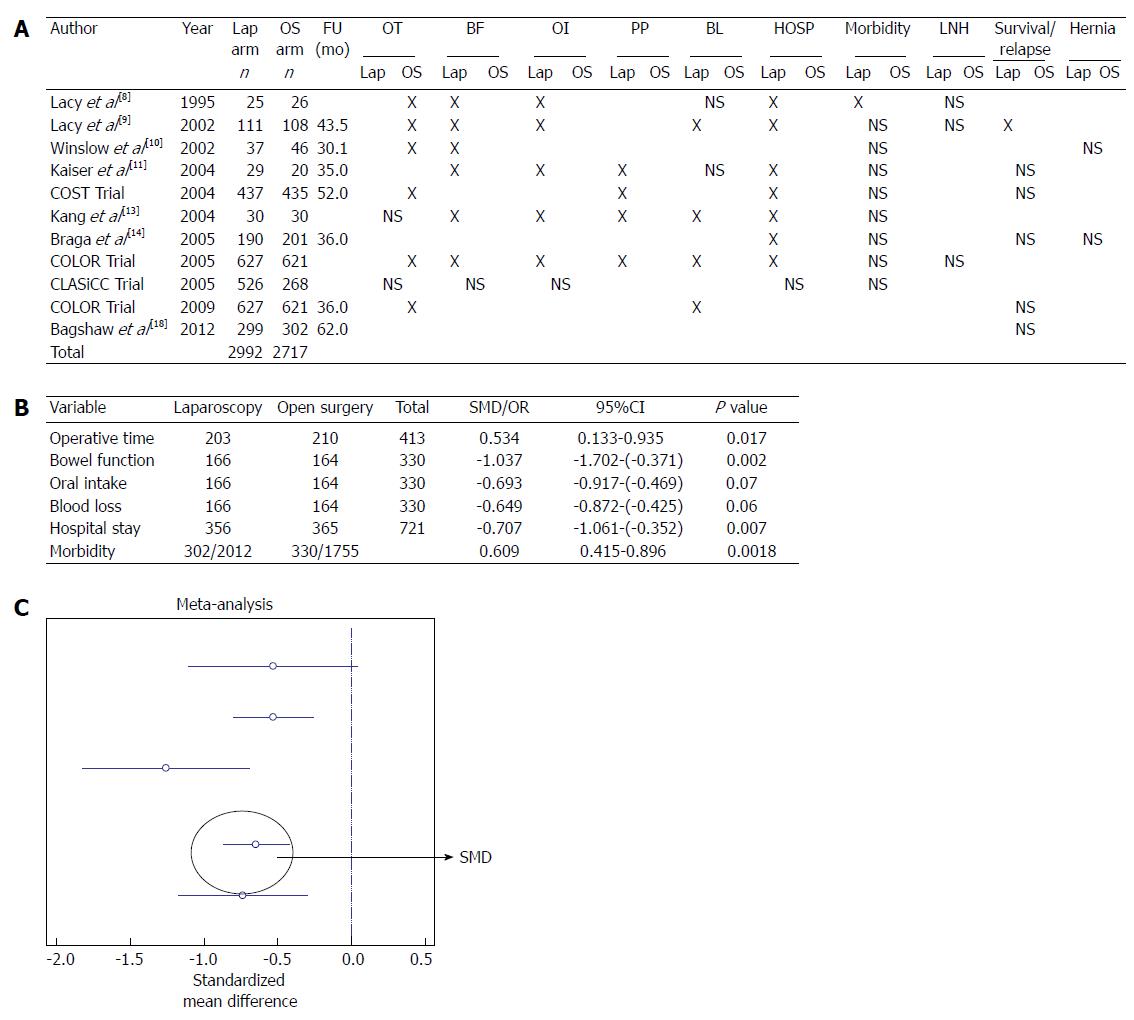
Figure 2 Randomized studies.
A: Randomized trails comparing laparoscopy and open surgery. X in the table refers to a statistical association provided in the studies; B: Meta-analysis of the out-come measures; C: Forest plot graph regarding studies investigating blood loss. Lap arm: Laparoscopy arm; OS arm: Open surgery arm; FU: Mean follow-up; OT: Operative time; BF: Bowel function; OI: Oral intake; PP: Post-operative Pain; BL: Blood loss; HOSP: Hospital stay; LNH: Lymph node harvest; NS: Not significant.
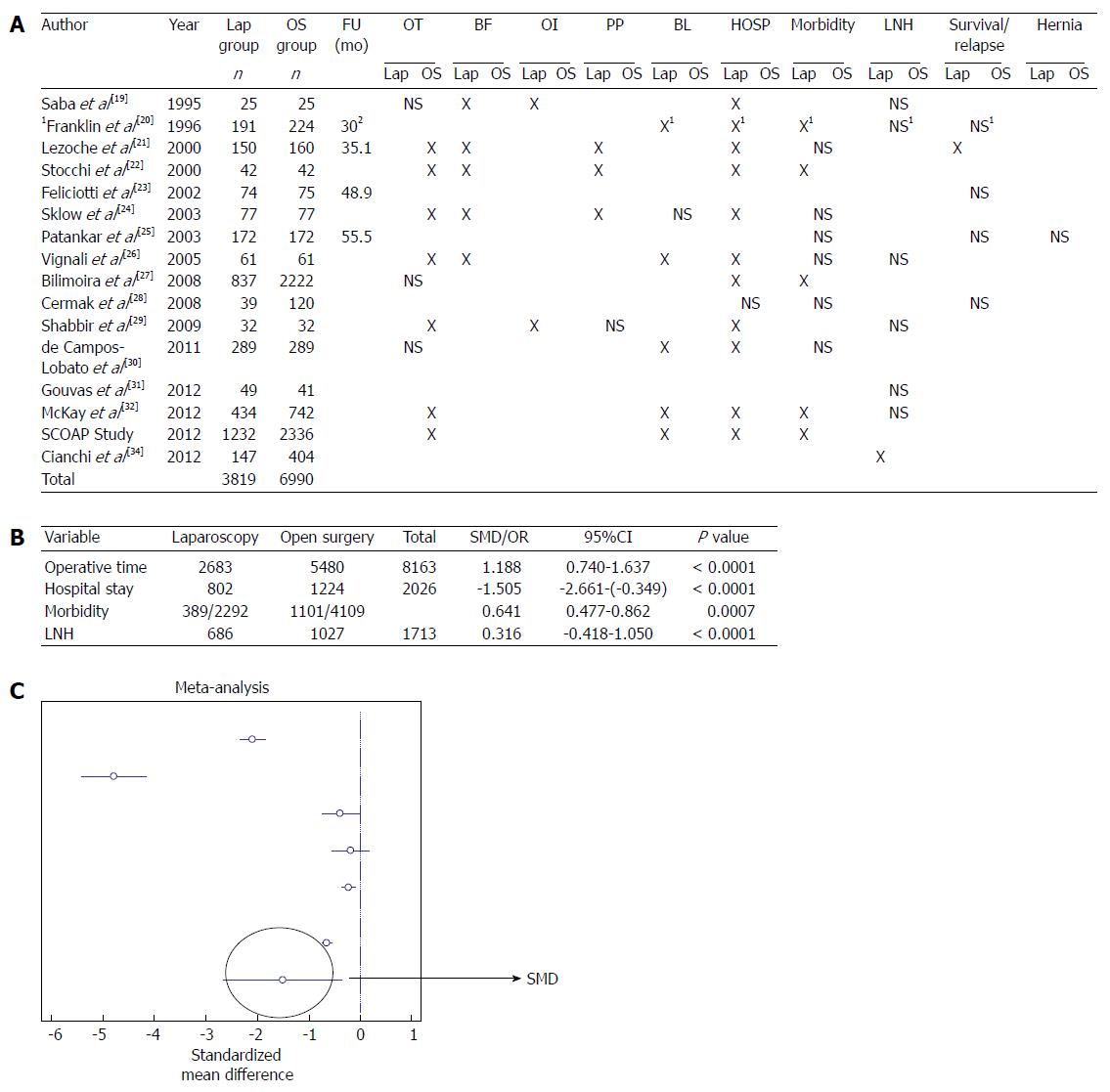
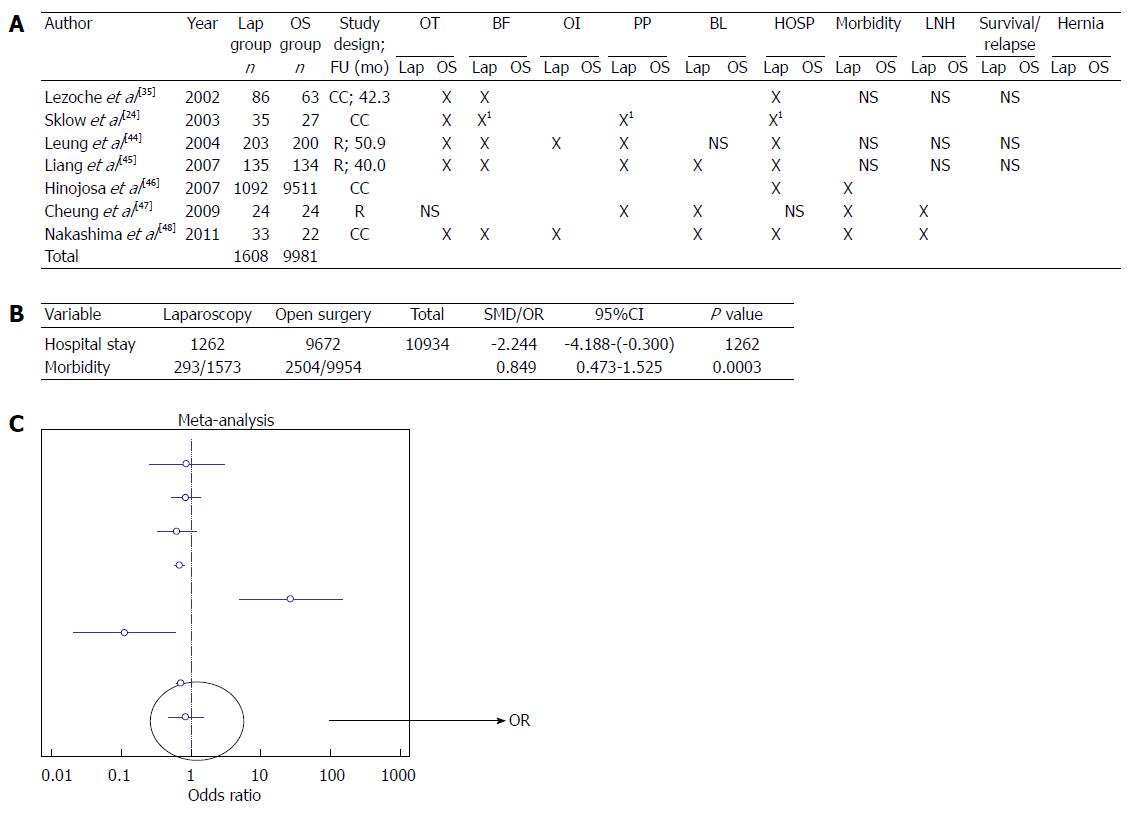
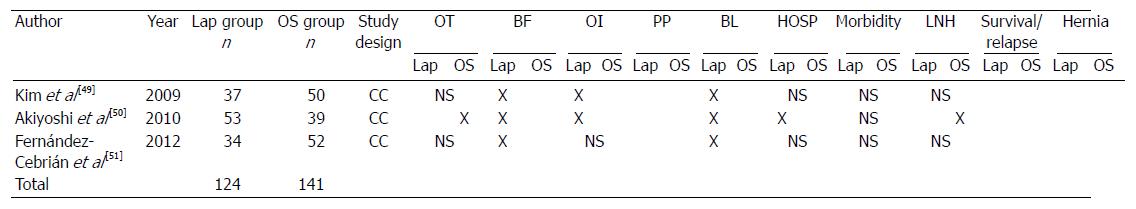
Figure 3 Non-randomized studies.
A: Case-control studies comparing laparoscopy and open surgery. X in the table refers to a statistical association provided in the studies; B: Meta-analysis of the out-come measures; C: Forest plot graph regarding studies investigating hospital stay. 1Statistic analysis not performed; 2Significant difference of follow-up according to the stage of the disease. Lap: Laparoscopy; OS: Open surgery; FU: Mean follow-up; OT: Operative time; BF: Bowel function; OI: Oral intake; PP: Post-operative Pain; BL: Blood loss; HOSP: Hospital stay; LNH: Lymph node harvest; NS: Not significant.
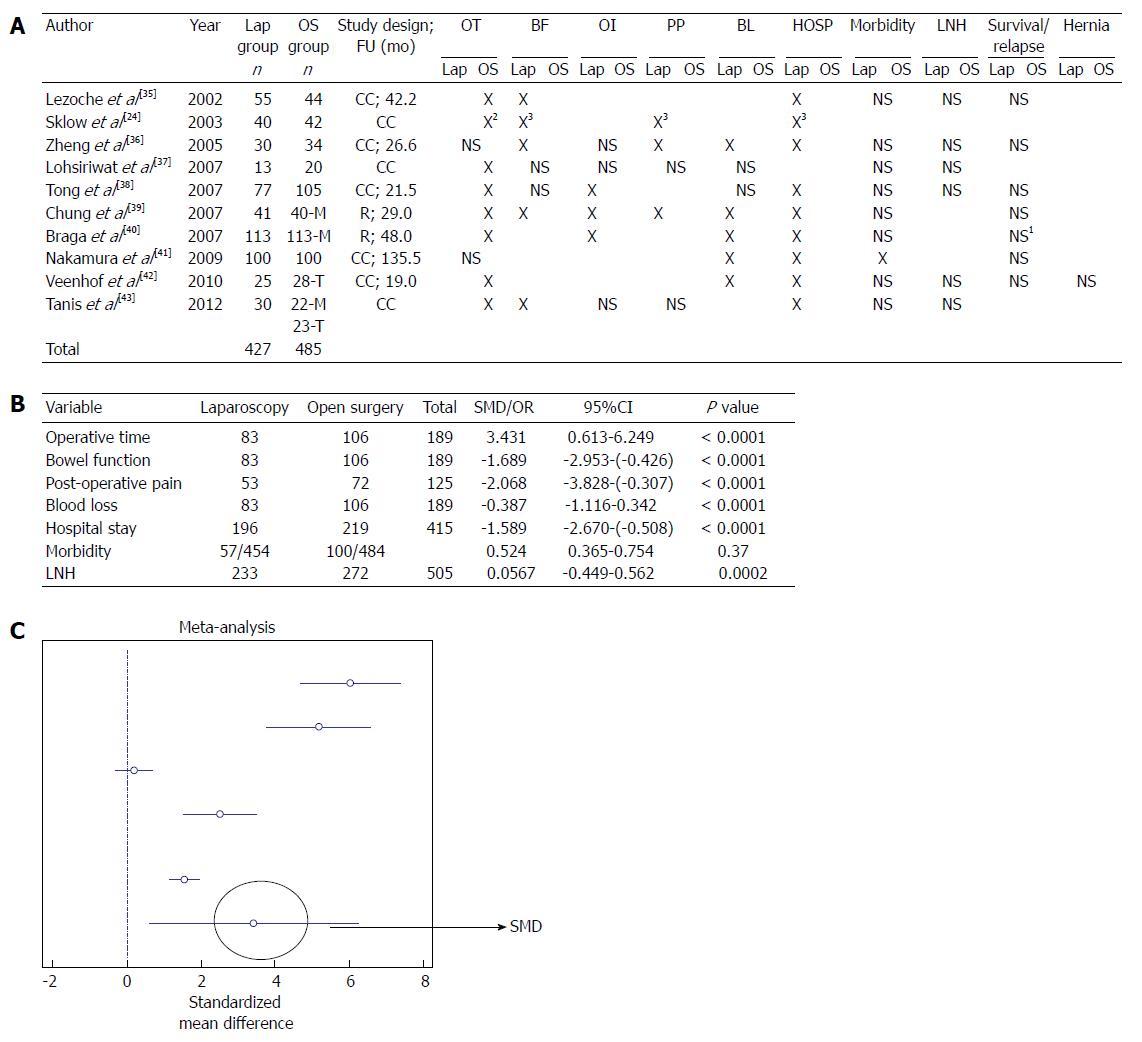
Figure 4 Right sided colectomies.
A: Studies comparing right-side laparoscopy colectomy and open surgery. X in the table refers to a statistical association provided in the studies; B: Meta-analysis of the out-come measures; C: Forest plot graph regarding studies investigating operative time. 1Statistic analysis not performed; 2Exclusively if patients > 75 years old; 3Exclusively if patients < 75 years old. Lap: Laparoscopy; OS: Open surgery; M: Midline incision; T: transverse incision R: Randomized, CC: Case-control; FU: Mean follow-up; OT: Operative time; BF: Bowel function; OI: Oral intake; PP: Post-operative Pain; BL: Blood loss; HOSP: Hospital stay; LNH: Lymph node harvest; NS: Not significant.
Figure 5 Left sided colectomies.
A: Studies comparing left-side laparoscopy colectomy and open surgery. X in the table refers to a statistical association provided in the studies; B: Meta-analysis of the out-come measures; C: Forest plot graph regarding studies investigating morbidity rate. 1Exclusively if patients > 75 years old. Lap: Laparoscopy; OS: Open surgery; M: Midline incision; T: transverse incision R: Randomized, CC: Case-control; FU: Mean follow-up; OT: Operative time; BF: Bowel function; OI: Oral intake; PP: Post-operative Pain; BL: Blood loss; HOSP: Hospital stay; LNH: Lymph node harvest; NS: Not significant.
Figure 6 Transverse colectomies.
Studies comparing transverse laparoscopy colectomy and open surgery. X in the table refers to a statistical association provided in the studies. Lap: Laparoscopy; OS: Open surgery; M: Midline incision; T: transverse incision; R: Randomized; CC: Case-control; OT: Operative time; BF: Bowel function; OI: Oral intake; PP: Post-operative Pain; BL: Blood loss; HOSP: Hospital stay; LNH: Lymph node harvest; NS: Not significant.
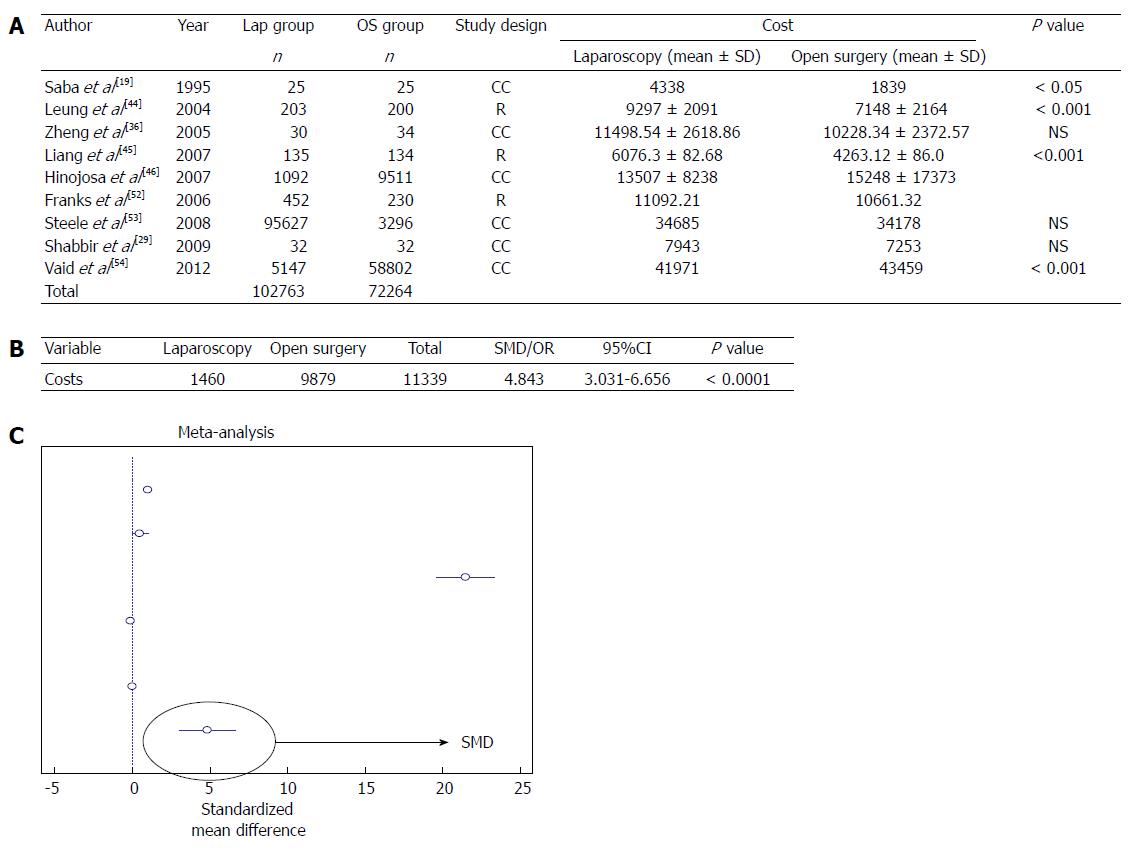
Figure 7 Costs analysis.
A: Studies comparing laparoscopy and open surgery: analysis of the costs; B: Meta-analysis; C: Forest plot graph. Lap: Laparoscopy; OS: Open surgery; NS: Not significant; R: Randomized; CC: Case-control.
-
Citation: Lorenzon L, La Torre M, Ziparo V, Montebelli F, Mercantini P, Balducci G, Ferri M. Evidence based medicine and surgical approaches for colon cancer: Evidences, benefits and limitations of the laparoscopic
vs open resection. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3680-3692 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3680.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3680